Abstract
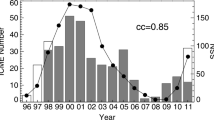
We aim to investigate the distribution function of the iron charge state, at 1 AU to check if it corresponds to a bimodal wind. We use data from the Solar Wind Ion Composition Spectrometer (SWICS) instrument on board the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) along 20 years. We propose the bi-Gaussian function as the probability distribution function that fits the average iron charge state, \(\langle Q_{\text{Fe}}\rangle \), distribution. We study the evolution of the parameters of the bimodal distribution with the solar cycle. We compare the outliers of the sample with the existing catalogs of interplanetary coronal mass ejections (ICMEs) and identify new ICMEs. The \(\langle Q_{\text{Fe}}\rangle \) at 1 AU shows a bimodal distribution related to the solar cycle. Our results confirm that \(\langle Q_{\text{Fe}}\rangle > 12 \) is a trustworthy proxy for ICME identification and a reliable signature in the ICME boundary definition.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bale, S.D., Badman, S.T., Bonnell, J.W., Bowen, T.A., Burgess, D., Case, A.W., Cattell, C.A., Chandran, B.D.G., Chaston, C.C., Chen, C.H.K., et al.: 2019, Highly structured slow solar wind emerging from an equatorial coronal hole. Nature 576, 237. DOI
Banaszkiewicz, M., Czechowski, A., Axford, W.I., McKenzie, J.F., Sukhorukova, G.V.: 1997, The fast solar wind and its source region. In: Wilson, A. (ed.) Correlated Phenomena at the Sun, in the Heliosphere and in Geospace, ESA-SP 415, 17. ADS.
Burlaga, L.F., King, J.H.: 1979, Intense interplanetary magnetic fields observed by geocentric spacecraft during 1963 – 1975. J. Geophys. Res. 84(A11), 6633. DOI. ADS.
Cid, C., Palacios, J., Saiz, E., Guerrero, A.: 2016, Redefining the boundaries of interplanetary coronal mass ejections from observations at the ecliptic plane. Astrophys. J. 828(1), 11. DOI.
Cranmer, S.R., Gibson, S.E., Riley, P.: 2017, Origins of the ambient solar wind: implications for space weather. Space Sci. Rev. 212(3 – 4), 1345. DOI. ADS.
Gloeckler, G., Cain, J., Ipavich, F.M., Tums, E.O., Bedini, P., Fisk, L.A., Zurbuchen, T.H., Bochsler, P., Fischer, J., Wimmer-Schweingruber, R.F., Geiss, J., Kallenbach, R.: 1998, Investigation of the composition of solar and interstellar matter using solar wind and pickup ion measurements with SWICS and SWIMS on the ACE spacecraft. Space Sci. Rev. 86(1), 497. DOI.
Gringauz, K.I.: 1961, Some results of experiments in interplanetary space by means of charged particle traps on Soviet space probes. Space Research II, 539. ADS.
Gringauz, K.I., Bezrukikh, V.V., Musatov, L.S.: 1967, Solar-wind observations with the Venus 3 probe. Cosm. Res. 5, 216. ADS.
Gringauz, K.I., Bezrokikh, V.V., Ozerov, V.D., Rybchinskii, R.E.: 1960, A study of the interplanetary ionized gas, high-energy electrons and corpuscular radiation from the Sun by means of the three-electrode trap for charged particles on the second Soviet cosmic rocket. Sov. Phys. Dokl. 5, 361. ADS.
Heidrich-Meisner, V., Peleikis, T., Kruse, M., Berger, L., Wimmer-Schweingruber, R.: 2016, Observations of high and low Fe charge states in individual solar wind streams with coronal-hole origin. Astron. Astrophys. 593, A70. DOI. ADS.
Hundhausen, A.J.: 1972, Coronal Expansion and Solar Wind. Physics and Chemistry in Space 5. DOI. ADS.
Jian, L.K., Russell, C.T., Luhmann, J.G.: 2011, Comparing solar minimum 23/24 with historical solar wind records at 1 AU. Solar Phys. 274(1 – 2), 321. DOI. ADS.
Jian, L., Russell, C.T., Luhmann, J.G., Skoug, R.M.: 2006, Properties of interplanetary coronal mass ejections at one AU during 1995 – 2004. Solar Phys. 239(1 – 2), 393. DOI. ADS.
Larrodera, C., Cid, C.: 2020, Bimodal distribution of the solar wind at 1 AU. Astron. Astrophys. 635, A44.
Lepri, S.T.: 2004, Iron charge state distributions as an indicator of hot ICMEs: possible sources and temporal and spatial variations during solar maximum. J. Geophys. Res. 109(A1), A01112. DOI.
Lepri, S.T., Zurbuchen, T.H., Fisk, L.A., Richardson, I.G., Cane, H.V., Gloeckler, G.: 2001, Iron charge distribution as an identifier of interplanetary coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 106(A12), 29231. DOI. ADS.
Li, K.J., Zhanng, J., Feng, W.: 2016, A statistical analysis of 50 years of daily solar wind velocity data. Astrophys. J. 151, 128. DOI. ADS.
Lionello, R., Riley, P., Linker, J.A., Mikić, Z.: 2005, The effects of differential rotation on the magnetic structure of the solar corona: magnetohydrodynamic simulations. Astrophys. J. 625(1), 463. DOI. ADS.
Neugebauer, M., Snyder, C.W.: 1966, Mariner 2 observations of the solar wind, 1, average properties. J. Geophys. Res. 71, 4469. DOI. ADS.
Neugebauer, M., Liewer, P.C., Smith, E.J., Skoug, R.M., Zurbuchen, T.H.: 2002, Sources of the solar wind at solar activity maximum. J. Geophys. Res. 107(A12), 1488. DOI. ADS.
Richardson, I.G., Cane, H.V.: 1995, Regions of abnormally low proton temperature in the solar wind (1965 – 1991) and their association with ejecta. J. Geophys. Res. 100(A12), 23397. DOI. ADS.
Richardson, I.G., Cane, H.V.: 2004, Identification of interplanetary coronal mass ejections at 1 AU using multiple solar wind plasma composition anomalies. J. Geophys. Res. 109(A9), A09104. DOI.
Richardson, I., Cane, H.: 2005, Survey of interplanetary coronal mass ejections in the near-Earth solar wind during 1996 – 2005. AGU Spring Meeting Abs. 2005, SH43A. ADS.
Rossi, B.: 1991, The interplanetary plasma. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 29, 1. DOI. ADS.
Schwenn, R.: 2006a, Solar wind sources and their variations over the solar cycle. Space Sci. Rev. 124, 51. DOI. ADS.
Schwenn, R.: 2006b, Space weather: the solar perspective. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 3(1), 2. DOI. ADS.
Viall, N.M., Borovsky, J.E.: 2020, Nine outstanding questions of solar wind physics. J. Geophys. Res.. DOI.
Vörös, Z., Leitner, M., Narita, Y., Consolini, G., Kovács, P., Tóth, A., Lichtenberger, J.: 2015, Probability density functions for the variable solar wind near the solar cycle minimum. J. Geophys. Res. 120(8), 6152. DOI. ADS.
Zhao, L., Zurbuchen, T.H., Fisk, L.A.: 2009, Global distribution of the solar wind during solar cycle 23: ACE observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 36(14), L14104. DOI. ADS.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the MINECO project AYA2016-80881-P (including FEDER funds). We thank the SWICS, SWEPAM and MAG instruments teams and the ACE Science Center for providing the ACE data. We acknowledge WDC-SILSO, Royal Observatory of Belgium, Brussels, for providing the sunspot number. We also acknowledge the information from the CME catalog generated and maintained at the CDAW Data Center by NASA and The Catholic University of America in cooperation with the Naval Research Laboratory. SOHO is a project of international cooperation between ESA and NASA. The authors want to thank an anonymous reviewer for the useful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larrodera, C., Cid, C. The Distribution Function of the Average Iron Charge State at 1 AU: From a Bimodal Wind to ICME Identification. Sol Phys 295, 156 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-020-01727-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-020-01727-8