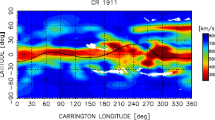
Abstract
The extended minimum of Solar Cycle 23, the extremely quiet solar-wind conditions prevailing and the mini-maximum of Solar Cycle 24 drew global attention and many authors have since attempted to predict the amplitude of the upcoming Solar Cycle 25, which is predicted to be the third successive weak cycle; it is a unique opportunity to probe the Sun during such quiet periods. Earlier work has established a steady decline, over two decades, in solar photospheric fields at latitudes above \(45^{\circ}\) and a similar decline in solar-wind micro-turbulence levels as measured by interplanetary scintillation (IPS) observations. However, the relation between the photospheric magnetic fields and those in the low corona/solar-wind are not straightforward. Therefore, in the present article, we have used potential-field source-surface (PFSS) extrapolations to deduce global magnetic fields using synoptic magnetograms observed with National Solar Observatory (NSO), Kitt Peak, USA (NSO/KP) and Solar Optical Long-term Investigation of the Sun (NSO/SOLIS) instruments during 1975 – 2018. Furthermore, we have measured the normalized scintillation index [\(m\)] using the IPS observations carried out at the Institute of Space–Earth Environment Research (ISEE), Japan during 1983 – 2017. From these observations, we have found that, since the mid-1990s, the magnetic field over different latitudes at \(2.5~\mathrm{R}_{\odot}\) and \(10~\mathrm{R}_{\odot}\) (extrapolated using the PFSS method) has decreased by \({\approx}\,11.3\,\mbox{--}\,22.2\%\). In phase with the declining magnetic fields, the quantity \(m\) also declined by \({\approx}\, 23.6\%\). These observations emphasize the inter-relationship among the global magnetic field and various turbulence parameters in the solar corona and solar-wind.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschuler, M.D., Newkirk, G.: 1969, Magnetic fields and the structure of the solar corona. I: Methods of calculating coronal fields. Solar Phys. 9, 131. DOI . ADS .
Ananthakrishnan, S., Coles, W.A., Kaufman, J.J.: 1980, Microturbulence in solar wind streams. J. Geophys. Res. 85, 6025. DOI . ADS .
Arnaud, J., Newkirk, G. Jr.: 1987, Mean properties of the polarization of the Fe XIII 10747 A coronal emission line. Astron. Astrophys. 178, 263. ADS .
Asai, K., Kojima, M., Tokumaru, M., Yokobe, A., Jackson, B.V., Hick, P.L., Manoharan, P.K.: 1998, Heliospheric tomography using interplanetary scintillation observations. III – Correlation between speed and electron density fluctuations in the solar wind. J. Geophys. Res. 103, 1991. DOI . ADS .
Bird, M.K.: 1981, Coronal sounding with pulsars. In: Rosenbauer, H. (ed.) Solar Wind 4, Max-Planck-Institute für Aeronomie, Lindau, 78. ADS .
Bird, M.K.: 1982, Coronal investigations with occulted spacecraft signals. Space Sci. Rev. 33, 99. DOI . ADS .
Bisoi, S.K., Janardhan, P., Ingale, M., Subramanian, P., Ananthakrishnan, S., Tokumaru, M., Fujiki, K.: 2014, A study of density modulation index in the inner heliospheric solar wind during solar cycle 23. Astrophys. J. 795, 69. DOI . ADS .
Celnikier, L.M., Muschietti, L., Goldman, M.V.: 1987, Aspects of interplanetary plasma turbulence. Astron. Astrophys. 181(1), 138. ADS .
Clette, F., Svalgaard, L., Vaquero, J.M., Cliver, E.W.: 2015, In: Balogh, A., Hudson, H., Petrovay, K., von Steiger, R. (eds.) Revisiting the Sunspot Number, ISSI Space Science Ser., Springer, New York, 35. DOI . ADS .
Fox, N.J., Velli, M.C., Bale, S.D., Decker, R., Driesman, A., Howard, R.A., Kasper, J.C., Kinnison, J., Kusterer, M., Lario, D., Lockwood, M.K., McComas, D.J., Raouafi, N.E., Szabo, A.: 2016, The solar probe plus mission: Humanity’s first visit to our star. Space Sci. Rev. 204, 7. DOI . ADS .
Freeland, S.L., Handy, B.N.: 1998, Data analysis with the SolarSoft system. Solar Phys. 182, 497. DOI . ADS .
Hale, G.E.: 1908, On the probable existence of a magnetic field in Sun-spots. Astrophys. J. 28, 315. DOI . ADS .
Harvey, J.W.: 1969, Magnetic fields associated with solar active-region prominences. Ph.D. thesis, Univ. Colorado, Boulder. ADS .
Hewish, A., Scott, P.F., Wills, D.: 1964, Interplanetary scintillation of small diameter radio sources. Nature 203, 1214. DOI . ADS .
Hoeksema, J.T.: 1984, Structure and evolution of the large scale solar and heliospheric magnetic fields. Ph.D. thesis, Stanford Univ., CA. sun.stanford.edu/~todd/Hoeksema1984.pdf . ADS .
Janardhan, P., Alurkar, S.K.: 1993, Angular source size measurements and interstellar scattering at 103 MHz using interplanetary scintillation. Astron. Astrophys. 269, 119. ADS .
Janardhan, P., Bisoi, S.K., Gosain, S.: 2010, Solar polar fields during cycles 21 – 23: Correlation with meridional flows. Solar Phys. 267, 267. DOI . ADS .
Janardhan, P., Balasubramanian, V., Ananthakrishnan, S., Dryer, M., Bhatnagar, A., McIntosh, P.S.: 1996, Travelling interplanetary disturbances detected using interplanetary scintillation at 327 MHz. Solar Phys. 166, 379. DOI . ADS .
Janardhan, P., Bisoi, S.K., Ananthakrishnan, S., Tokumaru, M., Fujiki, K.: 2011, The prelude to the deep minimum between solar cycles 23 and 24: Interplanetary scintillation signatures in the inner heliosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 38, L20108. DOI . ADS .
Janardhan, P., Bisoi, S.K., Ananthakrishnan, S., Tokumaru, M., Fujiki, K., Jose, L., Sridharan, R.: 2015, A 20 year decline in solar photospheric magnetic fields: Inner-heliospheric signatures and possible implications. J. Geophys. Res. 120, 5306. DOI . ADS .
Janardhan, P., Fujiki, K., Ingale, M., Bisoi, S.K., Rout, D.: 2018, Solar cycle 24: An unusual polar field reversal. Astron. Astrophys. 618, A148. DOI . ADS .
Kojima, M., Kakinuma, T.: 1990, Solar cycle dependence of global distribution of solar wind speed. Space Sci. Rev. 53(3 – 4), 173. DOI . ADS .
Lin, H., Penn, M.J., Tomczyk, S.: 2000, A new precise measurement of the coronal magnetic field strength. Astrophys. J. Lett. 541, L83. DOI . ADS .
Lopez, R.E., Freeman, J.W.: 1986, Solar wind proton temperature–velocity relationship. J. Geophys. Res. 91(A2), 1701. DOI . ADS .
Mackay, D.H., van Ballegooijen, A.A.: 2006, Models of the large-scale corona. I. Formation, evolution, and liftoff of magnetic flux ropes. Astrophys. J. 641, 577. DOI . ADS .
Manoharan, P.K.: 2010, Ooty interplanetary scintillation – Remote-sensing observations and analysis of coronal mass ejections in the heliosphere. Solar Phys. 265, 137. DOI . ADS .
Marians, M.: 1975, Computed scintillation spectra for strong turbulence. Radio Sci. 10, 115. DOI . ADS .
McComas, D.J., Barraclough, B.L., Funsten, H.O., Gosling, J.T., Santiago-Muñoz, E., Skoug, R.M., Goldstein, B.E., Neugebauer, M., Riley, P., Balogh, A.: 2000, Solar wind observations over Ulysses’ first full polar orbit. J. Geophys. Res. 105(A5), 10419. DOI . ADS .
Mickey, D.L.: 1973, Polarization measurements in the green coronal line. Astrophys. J. Lett. 181, L19. DOI . ADS .
Pesnell, W.D., Schatten, K.H.: 2018, An early prediction of the amplitude of solar cycle 25. Solar Phys. 293, 112. DOI . ADS .
Querfeld, C.W., Smartt, R.N.: 1984, Comparison of coronal emission-line structure and polarization. Solar Phys. 91, 299. DOI . ADS .
Ramesh, R., Kathiravan, C., Sastry, C.V.: 2010, Estimation of magnetic field in the solar coronal streamers through low frequency radio observations. Astrophys. J. 711, 1029. DOI . ADS .
Sasikumar Raja, K., Ramesh, R.: 2013, Low-frequency observations of transient quasi-periodic radio emission from the solar atmosphere. Astrophys. J. 775, 38. DOI . ADS .
Sasikumar Raja, K., Ramesh, R., Hariharan, K., Kathiravan, C., Wang, T.J.: 2014, An estimate of the magnetic field strength associated with a solar coronal mass ejection from low frequency radio observations. Astrophys. J. 796, 56. DOI . ADS .
Sasikumar Raja, K., Ingale, M., Ramesh, R., Subramanian, P., Manoharan, P.K., Janardhan, P.: 2016, Amplitude of solar wind density turbulence from 10 to 45 \(R_{\odot }\). J. Geophys. Res. 121, 11. DOI . ADS .
Sasikumar Raja, K., Subramanian, P., Ramesh, R., Vourlidas, A., Ingale, M.: 2017, Turbulent density fluctuations and proton heating rate in the solar wind from 9-20 \(R_{\odot }\). Astrophys. J. 850, 129. DOI . ADS .
Sasikumar Raja, K., Subramanian, P., Ingale, M., Ramesh, R.: 2019, Dissipation scale lengths of solar wind turbulence. Astrophys. J. 872, 77. DOI . ADS .
Sastry, C.V.: 2009, Polarization of the thermal radio emission from outer solar corona. Astrophys. J. 697, 1934. DOI . ADS .
Schatten, K.H., Wilcox, J.M., Ness, N.F.: 1969, A model of interplanetary and coronal magnetic fields. Solar Phys. 6, 442. DOI . ADS .
Schrijver, C.J., De Rosa, M.L.: 2003, Photospheric and heliospheric magnetic fields. Solar Phys. 212, 165. DOI . ADS .
Schrijver, C.J., Title, A.M.: 2003, The magnetic connection between the solar photosphere and the corona. Astrophys. J. Lett. 597, L165. DOI . ADS .
Stelzried, C.T., Levy, G.S., Sato, T., Rusch, W.V.T., Ohlson, J.E., Schatten, K.H., Wilcox, J.M.: 1970, The quasi-stationary coronal magnetic field and electron density as determined from a Faraday rotation experiment. Solar Phys. 14, 440. DOI . ADS .
Tokumaru, M., Kojima, M., Fujiki, K.: 2010, Solar cycle evolution of the solar wind speed distribution from 1985 to 2008. J. Geophys. Res. 115, A04102. DOI . ADS .
van Ballegooijen, A.A., Priest, E.R., Mackay, D.H.: 2000, Mean field model for the formation of filament channels on the Sun. Astrophys. J. 539, 983. DOI . ADS .
Venugopal, V.R., Ananthakrishnan, S., Swarup, G., Pynzar, A.V., Udaltsov, V.A.: 1985, Structure of PKS 1148-001. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 215, 685. DOI . ADS .
Wang, Y.-M., Sheeley, N.R. Jr.: 1992, On potential field models of the solar corona. Astrophys. J. 392, 310. DOI . ADS .
Zhao, X., Hoeksema, J.T.: 1995, Prediction of the interplanetary magnetic field strength. J. Geophys. Res. 100, 19. DOI . ADS .
Acknowledgments
K.S. Raja acknowledges Marc L. De Rosa for his valuable suggestions related to the PFSS extrapolation technique. K.S. Raja acknowledges the financial support from Centre National d’études Spatiales (CNES), France. This work utilizes SOLIS data obtained by the NSO Integrated Synoptic Program (NISP), managed by the National Solar Observatory, which is operated by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy (AURA), Inc. under a cooperative agreement with the National Science Foundation. Data storage supported by the University of Colorado Boulder “PetaLibrary.” Sunspot data from the World Data Center SILSO, Royal Observatory of Belgium, Brussels. The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewer for their constructive suggestions and comments, which helped in improving the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sasikumar Raja, K., Janardhan, P., Bisoi, S.K. et al. Global Solar Magnetic Field and Interplanetary Scintillations During the Past Four Solar Cycles. Sol Phys 294, 123 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-019-1514-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-019-1514-7