Abstract
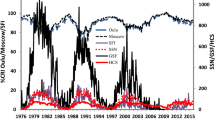
We analyzed modulation of cosmic-ray intensities (CRIs) during Solar Cycles 23 and 24 by using the international sunspot numbers (ISSN) and the maximum CME speed index (MCMESI) as proxies for solar activity. Temporal variations, cross-correlations, and hysteresis patterns of CRI, MCMESI, and ISSN data were investigated. As a result, we concluded that the MCMESI better describes solar modulation of the CRI as compared to the ISSN. This is mainly because the correlation between CRI and ISSN is caused by the general cyclic trend of solar activity, while the correlation between the CRI and the MCMESI is mainly due to short-term fluctuations related to Forbush decreases. In contrast to the ISSN, there is no time lag between the CRI and the MCMESI variations.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aslam, O.P.M., Badruddin: 2015, Study of cosmic-ray modulation during the recent unusual minimum and mini-maximum of Solar Cycle 24. Solar Phys. 290, 2333. DOI . ADS .
Badruddin, Singh, M., Singh, Y.P.: 2007, Modulation loops, time lag and relationship between cosmic ray intensity and tilt of the heliospheric current sheet. Astron. Astrophys. 466, 697. DOI . ADS .
Balasubrahmanyan, V.K.: 1969, Solar activity and the 11-year modulation of cosmic rays. Solar Phys. 7, 39. DOI . ADS .
Ball, P.C., Evans, R.: 1989, Temperature dependence of gas adsorption on a mesoporous solid: Capillary criticality and hysteresis. Langmuir 5, 714. DOI .
Belov, A.: 2000, Large scale modulation: View from the Earth. In: Bieber, J.W., Eroshenko, E., Evenson, P., Flückiger, E.O., Kallenbach, R. (eds.) Cosmic Rays and Earth, Springer, Dordrecht, 79.
Belov, A.V., Gushchina, R.T.: 2018, Index of the long-term influence of sporadic solar activity on cosmic ray modulation. Geomagn. Aeron. 58, 1. DOI . ADS .
Belov, A., Abunin, A., Abunina, M., Eroshenko, E., Oleneva, V., Yanke, V., Papaioannou, A., Mavromichalaki, H., Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S.: 2014, Coronal mass ejections and non-recurrent Forbush decreases. Solar Phys. 289, 3949. DOI . ADS .
Cane, H.V., Richardson, I.G., von Rosenvinge, T.T.: 1996, Cosmic ray decreases: 1964 – 1994. J. Geophys. Res. 101, 21561. DOI . ADS .
Chowdhury, P., Kudela, K., Moon, Y.-J.: 2016, A study of heliospheric modulation and periodicities of galactic cosmic rays during Cycle 24. Solar Phys. 291, 581. DOI . ADS .
Clette, F., Lefèvre, L.: 2016, The new sunspot number: Assembling all corrections. Solar Phys. 291, 2629. DOI . ADS .
Forbush, S.E.: 1938, On cosmic-ray effects associated with magnetic storms. Terr. Magn. Atmos. Electr. 43, 203. DOI .
Forbush, S.E.: 1954, World-wide cosmic-ray variations, 1937 – 1952. J. Geophys. Res. 59, 525. DOI . ADS .
Forbush, S.E.: 1958, Cosmic-ray intensity variations during two solar cycles. J. Geophys. Res. 63, 651. DOI . ADS .
Jones, G.H., Balogh, A., Smith, E.J.: 2003, Solar magnetic field reversal as seen at Ulysses. Geophys. Res. Lett. 30, 8028. DOI . ADS .
Kane, R.P.: 2003, Lags, hysteresis, and double peaks between cosmic rays and solar activity. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 108, 1379. DOI . ADS .
Kilcik, A., Yurchyshyn, V.B., Abramenko, V., Goode, P.R., Gopalswamy, N., Ozguc, A., Rozelot, J.P.: 2011, Maximum coronal mass ejection speed as an indicator of solar and geomagnetic activities. Astrophys. J. 727, 44. DOI . ADS .
Kramer, B.P., Fussenegger, M.: 2005, Hysteresis in a synthetic mammalian gene network. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 9517. DOI .
Krasnosel’skií, M.A., Pokrovskií, A.V.: 1989, Systems with Hysteresis, 1st edn. Springer, Berlin. 978-3-642-64782-6. DOI .
Lara, A., Gopalswamy, N., Caballero-López, R.A., Yashiro, S., Xie, H., Valdés-Galicia, J.F.: 2005, Coronal mass ejections and galactic cosmic-ray modulation. Astrophys. J. 625, 441. DOI . ADS .
Mavromichalaki, H., Paouris, E.: 2012, Long-term cosmic ray variability and the CME-index. Adv. Astron. 2012, 607172. DOI . ADS .
Mikić, Z., Lee, M.A.: 2006, An introduction to theory and models of CMEs, shocks, and solar energetic particles. Space Sci. Rev. 123, 57. DOI . ADS .
Mishra, V.K., Mishra, A.P.: 2016, Study of solar activity and cosmic ray modulation during Solar Cycle 24 in comparison to previous solar cycle. Indian J. Phys. 90, 1333. DOI . ADS .
Parker, E.N.: 1965, The passage of energetic charged particles through interplanetary space. Planet. Space Sci. 13, 9. DOI . ADS .
Penna, R.F., Quillen, A.C.: 2005, Decay of interplanetary coronal mass ejections and Forbush decrease recovery times. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 110, A09S05. DOI . ADS .
Preisach, F.: 1935, Über die magnetische Nachwirkung. Z. Phys. 94, 277. DOI . ADS .
Reid, G.C., Leinbach, H.: 1959, Low-energy cosmic-ray events associated with solar flares. J. Geophys. Res. 64, 1801. DOI . ADS .
Shea, M.A., Smart, D.F., Humble, J.E., Fluckiger, E.O., Gentile, L.C., Humble, J.E., Nichol, M., Shea, M.A., Smart, D.F.: 1987, A revised standard format for cosmic ray ground-level event data. In: Kozyarivsky, V.A., Lidvansky, A.S., Tulupova, T.I., Tayabuk, A.L., Voevodsky, A.V., Volgemut, N.S. (eds.) Internat. Cosmic Ray Conf. 3, Nauka, Moscow, 171. ADS .
Singh, S., Mishra, A.P.: 2018, Cosmic ray intensity increases during high solar activity period for the Solar Cycles 22 and 23. Indian J. Phys. DOI .
Snyder, C.W., Neugebauer, M., Rao, U.R.: 1963, The solar wind velocity and its correlation with cosmic-ray variations and with solar and geomagnetic activity. J. Geophys. Res. 68, 6361. DOI . ADS .
Stoner, E.C., Wohlfarth, E.P.: 1948, A mechanism of magnetic hysteresis in heterogeneous alloys. Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. London A, Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 240, 599. DOI . ADS .
Sun, W., Xue, Y.: 2018, An improved fuzzy comprehensive evaluation system and application for risk assessment of floor water inrush in deep mining. Geotech. Geolog. Eng. 37, 1135. DOI .
Tomassetti, N., Orcinha, M., Barão, F., Bertucci, B.: 2017, Evidence for a time lag in solar modulation of galactic cosmic rays. Astrophys. J. Lett. 849, L32. DOI . ADS .
Usoskin, I.G.: 2017, A history of solar activity over millennia. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 14, 3. DOI . ADS .
Usoskin, I.G., Mursula, K., Kangas, J.: 2001, On-line database of cosmic ray intensities. In: Kampert, K.H., Heinzelmann, G., Spirering, C. (eds.) Proc. 27th Internat. Cosmic Ray Conf. 9, Internat. Union Pure Appl. Phys., Hamburg, 3842. ADS .
Visintin, A.: 2006, Mathematical models of hysteresis. In: Bertotti, G., Mayergoyz, I.D. (eds.) The Science of Hysteresis, Elsevier, Oxford, 1. 978-0-12-480874-4. DOI .
Wawrzynczak, A., Alania, M.V.: 2008, Modeling of the recurrent Forbush effect of the galactic cosmic ray intensity and comparison with the experimental data. Adv. Space Res. 41, 325. DOI . ADS .
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the NMDB database , founded under the European Union’s FP7 programme (contract no. 213007) for providing Hermanus Neutron Monitor data. CRI data were also taken from Oulu Neutron Monitor . The ISSN data were taken from the World Data Center, Sunspot Index and Long-term Solar Observations (SILSO), Royal Observatory of Belgium. The MCMESI data were calculated by using the CME catalog provided by the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) mission’s Large Angle and Spectrometric Coronagraph (LASCO). This work was supported by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBİTAK) by the Project of 115F031.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarp, V., Kilcik, A., Yurchyshyn, V. et al. Cosmic Ray Modulation with the Maximum CME Speed Index During Solar Cycles 23 and 24. Sol Phys 294, 86 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-019-1481-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-019-1481-z