Abstract
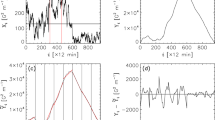
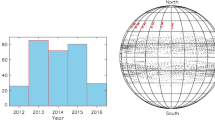
Solar active regions (ARs) that produce major flares typically exhibit strong plasma shear flows around photospheric magnetic polarity inversion lines (MPILs). It is therefore important to quantitatively measure such photospheric shear flows in ARs for a better understanding of their relation to flare occurrence. Photospheric flow fields were determined by applying the Differential Affine Velocity Estimator for Vector Magnetograms (DAVE4VM) method to a large data set of 2548 coaligned pairs of AR vector magnetograms with 12-min separation over the period 2012 – 2016. From each AR flow-field map, three shear-flow parameters were derived corresponding to the mean (\(\langle S\rangle \)), maximum (\(S_{\mathrm{max}}\)) and integral (\(S_{\mathrm{sum}}\)) shear-flow speeds along strong-gradient, strong-field MPIL segments. We calculated flaring rates within 24 h as a function of each shear-flow parameter and we investigated the relation between the parameters and the waiting time (\(\tau \)) until the next major flare (class M1.0 or above) after the parameter observation. In general, it is found that the larger \(S_{\mathrm{sum}}\) an AR has, the more likely it is for the AR to produce flares within 24 h. It is also found that among ARs which produce major flares, if one has a larger value of \(S_{\mathrm{sum}}\) then \(\tau \) generally gets shorter. These results suggest that large ARs with widespread and/or strong shear flows along MPILs tend to not only be more flare productive, but also produce major flares within 24 h or less.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amari, T., Luciani, J.F., Aly, J.J., Mikic, Z., Linker, J.: 2003, Coronal mass ejection: Initiation, magnetic helicity, and flux ropes. I. Boundary motion-driven evolution. Astrophys. J. 585, 1073. DOI . ADS .
Antiochos, S.K., DeVore, C.R., Klimchuk, J.A.: 1999, A model for solar coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 510, 485. DOI . ADS .
Barnes, G., Leka, K.D., Schrijver, C.J., Colak, T., Qahwaji, R., Ashamari, O.W., Yuan, Y., Zhang, J., McAteer, R.T.J., Bloomfield, D.S., Higgins, P.A., Gallagher, P.T., Falconer, D.A., Georgoulis, M.K., Wheatland, M.S., Balch, C., Dunn, T., Wagner, E.L.: 2016, A comparison of flare forecasting methods. I. Results from the all-clear workshop. Astrophys. J. 829, 89. DOI . ADS .
Bobra, M.G., Couvidat, S.: 2015, Solar flare prediction using SDO/HMI vector magnetic field data with a machine-learning algorithm. Astrophys. J. 798, 135. DOI . ADS .
Bobra, M.G., Sun, X., Hoeksema, J.T., Turmon, M., Liu, Y., Hayashi, K., Barnes, G., Leka, K.D.: 2014, The Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) vector magnetic field pipeline: SHARPs – Space-weather HMI Active Region Patches. Solar Phys. 289, 3549. DOI . ADS .
Chen, P.F., Shibata, K.: 2000, An emerging flux trigger mechanism for coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 545, 524. DOI . ADS .
Couvidat, S., Schou, J., Hoeksema, J.T., Bogart, R.S., Bush, R.I., Duvall, T.L., Liu, Y., Norton, A.A., Scherrer, P.H.: 2016, Observables processing for the helioseismic and magnetic imager instrument on the solar dynamics observatory. Solar Phys. 291, 1887. DOI . ADS .
Deng, N., Xu, Y., Yang, G., Cao, W., Liu, C., Rimmele, T.R., Wang, H., Denker, C.: 2006, Multiwavelength study of flow fields in flaring super active region NOAA 10486. Astrophys. J. 644, 1278. DOI . ADS .
Falconer, D., Barghouty, A.F., Khazanov, I., Moore, R.: 2011, A tool for empirical forecasting of major flares, coronal mass ejections, and solar particle events from a proxy of active-region free magnetic energy. Space Weather 9, S04003. DOI . ADS .
Fan, Y.: 2005, Coronal mass ejections as loss of confinement of kinked magnetic flux ropes. Astrophys. J. 630, 543. DOI . ADS .
Fan, Y.: 2016, Modeling the initiation of the 2006 December 13 coronal mass ejection in AR 10930: The structure and dynamics of the erupting flux rope. Astrophys. J. 824, 93. DOI . ADS .
Fang, F., Manchester, W. IV, Abbett, W.P., van der Holst, B.: 2012, Buildup of magnetic shear and free energy during flux emergence and cancellation. Astrophys. J. 754, 15. DOI . ADS .
Fisher, G.H., Welsch, B.T.: 2008, FLCT: A fast, efficient method for performing local correlation tracking. In: Howe, R., Komm, R.W., Balasubramaniam, K.S., Petrie, G.J.D. (eds.) Subsurface and Atmospheric Influences on Solar Activity, Astron. Soc. Pacific Conf. Ser. 383, 373. ADS .
Gallagher, P.T., Moon, Y.-J., Wang, H.: 2002, Active-region monitoring and flare forecasting I. Data processing and first results. Solar Phys. 209, 171. DOI . ADS .
Georgoulis, M.K.: 2012, Are solar active regions with major flares more fractal, multifractal, or turbulent than others? Solar Phys. 276, 161. DOI . ADS .
Georgoulis, M.K., Titov, V.S., Mikić, Z.: 2012, Non-neutralized electric current patterns in solar active regions: Origin of the shear-generating Lorentz force. Astrophys. J. 761, 61. DOI . ADS .
Hoeksema, J.T., Liu, Y., Hayashi, K., Sun, X., Schou, J., Couvidat, S., Norton, A., Bobra, M., Centeno, R., Leka, K.D., Barnes, G., Turmon, M.: 2014, The Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) vector magnetic field pipeline: Overview and performance. Solar Phys. 289, 3483. DOI . ADS .
Jing, J., Tan, C., Yuan, Y., Wang, B., Wiegelmann, T., Xu, Y., Wang, H.: 2010, Free magnetic energy and flare productivity of active regions. Astrophys. J. 713, 440. DOI . ADS .
Kazachenko, M.D., Fisher, G.H., Welsch, B.T., Liu, Y., Sun, X.: 2015, Photospheric electric fields and energy fluxes in the eruptive active region NOAA 11158. Astrophys. J. 811, 16. DOI . ADS .
Kontogiannis, I., Georgoulis, M.K., Park, S.-H., Guerra, J.A.: 2017, Non-neutralized electric currents in solar active regions and flare productivity. Solar Phys. 292, 159. DOI . ADS .
Kusano, K., Bamba, Y., Yamamoto, T.T., Iida, Y., Toriumi, S., Asai, A.: 2012, Magnetic field structures triggering solar flares and coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 760, 31. DOI . ADS .
Lee, K., Moon, Y.-J., Lee, J.-Y., Lee, K.-S., Na, H.: 2012, Solar flare occurrence rate and probability in terms of the sunspot classification supplemented with sunspot area and its changes. Solar Phys. 281, 639. DOI . ADS .
Leka, K.D., Barnes, G.: 2003, Photospheric magnetic field properties of flaring versus flare-quiet active regions. II. Discriminant analysis. Astrophys. J. 595, 1296. DOI . ADS .
Leka, K.D., Barnes, G.: 2007, Photospheric magnetic field properties of flaring versus flare-quiet active regions. IV. A statistically significant sample. Astrophys. J. 656, 1173. DOI . ADS .
Liu, Y., Schuck, P.W.: 2012, Magnetic energy and helicity in two emerging active regions in the Sun. Astrophys. J. 761, 105. DOI . ADS .
Liu, Y., Baldner, C., Bogart, R.S., Bush, R., Couvidat, S., Duvall, T.L., Hoeksema, J.T., Norton, A.A., Scherrer, P.H., Schou, J.: 2016, On HMI’s Mod-L sequence: Test and evaluation. Amer. Astron. Soc. Solar Phys. Div. Abs. 47, 8.10. ADS .
Manchester, W.: 2008, Shear flows driven by the Lorentz force: An energy source for coronal mass ejections and flares. In: Howe, R., Komm, R.W., Balasubramaniam, K.S., Petrie, G.J.D. (eds.) Subsurface and Atmospheric Influences on Solar Activity, Astron. Soc. Pacific Conf. Ser. 383, 91. ADS .
Mason, J.P., Hoeksema, J.T.: 2010, Testing automated solar flare forecasting with 13 years of Michelson Doppler imager magnetograms. Astrophys. J. 723, 634. DOI . ADS .
McCloskey, A.E., Gallagher, P.T., Bloomfield, D.S.: 2016, Flaring rates and the evolution of sunspot group McIntosh classifications. Solar Phys. 291, 1711. DOI . ADS .
Park, S-h., Chae, J., Wang, H.: 2010, Productivity of solar flares and magnetic helicity injection in active regions. Astrophys. J. 718, 43. DOI . ADS .
Park, S.-H., Kusano, K., Cho, K.-S., Chae, J., Bong, S.-C., Kumar, P., Park, S.-Y., Kim, Y.-H., Park, Y.-D.: 2013, Study of magnetic helicity injection in the active region NOAA 9236 producing multiple flare-associated coronal mass ejection events. Astrophys. J. 778, 13. DOI . ADS .
Pesnell, W.D., Thompson, B.J., Chamberlin, P.C.: 2012, The Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Solar Phys. 275, 3. DOI . ADS .
Roussev, I.I., Sokolov, I.V., Forbes, T.G., Gombosi, T.I., Lee, M.A., Sakai, J.I.: 2004, A numerical model of a coronal mass ejection: Shock development with implications for the acceleration of GeV protons. Astrophys. J. Lett. 605, L73. DOI . ADS .
Scherrer, P.H., Schou, J., Bush, R.I., Kosovichev, A.G., Bogart, R.S., Hoeksema, J.T., Liu, Y., Duvall, T.L., Zhao, J., Title, A.M., Schrijver, C.J., Tarbell, T.D., Tomczyk, S.: 2012, The Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) investigation for the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Solar Phys. 275, 207. DOI . ADS .
Schmieder, B., Aulanier, G., Vršnak, B.: 2015, Flare-CME models: An observational perspective (invited review). Solar Phys. 290, 3457. DOI . ADS .
Schrijver, C.J.: 2007, A characteristic magnetic field pattern associated with all major solar flares and its use in flare forecasting. Astrophys. J. Lett. 655, L117. DOI . ADS .
Schrijver, C.J.: 2009, Driving major solar flares and eruptions: A review. Adv. Space Res. 43, 739. DOI . ADS .
Schuck, P.W.: 2005, Local correlation tracking and the magnetic induction equation. Astrophys. J. Lett. 632, L53. DOI . ADS .
Schuck, P.W.: 2008, Tracking vector magnetograms with the magnetic induction equation. Astrophys. J. 683, 1134. DOI . ADS .
Tziotziou, K., Georgoulis, M.K., Raouafi, N.-E.: 2012, The magnetic energy-helicity diagram of solar active regions. Astrophys. J. Lett. 759, L4. DOI . ADS .
Wang, H., Liu, C., Ahn, K., Xu, Y., Jing, J., Deng, N., Huang, N., Liu, R., Kusano, K., Fleishman, G.D., Gary, D.E., Cao, W.: 2017, High-resolution observations of flare precursors in the low solar atmosphere. Nat. Astron. 1, 0085. DOI . ADS .
Welsch, B.T., Li, Y., Schuck, P.W., Fisher, G.H.: 2009, What is the relationship between photospheric flow fields and solar flares? Astrophys. J. 705, 821. DOI . ADS .
Yang, G., Xu, Y., Cao, W., Wang, H., Denker, C., Rimmele, T.R.: 2004, Photospheric shear flows along the magnetic neutral line of active region 10486 prior to an X10 flare. Astrophys. J. Lett. 617, L151. DOI . ADS .
Yang, K., Guo, Y., Ding, M.D.: 2015, On the 2012 October 23 circular ribbon flare: Emission features and magnetic topology. Astrophys. J. 806, 171. DOI . ADS .
Yang, K., Guo, Y., Ding, M.D.: 2016, Quantifying the topology and evolution of a magnetic flux rope associated with multi-flare activities. Astrophys. J. 824, 148. DOI . ADS .
Acknowledgements
The authors thank E. Pariat for constructive suggestions that helped clarify several topics discussed in the article. This work also benefited from discussions at the International Space Science Institute (Bern, Switzerland) International Working Team meetings on “Improving the Reliability of Solar Eruption Predictions to Facilitate the Determination of Targets-of-Opportunity for Instruments With a Limited Field-of-View” led by P.A. Higgins (later D.S. Bloomfield) and M.K. Georgoulis. The data used in this work are courtesy of the NASA SDO/HMI science team, as well as the GOES team. The SHARP CEA NRT vector magnetograms were provided by the MEDOC data and operations centre (CNES/CNRS/Univ. Paris-Sud; http://medoc.ias.u-psud.fr ). This research has made use of NASA Astrophysics Data System (ADS). This research was funded by the European Union Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No. 640216 (FLARECAST).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, SH., Guerra, J.A., Gallagher, P.T. et al. Photospheric Shear Flows in Solar Active Regions and Their Relation to Flare Occurrence. Sol Phys 293, 114 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-018-1336-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-018-1336-z