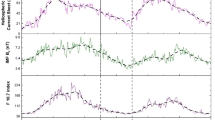
Abstract
We study the solar-activity and solar-polarity dependence of galactic cosmic-ray intensity (CRI) on the solar and heliospheric parameters playing a significant role in solar modulation. We utilize the data for cosmic-ray intensity as measured by neutron monitors, solar activity as measured by sunspot number (SSN), interplanetary plasma/field parameters, solar-wind velocity [V] and magnetic field [B], as well as the tilt of the heliospheric current sheet [Λ], and we analyze these data for Solar Cycles 20 – 24 (1965 – 2011). We divide individual solar cycles into four phases, i.e. low, high, increasing, and decreasing solar activity. We perform regression analysis to calculate and compare the CRI-response to changes in different solar/interplanetary parameters during
-
i)
different phases of solar activity and
-
ii)
similar activity phases but different polarity states.
We find that the CRI-response is different during negative (A<0) as compared to positive (A>0) polarity states not only with SSN and Λ but also with B and V. The relative CRI-response to changes in various parameters, in negative (A<0) as compared to positive (A>0) state, is solar-activity dependent; it is ≈ 2 to 3 times higher in low solar activity, ≈ 1.5 to 2 times higher in moderate (increasing/decreasing) activity, and it is nearly equal in high solar-activity conditions. Although our results can be ascribed to the preferential entry of charged particles via the equatorial/polar regions of the heliosphere as predicted by drift models, these results also suggest that we should look for any polarity-dependent response of solar-wind and transport parameters in modulating CRI in the heliosphere.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahluwalia, H.S.: 2005, J. Geophys. Res. 110, A10106.
Aslam, O.P.M., Badruddin: 2012, Solar Phys. 279, 269. doi: 10.1007/s11207-012-9970-3 .
Badruddin: 2011, Proc. 32nd Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. 11, SH3.5, 235. doi: 10.7529/ICRC2011/V11/0116 .
Badruddin, Singh, M., Singh, Y.P.: 2007, Astron. Astrophys. 466, 677.
Badruddin, Yadav, R.S., Yadav, N.R.: 1985, Planet. Space Sci. 33, 191.
Burlaga, L.F., McDonald, F.B., Goldstien, M.L., Lazarus, A.J.: 1985, J. Geophys. Res. 90, 12027.
Burlaga, L.F., Ness, N.F.: 1998, J. Geophys. Res. 103, 29719.
Cane, H.V., Wibberenz, G., Richardson, I.G., von Rosenvinge, T.T.: 1999, Geophys. Res. Lett. 26, 56.
Chaudhary, P., Dwivedi, B.N., Ray, P.C.: 2011, New Astron. 16, 430.
Chen, J., Bieber, J.W.: 1993, Astrophys. J. 405, 375.
Cliver, E.W., Ling, A.G.: 2001, Astrophys. J. Lett. 551, L189.
Cliver, E.W., Richardson, I.G., Ling, A.G.: 2013, Space Sci. Rev. 176, 3. doi: 10.1007/s11214-011-9746-3 .
Gopalswamy, N., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Makela, P.: 2010, In: Hassan, S.S., Rutten, R.J. (eds.) Magnetic Coupling Between the Interior and the Atmosphere of the Sun, Astrophys. Space Sci. Proc., Springer, Berlin, 289.
Gupta, V., Badruddin: 2009, Astrophys. Space Sci. 321, 185.
Heber, B.: 2013, Space Sci. Rev. 176, 265. doi: 10.1007/s11214-011-9784-x .
Jokipii, J.R., Davila, J.M.: 1981, Astrophys. J. 248, 1156.
Jokipii, J.R., Thomas, B.T.: 1981, Astrophys. J. 243, 1115.
Jokipii, J.R., Wibberenz, G.: 1998, Space Sci. Rev. 83, 365.
Kane, R.P.: 2003, J. Geophys. Rev. 108, 1379.
Kota, J.: 2013, Space Sci. Rev. 176, 391. doi: 10.1007/s11214-012-9870-8 .
Kota, J., Jokipii, J.R.: 1983, Astrophys. J. 265, 573.
Kota, J., Jokipii, J.R.: 1991, Geophys. Res. Lett. 18, 1797.
Kudela, K.: 2012, In: Lazar, M. (ed.) Exploring the Solar Wind, Intech, Rijeka, 285.
Laurenza, M., Vecchio, A., Storini, M., Carbone, V.: 2012, Astrophys. J. 749, 167.
Ma, L.H., Han, Y.B., Yin, Z.Q.: 2009, Solar Phys. 255, 187. doi: 10.1007/s11207-012-9970-3 .
Mavromichalaki, H., Belehaki, A., Rafios, X.: 1998, Astron. Astrophys. 330, 764.
McDonald, F.B., Lal, N., McGuire, R.E.: 1993, J. Geophys. Res. 98, 1243.
McDonald, F.B., Webber, W.R., Reames, D.V.: 2010, Geophys. Res. Lett. 37, L18101.
Modzelewska, R., Alania, M.V.: 2011, Adv. Space Res. 50, 716.
Parker, E.N.: 1965, Planet. Space Sci. 13, 9.
Pei, C., Bieber, J.W., Burger, R.A., Clem, J.: 2012, Astrophys. J. 744, 170.
Potgieter, M.S.: 2013, Space Sci. Rev. 176, 165. doi: 10.1007/s11214-001-9750-7 .
Potgieter, M.S.: 1995, Adv. Space Res. 16, 191.
Potgieter, M.S., Moraal, H.: 1985, Astrophys. J. 294, 425.
Reinecke, J.P.L., Moraal, H., McDonald, F.B.: 2000, J. Geophys. Res. 105, 12651.
Richardson, I.G., Cane, H.V., Wibberenz, G.: 1999, J. Geophys. Res. 104, 12549.
Sabbah, I.: 2000, Geophys. Res. Lett. 27, 1823.
Sabbah, I., Kudela, K.: 2011, J. Geophys. Res. 116, A04103.
Sabbah, I., Rybansky, M.: 2006, J. Geophys. Res. 111, A01105.
Singh, Y.P., Badruddin: 2007, J. Geophys. Res. 112, A05101.
Singh, M., Singh, Y.P., Badruddin: 2008, J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 70, 169.
Smith, E.J.: 1990, J. Geophys. Res. 95, 18731.
Smith, E.J., Thomas, B.T.: 1986, J. Geophys. Res. 91, 2933.
Storini, M., Borello-Filisetti, O., Mussino, V., Parisi, M., Sykora, J.: 1995, Solar Phys. 157, 375. doi: 10.1007/BF00680628 .
Strauss, R.D., Potgieter, M.S., Ferreira, S.E.S.: 2012, Adv. Space Res. 49, 392.
Usoskin, I.G., Kananen, H., Kovaltsov, G.A., Mursula, K., Tanskanen, P.: 1998, J. Geophys. Res. 103, 9567.
Van Allen, J.A.: 2000, Geophys. Res. Lett. 27, 2453.
Venkatesan, D., Badruddin: 1990, Space Sci. Rev. 52, 121.
Webber, W.R., Lockwood, J.A.: 1988, J. Geophys. Res. 93, 8735.
Wibberenz, G., Richardson, I.G., Cane, H.V.: 2002, J. Geophys. Res. 107, 1353.
Acknowledgements
We thank Station Manager Ilya Usoskin and the Sodankyla Geophysical Observatory for the online availability of Oulu neutron-monitor data. We also thank the National Science Foundation (supporting Bartol Research Institute neutron monitors) and Principal Investigator John W. Bieber for the online availability of Newark neutron-monitor data. Availability of solar and plasma/field data through the NASA/GSFC OMNI Web interface and the HCS inclination data (courtesy of J.T. Hoeksema) are also acknowledged. We also thank the reviewer for useful and constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aslam, O.P.M., Badruddin Similarities and Distinctions in Cosmic-Ray Modulation During Different Phases of Solar and Magnetic Activity Cycles. Sol Phys 289, 2247–2268 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-013-0459-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-013-0459-5