Abstract
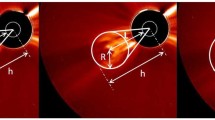
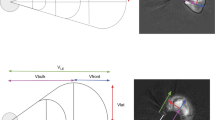
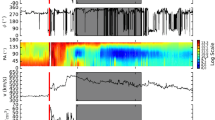
We report radial-speed evolution of interplanetary coronal mass ejections (ICMEs) detected by the Large Angle and Spectrometric Coronagraph onboard the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO/LASCO), interplanetary scintillation (IPS) at 327 MHz, and in-situ observations. We analyze solar-wind disturbance factor (g-value) data derived from IPS observations during 1997 – 2009 covering nearly the whole period of Solar Cycle 23. By comparing observations from SOHO/LASCO, IPS, and in situ, we identify 39 ICMEs that could be analyzed carefully. Here, we define two speeds [V SOHO and V bg], which are the initial speed of the ICME and the speed of the background solar wind, respectively. Examinations of these speeds yield the following results: i) Fast ICMEs (with V SOHO−V bg>500 km s−1) rapidly decelerate, moderate ICMEs (with 0 km s−1≤V SOHO−V bg≤500 km s−1) show either gradually decelerating or uniform motion, and slow ICMEs (with V SOHO−V bg<0 km s−1) accelerate. The radial speeds converge on the speed of the background solar wind during their outward propagation. We subsequently find; ii) both the acceleration and the deceleration are nearly complete by 0.79±0.04 AU, and those are ended when the ICMEs reach a 480±21 km s−1. iii) For ICMEs with (V SOHO−V bg)≥0 km s−1, i.e. fast and moderate ICMEs, a linear equation a=−γ 1(V−V bg) with γ 1=6.58±0.23×10−6 s−1 is more appropriate than a quadratic equation a=−γ 2(V−V bg)|V−V bg| to describe their kinematics, where γ 1 and γ 2 are coefficients, and a and V are the acceleration and speed of ICMEs, respectively, because the χ 2 for the linear equation satisfies the statistical significance level of 0.05, while the quadratic one does not. These results support the assumption that the radial motion of ICMEs is governed by a drag force due to interaction with the background solar wind. These findings also suggest that ICMEs propagating faster than the background solar wind are controlled mainly by the hydrodynamic Stokes drag.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACE:
-
Advanced Composition Explorer
- AU:
-
Astronomical unit
- CC:
-
Correlation coefficient
- CDAW:
-
Coordinated Data Analysis Workshop
- CME:
-
Coronal mass ejection
- CPI:
-
Comprehensive Plasma Instrumentation
- ESA:
-
European Space Agency
- FOV:
-
Field-of-view
- GSFC:
-
Goddard Space Flight Center
- ICME:
-
Interplanetary coronal mass ejection
- IDED:
-
IPS disturbance event day
- IDEDs:
-
IPS disturbance event days
- IMP:
-
Interplanetary Monitoring Platform
- IPS:
-
Interplanetary Scintillation
- LASCO:
-
Large Angle and Spectrometric Coronagraph
- LOS:
-
Line-of-sight
- MIT:
-
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Faraday Cup Experiment
- NASA:
-
National Aeronautics and Space Administration
- OMNI:
-
Operating Missions as Nodes on the Internet
- SOHO:
-
Solar and Heliospheric Observatory
- STEL:
-
Solar-Terrestrial Environment Laboratory
- STEREO:
-
Solar-Terrestrial Relations Observatory
- SWE:
-
Solar Wind Experiment
- SWEPAM:
-
Solar Wind Electron, Proton, and Alpha Monitor
References
Andrews, M.D.: 2001, LASCO and EIT observations of the Bastille Day 2000 solar storm. Solar Phys. 204, 181. doi: 10.1023/A:1014215923912 .
Asai, K., Ishida, Y., Kojima, M., Maruyama, K., Misawa, H., Yoshimi, N.: 1995, Multi-station system for solar wind observations using the interplanetary scintillation method. J. Geomagn. Geoelectr. 47, 1107.
Bellomo, A., Mavretic, A.: 1978, MIT plasma experiment on IMP H and J Earth orbited satellites. MIT Center for Space Research Technical Report CSR-TR-78-2.
Bisi, M.M., Breen, A.R., Jackson, B.V., Fallows, R.A., Walsh, A.P., Mikić, Z., Riley, P., Owen, C.J., Gonzalez-Esparza, A., Aguilar-Rodriguez, E., et al.: 2010, From the Sun to the Earth: the 13 May 2005 coronal mass ejection. Solar Phys. 265, 49. doi: 10.1007/s11207-010-9602-8 .
Brueckner, G.E., Howard, R.A., Kooman, M.J., Korendyke, C.M., Michels, D.J., Moses, J.D., Socker, D.G., Dere, K.P., Lamy, P.L., Llebaria, A., et al.: 1995, The large angle spectroscopic coronagraph (LASCO). Solar Phys. 162, 357. doi: 10.1007/BF00733434 .
Cargill, P.J.: 2004, On the aerodynamic drag force acting on interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Solar Phys. 221, 135. doi: 10.1023/B:SOLA-0000033366-10725-a2 .
Chen, J.: 1996, Theory of prominence eruption and propagation: interplanetary consequences. J. Geophys. Res. 101(A12), 27499. doi: 10.1029/96JA02644 .
Coles, W.A., Harmon, J.K., Lazarus, A.J., Sullivan, J.D.: 1978, Comparison of 74-MHz interplanetary scintillation and IMP 7 observations of the solar wind during 1973. J. Geophys. Res. 83(A7), 3337. doi: 10.1029/JA083iA07p03337 .
Frank, L.A., Ackerson, K.L., Paterson, W.R., Lee, J.A., English, M.R., Pickett, G.L.: 1994, The comprehensive plasma instrumentation (CPI) for the GEOTAIL spacecraft. J. Geomagn. Geoelectr. 46, 23.
Gapper, G.R., Hewish, A., Purvis, A., Duffett-Smith, P.J.: 1982, Observing interplanetary disturbances from the ground. Nature 296, 633. doi: 10.1038/296633a0 .
Gopalswamy, N., Lara, A., Lepping, R.P., Kaiser, M.L., Berdichevsky, D., St. Cyr, O.C.: 2000, Interplanetary acceleration of coronal mass ejections. Geophys. Res. Lett. 27(2), 145. doi: 10.1029/1999GL003639 .
Gopalswamy, N., Lara, A., Yashiro, S., Kaiser, M.L., Howard, R.A.: 2001, Predicting the 1-AU arrival times of coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 106(A12), 29207. doi: 10.1029/2001JA000177 .
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Liu, Y., Michalek, G., Vourlidas, A., Kaiser, M.L., Howard, R.A.: 2005, Coronal mass ejections and other extreme characteristics of the 2003 October – November solar eruptions. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A09S15. doi: 10.1029/2004JA010958 .
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Micharek, G., Stenborg, G., Vouridas, A., Freeland, S., Howard, R.: 2009, The SOHO/LASCO CME catalog. Earth Moon Planets 104, 295. doi: 10.1007/s11038-008-9282-7 .
Gosling, J.T., Hildner, E., MacQueen, R.M., Munro, R.H., Poland, A.I., Ross, C.L.: 1974, Mass ejections from the Sun: a view from Skylab. J. Geophys. Res. 79(31), 4581. doi: 10.1029/JA079i031p04581 .
Gosling, J.T., Bame, S.T., McComas, D.J., Phillips, J.L.: 1990, Coronal mass ejections and large geomagnetic storms. Geophys. Res. Lett. 17(7), 901. doi: 10.1029/GL017i007p00901 .
Hewish, A., Bravo, S.: 1986, The sources of large-scale heliospheric disturbances. Solar Phys. 106, 185. doi: 10.1007/BF00161362 .
Hewish, A., Scott, P.F., Wills, D.: 1964, Interplanetary scintillation of small diameter radio sources. Nature 203(4951), 1214. doi: 10.1038/2031214a0 .
Jackson, B.V., Hick, P.P.: 2002, Corotational tomography of heliospheric features using global Thomson scattering data. Solar Phys. 211, 345. doi: 10.1023/A:1022409530466 .
Jackson, B.V., Hick, P.P., Buffington, A., Bisi, M.M., Clover, J.M., Tokumaru, M., Kojima, M., Fujiki, K.: 2011, Three-dimensional reconstruction of heliospheric structure using iterative tomography: a review. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 73, 1214. doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2010.10.007 .
Kojima, M., Kakinuma, T.: 1990, Solar cycle dependence of global distribution of solar wind speed. Space Sci. Rev. 53, 173. doi: 10.1007/BF00212754 .
Lindsay, G.M., Luhmann, J.G., Russell, C.T., Gosling, J.T.: 1999, Relationships between coronal mass ejection speeds from coronagraph images and interplanetary characteristics of associated interplanetary coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 104(A6), 12515. doi: 10.1029/1999JA900051 .
Maloney, S.A., Gallagher, P.T.: 2010, Solar wind drag and the kinematics of interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. Lett. 724, L127. doi: 10.1088/2041-8205/724/2/L127 .
Manoharan, P.K.: 2006, Evolution of coronal mass ejections in the inner heliosphere: a study using white-light and scintillation images. Solar Phys. 235, 345. doi: 10.1007/s11207-006-0100-y .
Manoharan, P.K.: 2010, Ooty interplanetary scintillation – remote-sensing observations and analysis of coronal mass ejections in the heliosphere. Solar Phys. 265, 137. doi: 10.1007/s11207-010-9593-5 .
Manoharan, P.K., Kojima, M., Gopalswamy, N., Kondo, T., Smith, Z.: 2000, Radial evolution and turbulence characteristics of a coronal mass ejection. Astrophys. J. 530, 1061. doi: 10.1086/308378 .
McComas, D.J., Bame, S.J., Barker, P., Feldman, W.C., Phillips, J.L., Riley, P., Griffee, J.W.: 1998, Solar wind electron proton alpha monitor (SWEPAM) for the Advanced Composition Explorer. Space Sci. Rev. 86, 563. doi: 10.1023/A:1005040232597 .
Michalek, G., Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S.: 2003, A new method for estimating widths, velocities, and source location of halo coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 584, 472. doi: 10.1086/345526 .
Neugebauer, M.: 1975, Large-scale and solar-cycle variations of the solar wind. Space Sci. Rev. 17, 221. doi: 10.1007/BF00718575 .
Ogilvie, K.W., Chornay, D.J., Fritzenreiter, R.J., Hunsaker, F., Keller, J., Lobell, J., Miller, G., Scudder, J.D., Sittler, E.C. Jr., Torbert, R.B., et al.: 1995, SWE, a comprehensive plasma instrument for the Wind spacecraft. Space Sci. Rev. 71, 55. doi: 10.1007/BF00751326 .
Ontiveros, V., Vourlidas, A.: 2009, Quantitative measurements of coronal mass ejection-driven shocks from LASCO observations. Astrophys. J. 693, 267. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/693/1/267 .
Reiner, M.J., Kaiser, M.L., Bougeret, J.L.: 2007, Coronal and interplanetary propagation of CME/Shocks from radio, in situ and white-light observations. Astrophys. J. 663, 1369. doi: 10.1086/518683 .
Richardson, I.G., Cane, H.V.: 2010, Near-Earth interplanetary coronal mass ejections during solar cycle 23 (1996 – 2009): catalog and summary of properties. Solar Phys. 264, 189. doi: 10.1007/s11207-010-9568-6 .
Schwenn, R.: 1983, Direct correlations between coronal transients and interplanetary disturbances. Space Sci. Rev. 34, 85. doi: 10.1007/BF00221199 .
Schwenn, R., Mühlhäuser, K.H., Marsch, E.: 1981, In: Rosenbauer, H. (ed.) Solar Wind Four, Max-Planck-Inst f. Aeronomie, Katlenburg-Lindau, 126.
Stone, E.C., Frandsen, A.M., Mewaldt, R.A., Christian, E.R., Margolies, D., Ormes, J.F., Snow, F.: 1998, The advanced composition explorer. Space Sci. Rev. 86, 1. doi: 10.1023/A:1005082526237 .
Tappin, S.J.: 2006, The deceleration of an interplanetary transient from the Sun to 5 AU. Solar Phys. 233, 233. doi: 10.1007/s11207-006-2065-2 .
Tappin, S.J., Hewish, A., Gapper, G.R.: 1983, Tracking a major interplanetary disturbance. Planet. Space Sci. 31(10), 1171. doi: 10.1016/0032-0633(83)90106-X .
Temmer, M., Rollet, T., Möstl, C., Veronig, A., Vršnak, B., Odstrčil, D.: 2011, Influence of the ambient solar wind flow on the propagation behavior of interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 743, 101. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/743/2/101 .
Tokumaru, M., Kojima, M., Fujiki, K., Yokobe, A.: 2000a, Three-dimensional propagation of interplanetary disturbances detected with radio scintillation measurements at 327 MHz. J. Geophys. Res. 105(A5), 10435. doi: 10.1029/2000JA900001 .
Tokumaru, M., Kojima, M., Ishida, Y., Ohmi, T.: 2000b, Large-scale structure of solar wind turbulence near solar activity minimum. Adv. Space Res. 25(9), 1943. doi: 10.1016/S0273-1177(99)00630-4 .
Tokumaru, M., Kojima, M., Fujiki, K., Yamashita, M., Yokobe, A.: 2003, Toroidal-shaped interplanetary disturbance associated with the halo coronal mass ejection event on 14 July 2000. J. Geophys. Res. 108(A5), 1220. doi: 10.1029/2002JA009574 .
Tokumaru, M., Kojima, M., Fujiki, K., Yamashita, M.: 2006, Tracking heliospheric disturbances by interplanetary scintillation. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 13, 329.
Tsurutani, B.T., Gonzalez, W.D., Tang, F., Akasofu, S., Smith, E.J.: 1988, Origin of interplanetary southward magnetic fields responsible for major magnetic storms near solar maximum (1978 – 1979). J. Geophys. Res. 93(48), 8519. doi: 10.1029/JA093iA08p08519 .
Vlasov, V.I.: 1992, In: Marsch, E., Schwenn, R. (eds.) Solar Wind Seven, Proc. 3rd COSPAR Symp., Pergamon, New York, 301.
Vourlidas, A., Lynch, B.J., Howard, R.A., Li, Y.: 2012, How many CMEs have flux rope? Deciphering the signatures of shocks, flux ropes, and prominences in coronagraph observations of CMEs. Solar Phys. doi: 10.1007/s11207-012-0084-8 .
Vršnak, B., Gopalswamy, N.: 2002, Influence of the aerodynamic drag on the motion of interplanetary ejecta. J. Geophys. Res. 107(A2), 1019. doi: 10.1029/2001JA000120 .
Watanabe, T., Kakimuma, T.: 1986, Three-dimensional properties of interplanetary disturbances in 1978 – 1981. Astrophys. Space Sci. 118, 153. doi: 10.1007/BF00651120 .
Watanabe, T., Schwenn, R.: 1989, Large-scale propagation properties of interplanetary disturbances revealed from IPS and spacecraft observations. Space Sci. Rev. 51, 147. doi: 10.1007/BF00226272 .
Woo, R.: 1988, A synoptic study of Doppler scintillation transients in the solar wind. J. Geophys. Res. 93(A5), 3919. doi: 10.1029/JA093iA05p03919 .
Yashiro, S., Gopalswamy, N., Michalek, G., St. Cyr, O.C., Plunkett, S.P., Rich, N.B., Howard, R.A.: 2004, A catalog of white light coronal mass ejections observed by the SOHO spacecraft. J. Geophys. Res. 109, A07105. doi: 10.1029/2003JA010282 .
Young, A.T.: 1971, Interpretation of interplanetary scintillations. Astrophys. J. 168, 543. doi: 10.1086/151108 .
Acknowledgements
The IPS observations were carried out under the solar-wind program of the Solar-Terrestrial Environment Laboratory (STEL) of Nagoya University. We acknowledge use of the SOHO/LASCO CME catalog; this CME catalog is generated and maintained at the CDAW Data Center by NASA and the Catholic University of America in cooperation with the Naval Research Laboratory. SOHO is a project of international cooperation between ESA and NASA. We thank NASA/GSFC’s Space Physics Data Facility for use of the OMNIWeb service and OMNI data. We thank the IDL Astronomy User’s Library for the use of IDL software. We acknowledge use of the comprehensive ICME catalog compiled by I.G. Richardson and H.V. Cane. We also thank B.V. Jackson for useful help and comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iju, T., Tokumaru, M. & Fujiki, K. Radial Speed Evolution of Interplanetary Coronal Mass Ejections During Solar Cycle 23. Sol Phys 288, 331–353 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-013-0297-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-013-0297-5