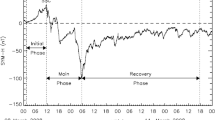Abstract
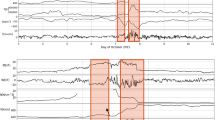
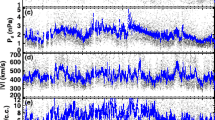
We discuss the temporal variations and frequency distributions of solar wind and interplanetary magnetic field parameters during the solar minimum of 2007 – 2009 from measurements returned by the IMPACT and PLASTIC instruments on STEREO-A. We find that the density and total field strength were significantly weaker than in the previous minimum. The Alfvén Mach number was higher than typical. This reflects the weakness of magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) forces, and has a direct effect on the solar wind–magnetosphere interactions. We then discuss two major aspects that this weak solar activity had on the magnetosphere, using data from Wind and ground-based observations: i) the dayside contribution to the cross-polar cap potential (CPCP), and ii) the shapes of the magnetopause and bow shock. For i) we find a low interplanetary electric field of 1.3±0.9 mV m−1 and a CPCP of 37.3±20.2 kV. The auroral activity is closely correlated to the prevalent stream–stream interactions. We suggest that the Alfvén wave trains in the fast streams and Kelvin–Helmholtz instability were the predominant agents mediating the transfer of solar wind momentum and energy to the magnetosphere during this three-year period. For ii) we determine 328 magnetopause and 271 bow shock crossings made by Geotail, Cluster 1, and the THEMIS B and C spacecraft during a three-month interval when the daily averages of the magnetic and kinetic energy densities attained their lowest value during the three years under survey. We use the same numerical approach as in Fairfield’s (J. Geophys. Res. 76, 7600, 1971) empirical model and compare our findings with three magnetopause models. The stand-off distance of the subsolar magnetopause and bow shock were 11.8 R E and 14.35 R E, respectively. When comparing with Fairfield’s (1971) classic result, we find that the subsolar magnetosheath is thinner by ∼1 R E. This is mainly due to the low dynamic pressure which results in a sunward shift of the magnetopause. The magnetopause is more flared than in Fairfield’s model. By contrast the bow shock is less flared, and the latter is the result of weaker MHD forces.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auster, H.U., Glassmeier, K.H., Magnes, W., Aydogar, O., Baumjohann, W., Constantinescu, D., Fischer, D., et al.: 2008, The THEMIS fluxgate magnetometer. Space Sci. Rev. 141, 235.
Balogh, A., Carr, C.M., Acũna, M.H., Dunlop, M.W., Beek, T.J., Brown, P., Fornacon, K.-H., et al.: 2001, The cluster magnetic field investigation: overview of in-flight performance and initial results. Ann. Geophys. 19, 1207.
Boyle, C.B., Reiff, P.H., Hairston, M.R.: 1997, Empirical polar cap potentials. J. Geophys. Res. 102, 111.
Burlaga, L.F., Lazarus, A.J.: 2000, Log-normal distributions and spectra of solar wind plasma fluctuations: Wind 1995 – 1998. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 2357.
Clette, F., Berghmans, D., Vanlommel, P.R., van der Linden, A.M., Koeckelenbergh, A., Wauters, L.: 2007, From the Wolf number to the international sunspot index: 25 years of SIDC. Adv. Space Res. 40, 919.
Cranmer, S.R., Hoeksema, J.T., Kohl, J.L. (eds.): 2010, SOHO-23: Understanding a Peculiar Solar Minimum. ASP CS-428.
Engebretson, M., Glassmeier, K.-H., Stellmacher, M., Hughes, E.J., Lühr, H.: 1998, The dependence of high-latitude PC5 wave power on solar wind velocity and on the phase of high-speed solar wind streams. J. Geophys. Res. 103, 26271.
Erkaev, N.V.: 1988, Results of the investigation of MHD flow around the magnetosphere. Geomagn. Aeron. 28, 455.
Fainberg, J., Osherovich, V.A.: 2002, Solar wind quasi-invariant as a heliospheric index of solar activity. In: Solar Variability: From Core to Outer Frontiers SP-506, ESA, Noordwijk, 43.
Fainberg, J., Osherovich, V.A., Stone, R.G.: 2001, Pioneer Venus Orbiter observations of a solar wind quasi-invariant. Geophys. Res. Lett. 28, 1447. doi: 10.1029/2000GL012160 .
Fairfield, D.H.: 1971, Average and unusual locations of the Earth’s magnetopause and bow shock. J. Geophys. Res. 76, 6700.
Farris, M.H., Russell, C.T.: 1994, Determining the standoff distance of the bow shock: Mach number dependence and use of models. J. Geophys. Res. 99, 17681.
Farrugia, C.J., Erkaev, N.V., Biernat, H.K., Burlaga, L.F.: 1995, Anomalous magnetosheath properties during Earth passage of an interplanetary magnetic cloud. J. Geophys. Res. 100, 19245.
Feynman, J., Ruzmaikin, A.: 2011, The Sun’s strange behavior: Maunder Minimum or Gleissberg Cycle? Solar Phys. 272, 351.
Galvin, A.B., Kistler, L.M., Popecki, M.A., Farrugia, C.J., Simunac, K.D.C., Ellis, E., Möbius, E., et al.: 2008, The Plasma and Suprathermal Ion Composition (PLASTIC) investigation on the STEREO observatories. Space Sci. Rev. 136, 437. doi: 10.1007/s11214-007-9296-x .
Gordeev, E.I., Sergeev, V., Pulkkinen, T.I., Palmroth, M.: 2011, Contribution of magnetotail reconnection to the cross-polar cap electric potential drop. J. Geophys. Res. 116, A08219. doi: 10.1029/2011JA016609 .
Gosling, J.T., Pizzo, V.J.: 1999, Formation and evolution of corotating interaction regions and their three dimensional structure. Space Sci. Rev. 89, 21.
Hairston, M.R., Hill, T.W., Heelis, R.A.: 2003, Observed saturation of the ionospheric polar cap potential during the 31 March 2001 storm. Geophys. Res. Lett. 30, 1325. doi: 10.1029/2002GL015894 .
Hairston, M.R., Drake, T.R., Skoug, R.: 2005, Saturation of the ionospheric polar cap potential during the October – November, 2003 superstorms. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A09S26. doi: 10.1029/2004JA010864 .
Harris, B.: 2011, Observational aspects of IMF draping around the magnetosphere. MS Thesis, UNH.
Kan, J.R., Lee, L.C.: 1979, Energy coupling function and solar wind-magnetosphere dynamo. Geophys. Res. Lett. 6, 577.
Kilpua, E.K.J., Pomoell, J., Voulidas, A., Vainio, R., Luhmann, J., Li, Y., Schroeder, P., Galvin, A.B., Simunac, K.: 2009, Stereo observations of interplanetary coronal mass ejections during solar minimum period. Ann. Geophys. 27, 4491.
King, J.H., Papitashvili, N.E.: 2005, Solar wind spatial scales in and comparisons of hourly Wind and ACE plasma and magnetic field data. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A02104. doi: 10.1029/2004JA010649 .
Kokubun, S., Yamamoto, T., Acũna, M.H., Hayashi, K., Shiokawa, K., Kawano, H.: 1995, The geotail magnetic field experiment. J. Geomagn. Geoelectr. 46, 7.
Kullen, A., Karlsson, T., Cumnock, J.A., Sundberg, T.: 2010, Occurrence and properties of substorms associated with pseudobreakups. J. Geophys. Res. 114, 115, A12310. doi: 10.1029/2010JA015866 .
Lavraud, B., Borovsky, J.E.: 2008, Altered solar wind-magnetosphere interaction at low Mach numbers: Coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 114, A00B08. doi: 10.0129/2008JA13192 .
Leitner, M., Farrugia, C.J.: 2010, Solar wind quasi-invariant within ICMEs. In: Solar Wind 12, AIP CP-1216, 652.
Leitner, M., Vörös, Z., Leubner, M.P.: 2009, Introducing log-kappa distributions for solar wind analysis. J. Geophys. Res. 114, A12104. doi: 10.1029/2009JA014476 .
Leitner, M., Farrugia, C.J., Vörös, Z.: 2011, Change of solar wind quasi-invariant in solar cycle 23 – analysis of PDFs. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 73, 290.
Leitner, M., Farrugia, C.J., Osherovich, V.A., Fainberg, J., Biernat, H.K., Ogilvie, K.W., Schwenn, R., Torbert, R.B.: 2005, The relative distribution of the magnetic and plasma kinetic energy densities in the inner heliosphere (< 1 AU). In: Solar Wind 11/SOHO 16, Connecting Sun and Heliosphere SP-592, ESA, Noordwijk, 743.
Leitner, M., Farrugia, C.J., Galvin, A., Biernat, H.K., Osherovich, V.A.: 2009, The solar wind quasi-invariant observed by STEREO-A and B at solar minimum 2007, and comparison with two other minima. Solar Phys. 259, 381. doi: 10.1007/s11207-009-9412-z .
Lepping, R.P., Acũna, M.H., Burlaga, L.F., Farrell, W.M., Slavin, J.A., Schatten, K.H., Mariani, F., et al.: 1995, The wind magnetic field investigation. Space Sci. Rev. 71, 207.
Lepping, R.P., Wu, C.C., Berdichevsky, D.B., Szabo, A.: 2011, Magnetic clouds at/near the 2007 – 2009 minimum: Frequency of occurrence and some unusual properties. Solar Phys. 274. doi: 10.1007/s11207-010-9646-9 .
Lockwood, M., Hairston, M., Finch, I., Rouillard, A.: 2009, Transpolar voltage and polar cap UX during the substorm cycle. J. Geophys. Res. 114, A0120. doi: 10.1029/2008JA013697 .
Luhmann, J., Zhang, T.L., Petrinec, S., Russell, C., Gazis, P., Barnes, A.: 1993, Solar cycle 21 effects on the interplanetary magnetic field and related parameters at 0.7 and 1.0 AU. J. Geophys. Res. 98, 5559.
Luhmann, J.G., Curtis, D.W., Schroeder, P., McCauley, J., Lin, R.P., Larson, D.E., Bale, S.D., et al.: 2008, STEREO IMPACT investigation goals, measurements, and data products. Space Sci. Rev. 136, 117.
McFadden, J.P., Carlson, C.W., Larson, D., Ludlam, M., Abiad, R., Elliott, B., Turin, P., et al.: 2008, The THEMIS ESA plasma instrument and in-flight calibration. Space Sci. Rev. 141, 277.
Merka, J., Szabo, A., Safrankova, J., Nemecek, S.: 2003, Earth’s bow shock and magnetopause in the case of a field-aligned upstream flow: Observation and model comparison. J. Geophys. Res. 108, 1269. doi: 10.1029/2002JA009697 .
Mukai, T., Machida, S., Hirahara, M., Teresawa, T., Kaya, N., Obara, T., Ejiri, M., Nishida, A.: 1994, The Low-Energy Particle (LEP) experiment onboard the Geotail satellite. J. Geomagn. Geoelectr. 46, 669.
Mühlbachler, S., Farrugia, C.J., Raeder, J., Biernat, H.K., Torbert, R.B.: 2005, A statistical investigation of dayside magnetosphere erosion showing saturation of response. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A11207. doi: 10.1029/2005JA011177 .
Ogilvie, K.W., Chornay, D.J., Fritzenreiter, R.J., Hunsaker, F., Keller, J., Lobell, J., Miller, G., et al.: 1995, SWE, A comprehensive plasma instrument for the Wind spacecraft. Space Sci. Rev. 71, 55.
Osherovich, V.A., Fainberg, J., Stone, R.G.: 1999, Solar wind quasi-invariant as a new index of solar activity. Geophys. Res. Lett. 26, 2597. doi: 10.1029/1999GL90058 .
Rème, H., Aoustin, C., Bosqued, J.M., Dandouras, I., Lavraud, B., Sauvaud, J.A., Barthe, A., et al.: 2001, First multi-spacecraft ion measurements in and near the Earth’s magnetosphere with the identical Cluster Ion Spectrometry (CIS) experiment. Ann. Geophys. 19, 1303.
Richardson, I.G., Cane, H.V.: 2010, Near-Earth interplanetary coronal mass ejections during solar cycle 23 (1996 – 2009): Catalog and summary of properties. Solar Phys. 264, 189.
Scherrer, P.H., Wilcox, J.M., Svalgaard, L., Duvall, T.L. Jr., Dittmer, P.H., Gustafson, E.K.: 1977, The mean magnetic field of the Sun: Observations at Stanford. Solar Phys. 54, 353.
Shue, J.-H., Song, P., Russell, C.T., Steinberg, J.T., Chao, J.K., Zastenker, G., Vaisberg, O.L., et al.: 1998, Magnetopause location under extreme solar wind conditions. J. Geophys. Res. 103, 17 691.
Sibeck, D.J., Lopez, R.E., Roelof, E.C.: 1991, Solar wind control of the magnetopause shape, location and motion. J. Geophys. Res. 96, 5489.
Siscoe, G.L., Erickson, E.M., Sonnerup, B.U.Ö., Maynard, N.C., Schoendorf, J.A., Siebert, K.D., Weimer, D.R., White, W.W., Wilson, G.R.: 2002, Hill model of transpolar potential saturation: Comparisons with MHD simulations. J. Geophys. Res. 107, 1075. doi: 10.1029/2001JA000109 .
Slavin, J.A., Holzer, R.E.: 1981, Solar wind flow about the terrestrial planets, 1. Modeling bow shock position and shape. J. Geophys. Res. 86, 11,401. doi: 10.1029/JA086iA13 .
Sonnerup, B.U.Ö.: 1974, Magnetopause reconnection rate. J. Geophys. Res. 79, 1546.
Tsurutani, B.T., Gonzalez, W.D.: 1987, The cause of high-intensity, long-duration, continuous AE activity (HILDCAAS): Interplanetary Alfvén wave trains. Planet. Space Sci. 35, 405.
Wang, Y.-M.: 2009, Coronal holes and open magnetic flux. Space Sci. Rev. 144, 383.
Wang, Y.-M., Robbrecht, E., Rouillard, A.P., Sheeley, N.R. Jr., Thernisien, A.F.R.: 2010, Formation and evolution of coronal holes following the emergence of active regions. Astrophys. J. 715, 39.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the referee for many helpful suggestions. We thank Marc Hairston, Jana Safrankova and Zdenek Nemecek for helpful comments. For the data used in the geomagnetic response section, we thank the World Data Center for Geomagnetism at the Kyoto web site, Japan; the OMNI website at Goddard Space Flight Center, USA; and the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) program, NOAA. Work at UNH was supported by NASA grants NNX10AQ29G and NAS5-03131. This work has received funding from the European Commissions’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007 – 2013) under the grant agreement No. 263253 [COMESEP]. V.O. was supported by NASA Grant NNXO9AR80G. M.T. greatly acknowledges the Austrian Science Fund (FWF): FWF V195-N16. This research was supported by a Marie Curie International Outgoing Fellowship within the 7th European Community Framework Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The Sun 360
Guest Editors: Bernhard Fleck, Bernd Heber, and Angelos Vourlidas
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farrugia, C.J., Harris, B., Leitner, M. et al. Deep Solar Activity Minimum 2007 – 2009: Solar Wind Properties and Major Effects on the Terrestrial Magnetosphere. Sol Phys 281, 461–489 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-012-0119-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-012-0119-1