Abstract
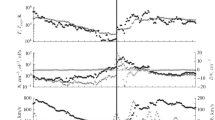
During the latitudinal alignment in 2004, ACE and Ulysses encountered two stream interaction regions (SIRs) each Carrington rotation from 2016 to 2018, at 1 and 5.4 AU, respectively. More SIR-driven shocks were observed at 5.4 AU than at 1 AU. Three small SIRs at 1 AU merged to form a strong SIR at 5.4 AU. We compare the Enlil model results with spacecraft observations from four aspects: i) the accuracy of the latest versions of models (WSA v2.2 and Enlil v2.7) vs. old versions (WSA v1.6 and Enlil v2.6), ii) the sensitivity to different solar magnetograms (MWO vs. NSO), iii) the sensitivity to different coronal models (WSA vs. MAS), iv) the predictive capability at 1 AU vs. 5.4 AU. We find the models can capture field sector boundaries with some time offset. Although the new versions have improved the SIR timing prediction, the time offset can be up to two days at 1 AU and four days at 5.4 AU. The models cannot capture some small-scale structures, including shocks and small SIRs at 1 AU. For SIRs, the temperature and total pressure are often underestimated, while the density compression is overestimated. For slow wind, the density is usually overestimated, while the temperature, magnetic field, and total pressure are often underestimated. The new versions have improved the prediction of the speed and density, but they need more robust scaling factors for magnetic field. The Enlil model results are very sensitive to different solar magnetograms and coronal models. It is hard to determine which magnetogram-coronal model combination is superior to others. Higher-resolution solar and coronal observations, a mission closer to the Sun, together with simulations of greater resolution and added physics, are ways to make progress for the solar wind modeling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschuler, M.A., Newkirk, G. Jr.: 1969, Magnetic fields and the structure of the solar corona. Solar Phys. 9, 131.
Arge, C.N., Pizzo, V.J.: 2000, Improvement in the prediction of solar wind conditions using real-time solar magnetic field updates. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 10465.
Arge, C.N., Odstrcil, D., Pizzo, V.J., Mayer, L.: 2002, Improved method for specifying solar wind speed near the Sun. In: Velli, M., Bruno, R. (eds.) Solar Wind Ten, AIP Conf. Proc. 679, 190.
Arge, C.N., Luhmann, J.G., Odstrcil, D., Schrijver, C.J., Li, Y.: 2004, Stream structure and coronal sources of the solar wind during the May 12th, 1997 CME. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 66, 1295.
Balogh, A., Beek, T.J., Forsyth, R.J., Hedgecock, P.C., Marquedant, R.J., Smith, E.J., Southwood, D.J., Tsurutani, B.T.: 1992, The magnetic field investigation on the Ulysses mission – Instrumentation and preliminary scientific results. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. 92, 221.
Bame, S.J., McComas, D.J., Barraclough, B.L., Phillips, J.L., Sofaly, K.J., Chavez, J.C., Goldstein, B.E., Sakurai, R.K.: 1992, The Ulysses solar wind plasma experiment. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. 92, 237.
Berdichevsky, D., Geiss, J., Gloeckler, G., Mall, U.: 1997, Excess heating of He2+ and O6+ relative to H+ downstream of interplanetary shocks. J. Geophys. Res. 102, 2623.
Cranmer, S.R.: 2000, Ion cyclotron wave dissipation in the solar corona: The summed effect of more than 2000 ion species. Astrophys. J. 532, 1197.
Cranmer, S.R.: 2004, Coronal heating versus solar wind acceleration. In: Walsh, R.W., Ireland, J., Danesy, D., Fleck, B. (eds.) Proc. SOHO-15 Workshop – Coronal Heating SP-575, ESA, Noordwijk, 154.
Dmitruk, P., Matthaeus, W.H., Seenu, N.: 2004, Test particle energization by current sheets and nonuniform fields in magnetohydrodynamic turbulence. Astrophys. J. 617, 667.
Dmitruk, P., Matthaeus, W.H., Milano, L.J., Oughton, S., Zank, G.P., Mullan, D.J.: 2002, Coronal heating distribution due to low-frequency, wave-driven turbulence. Astrophys. J. 575, 571.
Du, D., Wang, C., Hu, Q.: 2007, Propagation and evolution of a magnetic cloud from ACE to Ulysses. J. Geophys. Res. 112, A09101.
Harvey, J.W., Hill, F., Hubbard, R.P., Kennedy, J.R., Leibacher, J.W., Pintar, J.A., et al.: 1996, The Global Oscillation Network Group (GONG) project. Science 272, 1284.
Isenberg, P.A.: 2001, Heating of coronal holes and generation of the solar wind by ion-cyclotron resonance. Space Sci. Rev. 95, 119.
Jian, L.K., Russell, C.T., Luhmann, J.G.: 2011, Comparing solar minimum 23/24 with historical solar wind records at 1 AU. Solar Phys. doi: 10.1007/s11207-011-9737-2 .
Jian, L., Russell, C.T., Luhmann, J.G., Skoug, R.M.: 2006, Properties of stream interactions at one AU during 1995 – 2004. Solar Phys. 239, 337.
Jian, L.K., Russell, C.T., Luhmann, J.G., Skoug, R.M., Steinberg, J.T.: 2008a, Stream interactions and interplanetary coronal mass ejections at 0.72 AU. Solar Phys. 249, 85.
Jian, L.K., Russell, C.T., Luhmann, J.G., Skoug, R.M., Steinberg, J.T.: 2008b, Stream interactions and interplanetary coronal mass ejections at 5.3 AU near the solar ecliptic plane. Solar Phys. 250, 375.
Jian, L.K., Russell, C.T., Luhmann, J.G., Skoug, R.M.: 2008c, Evolution of solar wind structures from 0.72 to 1 AU. Adv. Space Res. 41, 259.
Jian, L.K., Russell, C.T., Strangeway, R.J., Leisner, J.S., Galvin, A.B.: 2009, Ion cyclotron waves in the solar wind observed by STEREO near 1 AU. Astrophys. J. Lett. 701, 105.
Jian, L.K., Russell, C.T., Luhmann, J.G., Anderson, B.J., Boardsen, S.A., Strangeway, R.J., Cowee, M.M., Wennmacher, A.: 2010, Observations of ion cyclotron waves in the solar wind near 0.3 AU. J. Geophys. Res. 115, A12115.
Kaiser, M.L., Kucera, T.A., Davila, J.M., St. Cyr, O.C., Guhathakurta, M., Christian, E.: 2008, The STEREO mission: An introduction. Space Sci. Rev. 136, 5.
Lee, C.O., Luhmann, J.G., Odstrcil, D., MacNeice, P.J., de Pater, I., Riley, P., Arge, C.N.: 2009, The solar wind at 1 AU during the declining phase of solar cycle 23: Comparison of 3D numerical model results with observations. Solar Phys. 254, 155.
Lee, L., Wu, B.: 2000, Heating and acceleration of protons and minor ions by fast shocks in the solar corona. Astrophys. J. 535, 1014.
Leibacher, J.W.: 1999, The global oscillation network group (GONG) project. Adv. Space Res. 24, 173.
MacNeice, P.: 2009, Validation of community models: 2. Development of a baseline using the Wang–Sheeley–Arge model. Space Weather 7, S12002.
Marsch, E., Marsden, R., Harrison, R., Wimmer-Schweingruber, R., Fleck, B.: 2005, Solar Orbiter – Mission profile, main goals and present status. Adv. Space Res. 36, 1360.
Matthaeus, W.H., Zank, G.P., Oughton, S., Mullan, D.J., Dmitruk, P.: 1999, Coronal heating by magnetohydrodynamic turbulence driven by reflected low-frequency waves. Astrophys. J. Lett. 523, 93.
McComas, D.J., Bame, S.J., Barker, P., Feldman, W.C., Phillips, J.L., Riley, P., Griffee, J.W.: 1998, Solar wind electron proton alpha monitor (SWEPAM) for the Advanced Composition Explorer. Space Sci. Rev. 86, 563.
McComas, D.J., Velli, M., Lewis, W.S., Acton, L.W., Balat-Pichelin, M., Bothmer, V., et al.: 2005, Probe Solar: Humanity’s first visit to a star. In: Fleck, B., Zurbuchen, T.H., Lacoste, H. (eds.) Proc. Solar Wind 11 / SOHO 16 Workshop – Connecting Sun and Heliosphere SP-592, ESA, Noordwijk, 279.
Neugebauer, M., Forsyth, R.J., Galvin, A.B., Harvey, K.L., Hoeksema, J.T., Lazarus, A.J., et al.: 1998, Spatial structure of the solar wind and comparisons with solar data and models. J. Geophys. Res. 103, 14587.
Odstrcil, D.: 2003, Modeling 3D solar wind structure. Adv. Space Res. 32, 497.
Odstrcil, D., Linker, J.A., Lionello, R., Mikić, Z., Riley, P., Pizzo, V.J., Luhmann, J.G.: 2002, Merging of coronal and heliospheric numerical two-dimensional MHD models. J. Geophys. Res. 107, 1493.
Owens, M.J., Arge, C.N., Spence, H.E., Pembroke, A.: 2005, An event-based approach to validating solar wind speed predictions: High-speed enhancements in the Wang–Sheeley–Arge model. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A12105.
Owens, M.J., Spence, H.E., McGregor, S., Hughes, W.J., Quinn, J.M., Arge, C.N., Riley, P., Linker, J., Odstrcil, D.: 2008, Metrics for solar wind prediction models: Comparison of empirical, hybrid, and physics-based schemes with 8 years of L1 observations. Space Weather 6, S08001.
Parker, E.N.: 1963, Interplanetary Dynamical Processes, Wiley-Interscience, New York.
Pierce, A.K.: 1969, The solar program of the Kitt Peak National Observatory. Solar Phys. 6, 498.
Richardson, I.G., Cliver, E.W., Cane, H.V.: 2000, Sources of geomagnetic activity over the solar cycle: Relative importance of coronal mass ejections, high-speed streams, and slow solar wind. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 18203.
Riley, P., Linker, J.A., Mikić, Z.: 2001, An empirically-driven global MHD model of the solar corona and inner heliosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 15889.
Riley, P., Linker, J.A., Mikić, Z., Lionello, R.: 2001, MHD modeling of the solar corona and inner heliosphere: Comparison with observations. In: Song, P., Singer, H.J., Siscoe, G.L. (eds.) Space Weather, AGU Geophys. Monogr. 125, 159.
Riley, P., Linker, J.A., Mikić, Z., Lionello, R., Ledvina, S.A., Luhmann, J.G.: 2006, A comparison between global solar magnetohydrodynamic and potential field source surface model results. Astrophys. J. 653, 1510.
Russell, C.T., Jian, L.K., Luhmann, J.G., Zhang, T.L., Neubauer, F.M., Skoug, R.M., Blanco-Cano, X., Omidi, N., Cowee, M.M.: 2008, Mirror mode waves: Messengers from the coronal heating region. Geophys. Res. Lett. 35, L15101.
Schatten, K.H.: 1971, Current sheet magnetic model for the solar corona. Cosm. Electrodyn. 2, 232.
Schatten, K.H., Wilcox, J.M., Ness, N.F.: 1969, A model of interplanetary and coronal magnetic fields. Solar Phys. 6, 442.
Scherrer, P.H., Bogart, R.S., Bush, R.I., Hoeksema, J.T., Kosovichev, A.G., Schou, J., et al.: 1995, The solar oscillation investigation – Michelson Doppler Imager. Solar Phys. 162, 129.
Skoug, R.M., Feldman, W.C., Gosling, J.T., McComas, D.J., Reisenfeld, D.B., Smith, C.W., Lepping, R.P., Balogh, A.: 2000, Radial variation of solar wind electrons inside a magnetic cloud observed at 1 and 5 AU. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 27269.
Smith, E.J., Wolfe, J.H.: 1976, Observations of interaction regions and corotating shocks between one and five AU: Pioneers 10 and 11. J. Geophys. Res. 3, 137.
Smith, C.W., L’Heureux, J., Ness, N.F., Acuña, M.H., Burlaga, L.F., Scheifele, J.: 1998, The ACE magnetic field experiment. Space Sci. Rev. 86, 613.
Toth, G., Odstrcil, D.: 1996, Comparison of some flux corrected transport and total variation diminishing numerical schemes for hydrodynamic and magnetohydrodynamic problems. J. Comput. Phys. 128, 82.
Ulrich, R.K., Evans, S., Boyden, J.E., Webster, L.: 2002, Mount Wilson synoptic magnetic fields: Improved instrumentation, calibration, and analysis applied to the 14 July 2000 flare and to the evolution of the dipole field. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 139, 259.
Wang, Y.M., Sheeley, N.R.: 1990a, Solar wind speed and coronal flux-tube expansion. Astrophys. J. 355, 726.
Wang, Y.M., Sheeley, N.R.: 1990b, Magnetic flux transport and the sunspot-cycle evolution of coronal holes and their wind streams. Astrophys. J. 365, 372.
Wenzel, K.P., Marsden, R.G., Page, D.E., Smith, E.J.: 1989, Ulysses: The first high-latitude heliospheric mission. Adv. Space Res. 9(4), 25.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jian, L.K., Russell, C.T., Luhmann, J.G. et al. Comparison of Observations at ACE and Ulysses with Enlil Model Results: Stream Interaction Regions During Carrington Rotations 2016 – 2018. Sol Phys 273, 179–203 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-011-9858-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-011-9858-7