Abstract
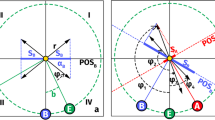
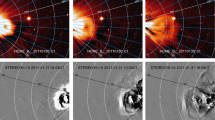
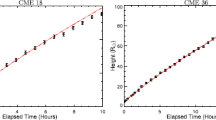
In this paper, ten CME events viewed by the STEREO twin spacecraft are analyzed to study the deflections of CMEs during their propagation in the corona. Based on the three-dimensional information of the CMEs derived by the graduated cylindrical shell (GCS) model (Thernisien, Howard, and Vourlidas in Astrophys. J. 652, 1305, 2006), it is found that the propagation directions of eight CMEs had changed. By applying the theoretical method proposed by Shen et al. (Solar Phys. 269, 389, 2011) to all the CMEs, we found that the deflections are consistent, in strength and direction, with the gradient of the magnetic energy density. There is a positive correlation between the deflection rate and the strength of the magnetic energy density gradient and a weak anti-correlation between the deflection rate and the CME speed. Our results suggest that the deflections of CMEs are mainly controlled by the background magnetic field and can be quantitatively described by the magnetic energy density gradient (MEDG) model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brueckner, G.E., Howard, R.A., Koomen, M.J., Korendyke, C.M., Michels, D.J., Moses, J.D., Socker, D.G., Dere, K.P., Lamy, P.L., Llebaria, A., Bout, M.V., Schwenn, R., Simnett, G.M., Bedford, D.K., Eyles, C.J.: 1995, The Large Angle Spectroscopic Coronagraph (LASCO). Solar Phys. 162, 357.
Byrne, J.P., Maloney, S.A., McAteer, R.T., Refojo, J.M., Gallagher, P.T.: 2010, Propagation of an Earth-directed coronal mass ejection in three dimensions. Nature Commun. 1, 74.
Chané, E., Jacobs, C., van der Holst, B., Poedts, S., Kimpe, D.: 2005, On the effect of the initial magnetic polarity and of the background wind on the evolution of CME shocks. Astron. Astrophys. 432, 331.
Colaninno, R.C., Vourlidas, A.: 2009, First determination of the true mass of coronal mass ejections: A novel approach to using the two STEREO viewpoints. Astrophys. J. 698, 852.
Cremades, H., Bothmer, V.: 2004, On the three-dimensional configuration of coronal mass ejections. Astron. Astrophys. 422, 307.
Cremades, H., Bothmer, V., Tripathi, D.: 2006, Properties of structured coronal mass ejections in solar cycle 23. Adv. Space Res. 38, 461.
Davis, C.J., Davies, J.A., Lockwood, M., Rouillard, A.P., Eyles, C.J., Harrison, R.A.: 2009, Stereoscopic imaging of an Earth-impacting solar coronal mass ejection: A major milestone for the STEREO mission. Geophys. Res. Lett. 36, L08102.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Krucker, S., Stenborg, G., Howard, R.A.: 2004, Intensity variation of large solar energetic particle events associated with coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 109, A12105.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Michalek, G., Xie, H., Lepping, R.P., Howard, R.A.: 2005, Solar source of the largest geomagnetic storm of cycle 23. Geophys. Res. Lett. 32, L12S09.
Gopalswamy, N., Mäkelä, P., Xie, H., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S.: 2009, CME interactions with coronal holes and their interplanetary consequences. J. Geophys. Res. 114, A00A22.
Howard, R.A., Moses, J.D., Vourlidas, A., Newmark, J.S., Socker, D.G., Plunkett, S.P., Korendyke, C.M., Cook, J.W., Hurley, A., Davila, J.M., Thompson, W.T., St. Cyr, O.C., Mentzell, E., Mehalick, K., Lemen, J.R., Wuelser, J.P., Duncan, D.W., Tarbell, T.D., Wolfson, C.J., Moore, A., Harrison, R.A., Waltham, N.R., Lang, J., Davis, C.J., Eyles, C.J., Mapson-Menard, H., Simnett, G.M., Halain, J.P., Defise, J.M., Mazy, E., Rochus, P., Mercier, R., Ravet, M.F., Delmotte, F., Auchere, F., Delaboudiniere, J.P., Bothmer, V., Deutsch, W., Wang, D., Rich, N., Cooper, S., Stephens, V., Maahs, G., Baugh, R., McMullin, D., Carter, T.: 2008, Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation (SECCHI). Space Sci. Rev. 136, 67.
Isenberg, P.A., Forbes, T.G.: 2007, A three-dimensional line-tied magnetic field model for solar eruptions. Astrophys. J. 670, 1453.
Kaiser, M.L., Kucera, T.A., Davila, J.M., St. Cyr, O.C., Guhathakurta, M., Christian, E.: 2008, The STEREO mission: An introduction. Space Sci. Rev. 136, 5.
Kilpua, E.K.J., Pomoell, J., Vourlidas, A., Vainio, R., Luhmann, J., Li, Y., Schroeder, P., Galvin, A.B., Simunac, K.: 2009, STEREO observations of interplanetary coronal mass ejections and prominence deflection during solar minimum period. Ann. Geophys. 27, 4491.
Liu, Y., Davies, J.A., Luhmann, J.G., Vourlidas, A., Bale, S.D., Lin, R.P.: 2010a, Geometric triangulation of imaging observations to track coronal mass ejections continuously out to 1 AU. Astrophys. J. 710, 82.
Liu, Y., Thernisien, A., Luhmann, J.G., Vourlidas, A., Davies, J.A., Lin, R.P., Bale, S.D.: 2010b, Reconstructing coronal mass ejections with coordinated imaging and in situ observations: Global structure, kinematics, and implications for space weather forecasting. Astrophys. J. 722, 1762.
Lugaz, N., Manchester, W.B., IV, Gombosi, T.I.: 2005, The evolution of coronal mass ejection density structures. Astrophys. J. 627, 1019.
Lugaz, N., Hernandez-Charpak, J.N., Roussev, I.I., Davis, C.J., Vourlidas, A., Davies, J.A.: 2010, Determining the azimuthal properties of coronal mass ejections from multi-spacecraft remote-sensing observations with STEREO SECCHI. Astrophys. J. 715, 493.
Lynch, B.J., Antiochos, S.K., Li, Y., Luhmann, J.G., DeVore, C.R.: 2009, Rotation of coronal mass ejections during eruption. Astrophys. J. 697, 1918.
MacQueen, R.M., Hundhausen, A.J., Conover, C.W.: 1986, The propagation of coronal mass ejection transients. J. Geophys. Res. 91, 31.
Möstl, C., Miklenic, C., Farrugia, C.J., Temmer, M., Veronig, A., Galvin, A.B., Vršnak, B., Biernat, H.K.: 2008, Two-spacecraft reconstruction of a magnetic cloud and comparison to its solar source. Ann. Geophys. 26, 3139.
Ness, N.F., Wilcox, J.M.: 1964, Solar origin of the interplanetary magnetic field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 13, 461.
Poomvises, W., Zhang, J., Olmedo, O.: 2010, Coronal mass ejection propagation and expansion in three-dimensional space in the heliosphere based on STEREO/SECCHI observations. Astrophys. J. Lett. 717, 159.
Shen, C., Wang, Y., Ye, P., Zhao, X.P., Gui, B., Wang, S.: 2007, Strength of coronal mass ejection-driven shocks near the Sun, and its importance in prediction of solar energetic particle events. Astrophys. J. 670, 849.
Shen, C., Wang, Y., Gui, B., Ye, P., Wang, S.: 2011, Kinematic evolution of a slow CME in corona viewed by STEREO-B on 8 October 2007. Solar Phys. 269, 389.
Shiota, D., Kusano, K., Miyoshi, T., Shibata, K.: 2010, Magnetohydrodynamic modeling for a formation process of coronal mass ejections: Interaction between an ejecting flux rope and an ambient field. Astrophys. J. 718, 1305.
Thernisien, A., Howard, R.A., Vourlidas, A.: 2006, Modeling of flux rope coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 652, 763.
Thernisien, A., Vourlidas, A., Howard, R.A.: 2009, Forward modeling of coronal mass ejections using STEREO/SECCHI data. Solar Phys. 256, 111.
Thompson, W.T.: 2006, Coordinate systems for solar image data. Astron. Astrophys. 449, 791.
Török, T., Kliem, B.: 2003, The evolution of twisting coronal magnetic flux tubes. Astron. Astrophys. 406, 1043.
Vourlidas, A., Subramanian, P., Dere, K.P., Howard, R.A.: 2000, Large-Angle Spectrometric Coronagraph measurements of the energetics of coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 534, 456.
Wang, Y., Zhang, J.: 2007, A comparative study between eruptive X-class flares associated with coronal mass ejections and confined X-class flares. Astrophys. J. 665, 1428.
Wang, Y., Ye, P., Wang, S., Zhou, G., Wang, J.: 2002, A statistical study on the geoeffectiveness of Earth-directed coronal mass ejections from March 1997 to December 2000. J. Geophys. Res. 107, 1340.
Wang, Y., Shen, C., Wang, S., Ye, P.: 2004, Deflection of corona mass ejection in the interplanetary medium. Solar Phys. 222, 329.
Wang, Y., Xue, X., Shen, C., Ye, P., Wang, S., Zhang, J.: 2006a, Impact of the major coronal mass ejections on geo-space during September 7 – 13, 2005. Astrophys. J. 646, 625.
Wang, Y., Zhou, G., Ye, P., Wang, S., Wang, J.: 2006b, A study on the orientation of interplanetary magnetic clouds and solar filaments. Astrophys. J. 651, 1245.
Wang, Y., Chen, C., Gui, B., Shen, C., Ye, P., Wang, S.: 2011, Statistical study of CME source locations: I. Understanding CMEs viewed in coronagraphs. J. Geophys. Res. 116, A04104.
Yurchyshyn, V., Abramenko, V., Tripathi, D.: 2009, Rotation of white-light coronal mass ejection structures as inferred from LASCO coronagraph. Astrophys. J. 705, 426.
Yurchyshyn, V., Hu, Q., Lepping, R.P., Lynch, B.J., Krall, J.: 2007, Orientations of LASCO halo CMEs and their connection to the flux rope structure of interplanetary CMEs. Adv. Space Res. 40, 1821.
Zhao, X.P., Hoeksema, J.T.: 1995, Prediction of the interplanetary magnetic field strength. J. Geophys. Res. 100, 19.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gui, B., Shen, C., Wang, Y. et al. Quantitative Analysis of CME Deflections in the Corona. Sol Phys 271, 111–139 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-011-9791-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-011-9791-9