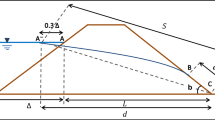
The softening and degradation effects of water on soil mass, increase of pore water pressure, and reduction of matric suction are usually considered for analyzing the contributions of rainfall to the failure of shallow soil slope. However, the effect of drag force at the fluid-solid interface due to slope surface runoff also deserves to be taken into account. To quantitatively investigate this effect, a modified approach based on the limit equilibrium method is proposed by establishing a nonlinear coupled mathematical model. The calculation results show that the effect of drag force at the fluid-solid interface should not be neglected especially when the runoff on shallow soil slopes is relatively deep.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. W. Brand, "Some thoughts on rainfall induced slope failures," Proc. 10th Int. Conf. Soil Mech. and Found. Eng., Stockholm, Sweden, 3, 373-376 (1981).
E. W. Brand, "Relationship between rainfall and landslides in Hong Kong," Proc. 4th Int. Symp. on Landslides, Ontario, Canada, 377-384 (1984).
D. G. Fredlund and H. Rahardjo, "Hillside slope stability assessment in unsaturated residual soils," In: IKRAM Seminar on the Geotechnical Aspects of Hillside Development, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1-41 (1994).
H. Rahardjo, M. F. Chang, and T. T. Lim, "Stability of residual soil slopes as affected by rainfalls," Proc. 7th Int. Symp. on Landslides, Trondheim, Norway, Balkema, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1109-1114 (1996).
T. T. Lim, H. Rahardjo, M. F. Chang, et al., "Effect of rainfall on matrix suction in a residual soil slope," Can. Geotech. J., 33(4), 618-628 (1996).
Y. Tsukamoto, K. Ishihara, and Y. Nosaka, "On the initiation of rainfall induced soil failure," Proc. 11th Danube-European Conf. Soil Mech. Geotech. Eng., Porec, Croatia, Balkema, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 883-890 (1998).
L. Montrasio, R. Valentino, and G. L. Losi, "Rainfall-induced shallow landslides: a model for the triggering mechanism of some case studies in Northern Italy," Landslides, 6(3), 241-251 (2009).
S. E. Cho, "Stability analysis of unsaturated soil slope considering rainfall infiltration by two-pahse flow model," J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig, 15(6), 321-329 (2015).
Q. Zhang, "Rainfall infiltration depth and formation mechanism of slow-inclination soil landslides in Nanjiang," Chin. J. Geotech. Eng., 38(8), 1447-1455 (2016).
Y. Q. Xu, "12.20" Guangming new district landslide, Shenzhen," Chin. J. Geol. Hazard Control, 28(1), 11-14 (2016).
K. Terzaghi, "Mechanism of landslides," Application of Geology to Engineering Practice, New York, 83-123 (1950).
R. C. Sidle, and D. N. Swanston, "Analysis of a small debris slide in coastal Alaska," Can. Geotech. J., 19(2), 167-174 (1982).
S. Matsuura, S. Asano, and T. Okamoto, "Relationship between rain and/or meltwater, pore-water pressure and displacement of a reactivated landslide," Eng. Geol., 101(2), 49-59 (2008).
M. Xia, G. M. Ren, and X. L. Ma, "Deformation and mechanism of landslide influenced by the effects of reservoir water and rainfall," Three Gorges, China. Nat. Hazards, 68(2), 467-482 (2013).
M. Xia, and G. M. Ren, "Relationship between landslide stability and reservoir water level variation," Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ., 74(3), 909-917 (2015).
R.P. Brenner, H.K. Tam, and E.W. Brand, "Field stress path simulation of rain-induced slope failure," Proc. 11th Int. Conf. Soil Mech. Found. Eng., 2, 373-376 (1985).
G. Liu, G. Rong, and J. Peng, "Numerical simulation on undrained triaxial behavior of saturated soil by a fluid coupled-DEM model," Eng. Geol., 193(2), 256-266 (2015).
G. H. Wang, and K. Sassa, "Seismic loading impacts on excess pore-water pressure maintain landslide triggered flowslides," Earth Surf. Proc. Land, 34(2), 234-241 (2009).
H. J. Wilson, "Stokes flow past three spheres," J. Comput. Phys., 245(15), 302-316 (2013).
R.R. Rumer, and P.A. Drinker, "Resistance to laminar flow through porous media," J. Hydraul. Div., 92, 155-163 (1966).
J. R. Chai, "Drag forces applied on rock matrix by fluid flow through fracture network in rock mass," Comput. Meth. Eng. Sci., 291-291 (2006).
G. Neale, and W. Nader, "Practical significance of brinkman's extension of Darcy's law: Coupled parallel flows within a channel and a bounding porous medium," Can. J. Chem. Eng., 52(4), 475-478 (2009).
C. Deng, and D.M. Martinez, "Viscous flow in a channel partially filled with a porous medium and with wall suction," Chem. Eng. Sci., 60(2), 329-336 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Osnovaniya, Fundamenty i Mekhanika Gruntov, No. 1, pp. 7-13, January-February, 2019.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, F., Fu, W., Yuan, X. et al. Drag Force Effect of Surface Runoff on Stability of Shallow Soil Slope. Soil Mech Found Eng 56, 12–20 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11204-019-09563-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11204-019-09563-0