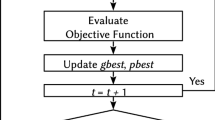
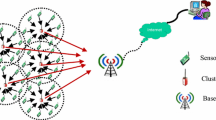
In order to solve the multi-factor conflict problem in a cluster head selection process, to optimize it and prolong the network life cycle, a chaotic particle swarm optimization method based on the multi-factor conflict is proposed for clustering the sensor networks. The object of study is a sensor network with a hierarchical clustering network topology, which includes cluster member nodes, cluster head nodes and sink nodes. The energy consumption model of data acquisition and processing in the network nodes is constructed. Four kinds of multi-factor collision problems of the node residual energy, the inter-nodal energy balance and the distance between the base stations, as well as the probability of the node acting as a cluster head are discussed. An energy balance index based on the standard deviation of the node residual energy is introduced to construct an adaptive degree function to obtain the relationship between the current and the previous adaptive degrees of particles. Then, the inertia weight is determined. The chaotic particle swarm optimization algorithm based on the adaptive inertia weight is used to optimize the cluster head selection. The nodes in the communication area are regarded as the cluster members. The cluster head number can meet the optimal cluster head number, which further improves the network energy efficiency. The simulation results show that the death time of the first node, the half node and the last node of the sensor network clustered by this method is 83.33%, 34.14% and 43.14% longer than that of the LEACH method, respectively. The energy consumption of the sensor network clustering is low, the network life cycle is long and the clustering effect is good.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. C. S. Rao, P. K. Jana and H. A. Banka., Wirel. Netw., 23, No. 7, 2005–2020 (2017).
T. Kang and S. F. Wei, Int. Tech. Sens., No.1, 122–125 (2019)
D. F. Zhong, J. J. Xue, F. He, et al., Chin. High Technol. Lett., 27, No. 6, 530–536 (2017).
Y. W. Du, K. Feng and Y. X. Lian, J. Chin. Comput. Syst., 38, No. 10, 2221–2225 (2017).
W. He, H. Ling, Z. Zhang, et al., Int. J. Geogr. Inform. Sci., 32, No. 4, 827–846 (2018).
G. Li and W. Wang, Control Eng. Chin., 24, No. 7, 1359–1365 (2017).
S. Q. Tian, B. H. Lang and T. L. Han, J. Jilin Univ., (Inf. Sci. Ed.), 36, No. 1, 19–21 (2018).
D. D. Dong, B. F. Liu, X. Dong, et al. Chin. J. Sens. Actuator., 30, No. 12, 1918–1924 (2017).
X. W. Li, Comput. Simulation, 35, No. 3, 205–209 (2018).
Z. Z. Liu and Liu Y., J. Chin. Comput. Syst., 38, No. 10, 2207–2210 (2017).
Y. J. Sun, Wool Text. J., 45, No. 9, 80–85 (2017).
Q. Yu, J. H. Li, Q. F. Zhao, et al., Elect. Meas. Instrum., 54, No. 13, 110–114 (2017).
B. Wu, C. Cui, J. Yu, et al., Comput. Sci., No. 2, 157–162 (2017).
L. S. Li and X. J. Zhang, Comput. Eng. Appl., 54, No. 9, 139–144 (2018).
J. Zhao, Z. G. Yu, X. Feng, et al., J. Chin. Acad. Electron. Inf. Technol., 13, No. 03, 38–45 (2018).
Z. Li, Y. F. Chen., B. Zhang, et al., J. Pow. Supply, 15, No. 3, 148–155 (2017).
P. Peng, H. X. Cheng, X. C. Chen, et al., Chin. J. Pow. Source., 41, No. 11, 1541–1544 (2017).
Y.G. Hu, X.L. Meng, C. Zhao, et al., Automation Instrum., No. 6, 14–15 (2015).
C. H. Wang, W. N. Shen and H. S. Hu, J. Jilin Univ. (Sci. Ed.), 56, No. 3, 169–176 (2018).
H. J. Dong, S. Y. Wei, X. C. Liu, et al., Comput. Sci., 45, No. 1, 14–23 (2018).
J. Chen, Comput. Simulat., 34, No. 10, 277–280 (2017).
A. Atangana and R. T. Alqahtani, Math. Modell. Nat. Ph., 14, No. 3, 313 (2019).
K. M. Saad, D. Baleanu and A. Atangana, Comput. Appl. Math., 37, No. 4, 5203–5216 (2018).
Z. Xiong, et al., Multimedia Tools App., 78, No. 22, 31035–31055 (2019).
H. G. Citil, Appl. Math. Nonlinear Sci., 4, No. 2, 407–416 (2019).
R. A. Mundewadi, and S. Kumbinarasaiah, Appl. Math. Nonlinear Sci., 4, No. 2, 395–406 (2019).
M. Naeem, M. K. Siddiqui, J. L. G. Guirao, et al., Appl. Math. Nonlinear Sci., 3, No. 1, 209–228 (2020).
S. B. Venkatesha, Appl. Math. Nonlinear Sci., 5, No. 1, 85–92 (2020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Izvestiya Vysshikh Uchebnykh Zavedenii, Fizika, No. 8, pp. 99–108, August, 2021.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Qian, J., Zhou, A. et al. Clustering Method of Chaotic Particle Swarm Optimization Sensor Networks Based on Multifactor Conflict. Russ Phys J 64, 1485–1497 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-021-02481-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-021-02481-5