Abstract
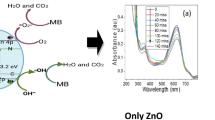
ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles sensitized by C-modified TiO2 hybrids (ZnFe2O4–TiO2/C) were successfully prepared by a feasible method. The ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles were prepared by mechanical alloying and annealing. The residual organic compounds in the synthetic process of TiO2 were selected as the carbon source. The as-prepared composites were characterized by X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, X-ray fluorescence, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, ultraviolet–visible light diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (UV–Vis) and N2 adsorption–desorption analysis. The photocatalytic activity of the photocatalysts was measured by degradation of methyl orange under ultraviolet (UV) light and simulated solar irradiation, respectively. The results show that the carbon did not enter the TiO2 lattice but adhered to the surface of TiO2. The photocatalytic activity of the as-prepared C-modified TiO2 (TiO2/C) improved both under UV and simulated solar light irradiation, but the improvement was not dramatic. Introduction of ZnFe2O4 into the TiO2/C could enhance the absorption spectrum range. The ZnFe2O4–TiO2/C hybrids exhibited a higher photocatalytic activity both than that of the pure TiO2 and TiO2/C under either UV or simulated solar light irradiation. The complex synergistic effect plays an important role in improving the photocatalytic performance of ZnFe2O4–TiO2/C composites. The optimum photocatalytic performance was obtained from the ZnFe2O4(0.8 wt%)–TiO2/C sample.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Liu, R. Inde, M. Nishikawa, X.Q. Qiu, D. Atarashi, E. Sakai, Y. Nosaka, K. Hashimoto, M. Miyauchi, Enhanced photoactivity with nanocluster-grafted titanium dioxide photocatalysts. ACS Nano 8, 7229–7238 (2014)
Q. Xu, J. Feng, L. Li, Q. Xiao, J. Wang, Hollow ZnFe2O4/TiO2 composites: high-performance and recyclable visible-light photocatalyst. J. Alloys Compd. 641, 110–118 (2015)
Y. Yao, J. Qin, H. Chen, F. Wei, X. Liu, J. Wang, S. Wang, One-pot approach for synthesis of N-doped TiO2/ZnFe2O4 hybrid as an efficient photocatalyst for degradation of aqueous organic pollutants. J. Hazard. Mater. 291, 28–37 (2015)
G. Xiao, H. Su, T. Tan, Synthesis of core–shell bioaffinity chitosan-TiO2 composite and its environmental applications. J. Hazard. Mater. 283, 888–896 (2015)
K. Nagaveni, M.S. Hegde, N. Ravishankar, G.N. Subbanna, G. Madras, Synthesis and structure of nanocrystalline TiO2 with lower band gap showing high photocatalytic activity. Langmuir 20, 2900–2907 (2004)
S.K. Parayil, H.S. Kibombo, C. Wu, R. Peng, J. Baltrusaitis, R.T. Koodali, Enhanced photocatalytic water splitting activity of carbon-modified TiO2 composite materials synthesized by a green synthetic approach. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 37, 8257–8267 (2012)
Y. Zhang, P. Zhang, Y. Huo, D. Zhang, G. Li, H. Li, Ethanol supercritical route for fabricating bimodal carbon modified mesoporous TiO2 with enhanced photocatalytic capability in degrading phenol. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 115–116, 236–244 (2012)
S.D. Kulkarni, S. Kumbar, S.G. Menon, K.S. Choudhari, C. Santhosh, Magnetically separable core–shell ZnFe2O4@ZnO nanoparticles for visible light photodegradation of methyl orange. Mater. Res. Bull. 77, 70–77 (2016)
R. Shao, L. Sun, L. Tang, Z. Chen, Preparation and characterization of magnetic core–shell ZnFe2O4@ZnO nanoparticles and their application for the photodegradation of methylene blue. Chem. Eng. J. 217, 185–191 (2013)
Z. Yuan, L. Zhang, Synthesis, characterization and photocatalyticactivity of ZnFe2O4/TiO2 nanocomposite. J. Mater. Chem. 11, 1265–1268 (2001)
M. Wang, L. Sun, J. Cai, P. Huang, Y. Su, C. Lin, A facile hydrothermal deposition of ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles on TiO2 nanotube arrays for enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity. J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 12082–12087 (2013)
S.H. Yu, T. Fujino, M. Yoshimura, Hydrothermal synthesis of ZnFe2O4 ultrafine particles with high magnetization. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 256, 420–424 (2003)
L. Wang, Q. Zhou, F. Li, Ionic disorder and yaffet–kittel angle in nanoparticles of ZnFe2O4 prepared by sol-gel method. Phys. Stat. Sol. (b) 241, 377–382 (2004)
H. Lee, J.C. Jung, H. Kim, Y.M. Chung, T.J. Kim, S.J. Lee, S.H. Oh, Y.S. Kim, I.K. Song, Preparation of ZnFe2O4 catalysts by a co-precipitation method using aqueous buffer solution and their catalytic activity for oxidative dehydrogenation of n-butene to 1, 3-butadiene. Catal. Lett. 122, 281–286 (2008)
Y. Zhou, S. Xi, C. Sun, H. Wu, Facile synthesis of Cu2ZnSnS4 powders by mechanical alloying and annealing. Mater. Lett. 169, 176–179 (2016)
T.F. Marinca, B.V. Neamţu, F. Popa, V.F. Tarţa, P. Pascuta, A.F. Takacs, I. Chicinas, Synthesis and characterization of the NiFe2O4/Ni3Fe nanocomposite powder and compacts obtained by mechanical milling and spark plasma sintering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 285P, 2–9 (2013)
T. Marinca, I. Chicinas, O. Isnard, V. Pop, Structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline ZnFe2O4 powder synthesized by reactive ball milling. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 5, 39–43 (2011)
D.H. Wang, L. Jia, X.L. Wu, L.Q. Lu, A.W. Xu, One-step hydrothermal synthesis of N-doped TiO2/C nanocomposites with high visible light photocatalytic activity. Nanoscale 4, 576–584 (2012)
A. Najafian, R. Rahimi, S. Zargari, M.M. Moghaddas, A. Nazemi, Synthesis and photocatalytic activity of V-doped mesoporous TiO2 photosensitized with porphyrin supported by SBA-15. Res. Chem. Intermed. 42, 3441–3458 (2016)
S. Cao, M. Shi, H. Wang, F. Yu, X. Weng, Y. Liu, Z. Wu, A two-stage Ce/TiO2–Cu/CeO2 catalyst with separated catalytic functions for deep catalytic combustion of CH2Cl2. Chem. Eng. J. 290, 147–153 (2016)
A. Eshaghi, S. Hayeripour, A. Eshaghi, Photocatalytic decolorization of reactive red 198 dye by a TiO2—activated carbon nano-composite derived from the sol–gel method. Res. Chem. Intermed. 42, 2461–2471 (2016)
P. Xiong, L. Wang, X. Sun, B. Xu, X. Wang, Ternary titania-cobalt ferrite-polyaniline nanocomposite: a magnetically recyclable hybrid for adsorption and photodegradation of dyes under visible light. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 52, 10105–10113 (2013)
Y. Liu, W. Zhang, L. Bian, W. Liang, J. Zhang, B. Yu, Structure, morphology and photocatalytic activity of Cu2O/Pt/TiO2 three-layered nanocomposite films. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 21, 26–32 (2014)
J. Zhang, J. Song, H. Niu, C. Mao, S. Zhang, Y. Shen, ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and enhanced gas sensing property for acetone. Sensor. Actuat. B Chem. 221, 55–62 (2015)
I. Ismail, M. Hashim, K.A. Matori, R. Alias, J. Hassan, Milling time and BPR dependence on permeability and losses of Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 synthesized via mechanical alloying process. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 1470–1476 (2011)
S. Bid, S.K. Pradhan, Preparation of zinc ferrite by high-energy ball-milling and microstructure characterization by Rietveld’s analysis. Mater. Chem. Phys. 82, 27–37 (2003)
L. Wu, T. Wu, M. Mao, M. Zhang, T. Wang, Electrospinning synthesis of Ni°, Fe° codoped ultrafine-ZnFe2O4/C nanofibers and their properties for lithium ion storage. Electrochim. Acta 194, 357–366 (2016)
A.P. Grosvenor, B.A. Kobe, M.C. Biesinger, N.S. McIntyre, Investigation of multiplet splitting of Fe 2p XPS spectra and bonding in iron compounds. Surf. Interface Anal. 36, 1564–1574 (2004)
T. Yamashita, P. Hayes, Analysis of XPS spectra of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions in oxide materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 254, 2441–2449 (2008)
C.S. Luo, H. Luo, X.Y. He, Research on 304,321,316 lect. Stainless steel corrosion under the calcinating gas atmosphere of ammonium paramolybdate. Adv. Mater. Res. 602–604, 421–425 (2012)
H. Lin, H. Zhang, L.W. Hou, Degradation of C. I. Acid orange 7 in aqueous solution by a novel electro/Fe3O4/PDS process. J. Hazard. Mater. 276C, 182–191 (2014)
L. Han, X. Zhou, L. Wan, Y. Deng, S. Zhan, Synthesis of ZnFe2O4 nanoplates by succinic acid-assisted hydrothermal route and their photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B under visible light. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2, 123–130 (2014)
Z. Lei, Y. Xiao, L. Dang, W. You, G. Hu, J. Zhang, Nickel-catalyzed fabrication of SiO2, TiO2/graphitized carbon, and the resultant graphitized carbon with periodically macroporous structure. Chem. Mater. 19, 477–484 (2007)
H.J. Yun, H. Lee, J.B. Joo, N.D. Kim, M.Y. Kang, J.Y. Yun, Facile preparation of high performance visible light sensitive photo-catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 94, 241–247 (2010)
F. Jia, Z. Yao, Z. Jiang, C. Li, Preparation of carbon coated TiO2 nanotubes film and its catalytic application for H2 generation. Catal. Commun. 12, 497–501 (2011)
B. Xin, P. Wang, D. Ding, J. Liu, Z. Ren, H. Fu, Effect of surface species on Cu–TiO2 photocatalytic activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 254, 2569–2574 (2008)
L. Zhao, X. Chen, X. Wang, Y. Zhang, W. Wei, Y. Sun, M. Antonietti, M.M. Titirici, One-step solvothermal synthesis of a carbon@TiO2 dyade structure effectively promoting visible-light photocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 22, 3317–3321 (2010)
S. Wu, P. Wang, Y. Cai, D. Liang, Y. Ye, Z. Tian, J. Liu, C. Liang, Reduced graphene oxide anchored magnetic ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity. RSC Adv. 5, 9069–9074 (2015)
H. Hiura, T.W. Ebbesen, K. Tanigaki, Opening and purification of carbon nanotubes in high yields. Adv. Mater. 7, 275–276 (1995)
S. Hou, S. Su, M.L. Kasner, P. Shah, K. Patel, C.J. Madarang, Formation of highly stable dispersions of silane-functionalized reduced graphene oxide. Chem. Phys. Lett. 501, 68–74 (2010)
H. Irie, Y. Watanabe, K. Hashimoto, Carbon-doped anatase TiO2 powders as a visible-light sensitive photocatalyst. Chem. Lett. 32, 772–773 (2003)
J. Lee, S. Han, J. Kim, Y. Lee, A. Ko, B. Roh, I. Hwang, K. Park, TiO2@carbon core–shell nanostructure supports for platinum and their use for methanol electrooxidation. Carbon 48, 2290–2296 (2010)
M. Mohameda, W.N.W. Salleh, J. Jaafar, Z. Hir, M. Rosmid, M.A. Mutalib, A. Ismail, M. Tanemuraea, Regenerated cellulose membrane as bio-template for in situ growthof visible-light driven C-modified mesoporous titania. Carbohydr. Polym. 146, 166–173 (2016)
M.A. Nawi, I. Nawawi, Preparation and characterization of TiO2 coated with a thin carbon layer for enhanced photocatalytic activity under fluorescent lamp and solar light irradiations. App. Catal. A Gen. 453, 80–91 (2013)
J. Yu, G. Dai, Q. Xiang, M. Jaroniec, Fabrication and enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity of carbon self-doped TiO2 sheets with exposed 001 facets. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 1049–1057 (2011)
X. Shao, W. Lu, R. Zhang, F. Pan, Enhanced photocatalytic activity of TiO2–C hybrid aerogels for methylene blue degradation. Sci. Rep. 3, 3018 (2013)
Z.L. Zhang, M. Wan, Y.L. Mao, Enhanced photovoltaic effect of TiO2-based composite ZnFe2O4/TiO2. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 233, 15–19 (2012)
Acknowledgments
The project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51271143).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Guo, C., Xi, S. et al. Preparation of ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles by mechanical alloying and annealing for sensitizing C-modified TiO2 and acquirement of efficient photocatalyst. Res Chem Intermed 43, 1495–1512 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-016-2711-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-016-2711-8