Abstract
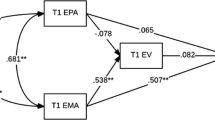
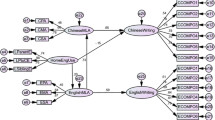
How are metalinguistic skills associated with vocabulary knowledge in languages with contrasting phonological and morphological properties? To address this question, tasks of phonological awareness and morphological awareness, other reasoning and literacy-related skills, and measures of vocabulary knowledge in Chinese and English, were administered to 217 Hong Kong Chinese kindergarten children learning English as a second language. Syllable-level awareness but not phoneme onset awareness was strongly associated with Chinese vocabulary knowledge; phoneme onset awareness but not syllable awareness was associated with English vocabulary knowledge. In hierarchical regression equations, phonological awareness in English explained unique variance in English vocabulary knowledge but not in Chinese vocabulary knowledge. In contrast, measures of morphological awareness, which were strongly associated with syllable awareness, uniquely explained 13% of the variance in Chinese vocabulary knowledge apart from all other measures included but were not uniquely associated with English vocabulary knowledge. Findings highlight the strong overlap across phonological and morphological awareness in Chinese and the different associations of each to vocabulary acquisition in Chinese (L1) and English (L2) languages.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams M. J. (1990). Beginning to read: Thinking and learning about print.. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
Avons S. E., Christopher A., Cupples L. and Lovegrove W. J. (1998). Measures of phonological short-term memory and their relationship to vocabulary development. Applied Psycholinguistics 19(4): 583–601
Berko J. (1958). The child’s learning of English morphology. Word 14: 150–177
Baker S. K., Simmons D. C. and Kameenui E. J. (1998). Vocabulary acquisition: Research bases. In: Simmons, D. C. and Kameenui, E. J. (eds) What reading research tells us about children with diverse learning needs: Bases and basics, pp 183–217. Lawrence, Mahwah, NJ, US
Bowey J. A. (2001). Nonword repetition and young children’s receptive vocabulary: A longitudinal study. Applied Psycholinguistics 22(3): 441–469
Castles A. and Coltheart M. (2004). Is there a causal link from phonological awareness to success in learning to read?. Cognition 91(1): 77–111
Carlisle J. F., Beeman M., Davis L. H. and Spharim G. (1999). Relationship of metalinguistic capabilities and reading achievement for children who are becoming bilingual. Applied Psycholinguistics 20(4): 459–478
Carlisle J. -F. and Fleming J. (2003). Lexical processing of morphologically complex words in the elementary years. Scientific Studies of Reading 7(3): 239–253
Cheung H., Chen H. C., Yip L. C., Wong O. C. and Hills M. (2001). The development of phonological awareness: Effects of spoken language experience and orthography. Cognition 81(3): 227–241
Cheung P. S. P., Lee K. Y. S. and Lee L. W. T. (1997). The development of the ‘Cantonese Receptive Vocabulary Test’ for children aged 2–6 in Hong Kong. European Journal of Disorders of Communication 32: 127–138
Chomsky C. (1976). Creativity and innovation in child language. Journal of Education, Boston 158(2): 12–24
Clark E. V., Gelman S. A. and Lane N. M. (1985). Compound nouns and category structure in young children. Child Development 56(1): 84–94
Clark E. V. (1995). The lexicon and syntax. In: Miller, J. L. and Eismas, P. D. (eds) Speech, language and communication., pp 303–337. Academic Press, San Diego
Comeau L., Cormier P., Grandmaison E. and Lacroix D. (1999). A longitudinal study of phonological processing skills in children learning to read in a second language. Journal of Educational Psychology 91(1): 29–43
Dunn L. M. and Dunn L. M. (1997). Peabody Picture Vocabulary Test – 3rd edition:. American Guidance Service, Circle Pines, MN
Durgunoglu A. Y., Nagy W. E. and Hancin-Bhatt B. J. (1993). Cross-language transfer of phonological awareness. Journal of Educational Psychology 85(3): 453–465
Fowler A. E. (1991). How early phonological development might set the stage for phoneme awareness. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Hillsdale, NJ, England
Gathercole S. E., Willis C. S., Emslie H. and Baddeley A.D. (1992). Phonological memory and vocabulary development during the early school years: A longitudinal study. Developmental Psychology 28(5): 887–898
Ho C. S. H. and Bryant P. (1997). Phonological skills are important in learning to read Chinese. Developmental Psychology 33: 946–951
Ho C. S.-H., Chan D. W.-O., Tsang S. M. and Lee L. H. (2000). The Hong Kong Test of Specific Learning Disabilities in Reading and Writing (HKT-SpLD). Chinese University of Hong Kong and Education Department, HKSAR Government, Hong Kong, China
Ku Y. M. and Anderson R. C. (2003). Development of morphological awareness in Chinese and English. Reading and Writing 16(5): 399–422
Lindsey K. A., Manis F. R. and Bailey C. E. (2003). Prediction of first-grade reading in Spanish-speaking English-language learners. Journal of Educational Psychology 95: 482–494
Mann V. A. (2000). Introduction to special issue on morphology and the acquisition of alphabetic writing systems Reading and Writing. An Interdisciplinary Journal 12: 143–147
Metsala J. L. and Walley A. C. (1998). Spoken vocabulary growth and the segmental restructuring of lexical representations: Precursors to phonemic awareness and early reading ability. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Mahwah, NJ, US
Metsala J. -L. (1999). Young children’s phonological awareness and nonword repetition as a function of vocabulary development. Journal of Educational Psychology 91(1): 3–19
McBride-Chang C., Bialystok E., Chong K. -K. Y. and Li Y. (2004). Levels of phonological awareness in three cultures. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology 89(2): 93–111
McBride-Chang C. and Ho C. S. -H. (2000). Developmental issues in Chinese children’s character acquisition. Journal of Educational Psychology 92: 1–6
McBride-Chang C. and Kail R. V. (2002). Cross-cultural similarities in the predictors of reading acquisition. Child Development 73: 392–407
McBride-Chang C., Shu H., Zhou A., Wat C. P. and Wagner R. K. (2003). Morphological awareness uniquely predicts young children’s Chinese Character Recognition. Journal of Educational Psychology 95: 743–751
McBride-Chang, C., & Treiman, R. (2003). Hong Kong Chinese kindergartners learn to read English analytically. Psychological Science, 14, 138–143
McBride-Chang, C., Wagner, R. K., Muse, A., Chow, B. W.-Y., & Shu, H. (2005). The role of morphological awareness in children's vocabulary acquisition in English. Applied Psycholinguistics, 26, 415–435
McBride-Chang, C., Wagner, R. K., Muse, A., Chow, B. W. -Y., & Shu, H. (in press). The role of morphological awareness in children’s vocabulary acquisition in english. Applied Psycholinguistics, 26, 415–435
Meador D., Flege J. E. and Mackay I. R. (2000). Factors affecting the recognition of words in a second language. Bilingualism Language and Cognition 3: 55–67
Nagy W. E. and Anderson R. C. (1984). How many words are there in printed school English?. Reading Research Quarterly 19: 304–330
Packard J. L. (2000). The morphology of Chinese: A linguistic and cognitive approach.. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Pounder A. (2000). Processes and paradigms in word-formation morphology. M. de Gruyter, Hawthorne, NY
Raven J. C., Court J.H. and Raven J. (1995). Raven’s Colored Progressive Matrices.. Oxford Psychologists Press, UK
Shankweiler D. (1999). Words to meanings. Scientific Studies of Reading 3(2): 113–127
Stanovich K. E. (1986). Matthew effects in reading: Some consequences of individual differences in the acquisition of literacy. Reading Research Quarterly 21: 360–407
Stanovich K. E. (2000). Progress in understanding reading. Guilford Press, London
White T. G., Power M. A. and White S. (1989). Morphological analysis: Implications for teaching and understanding vocabulary growth. Reading Research Quarterly 24(3): 283–304
Woodcock R. W. (1987). Woodcock Reading Mastery Tests. American Guidance Service, Circle Pines, MN
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McBride-Chang, C., Cheung, H., Chow, B.WY. et al. Metalinguistic skills and vocabulary knowledge in Chinese (L1) and English (L2). Read Writ 19, 695–716 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-005-5742-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-005-5742-x