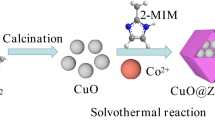
Abstract
The present work aims to synthesize bimetallic CuZn-ZIFs using a solvothermal method to degrade Basic Fuchsin in an aqueous solution in the presence of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) under ambient conditions. Zn and Cu were loaded successfully on the ZIF structure due to the linkage of Cu–N and Zn-N found by FT-IR. The combination of Cu/Zn on the ZIF structure enhanced the specific surface area up to 1568.4 m2 g−1 and 0.48 cm3 g−1 of pore volume, which can facilitate the performance of BF degradation. Under the optimum conditions, including a reaction time of 20 min, an initial BF concentration of 30 mg L−1, and catalyst dosage of 0.1 g L−1, H2O2 level of 0.03 mol L−1, the efficiency degradation of BF achieved significantly high with above 96% through Fenton-like mechanism. CuZn-ZIFs also performed higher catalytic activity compared to some homogeneous and other heterogeneous catalysts. Notably, it was observed that the catalytic activity of CuZn-ZIFs mostly remained after five cycles. The study offers valuable insights into the utilization of novel materials for potential applications in pollutant treatment and environmental remediation.
Graphical Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
El Qada EN, Allen SJ, Walker GM (2008) Adsorption of basic dyes from aqueous solution onto activated carbons. Chem Eng J 135:174–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2007.02.023
Bayramoglu G, Altintas B, Arica MY (2009) Adsorption kinetics and thermodynamic parameters of cationic dyes from aqueous solutions by using a new strong cation-exchange resin. Chem Eng J 152:339–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.04.051
Ong S-T, Tan S-Y, Khoo E-C, Lee S-L, Ha S-T (2012) Equilibrium studies for basic blue 3 adsorption onto durian peel (Durio zibethinus Murray). Desalin Water Treat 45:161–169. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2012.692037
Zargar B, Parham H, Hatamie A (2009) Modified iron oxide nanoparticles as solid phase extractor for spectrophotometeric determination and separation of basic fuchsin. Talanta 77:1328–1331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2008.09.011
Hazra D, Krithika M, Shenoy VP, Chawla K (2022) Evaluation of phenol ammonium sulfate basic fuchsin and auramine O staining by pot technique for the detection of acid-fast bacilli among patients suspected of pulmonary tuberculosis. Biomedicine 42:757–760. https://doi.org/10.51248/.v42i4.1472
Ahmed H, Salihi K, Kaufhold S, Aziz B, Radha MH, Karim L, Nooralddin H (2023) Efficient removal of basic fuchsin from synthetic medical wastewater and competitive adsorption in the mixture. Adsorp Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/4672622
Fung DY, Miller RD (1973) Effect of dyes on bacterial growth. Appl Microbiol 25:793–799. https://doi.org/10.1128/am.25.5.793-799.1973
Yu L, Xue W, Cui L, Xing W, Cao X, Li H (2014) Use of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin/polyethylene glycol 400, modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles for congo red removal. Int J Biol Macromol 64:233–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.12.009
Bianchi CL, Djellabi R, Della Pina C, Falletta E (2022) Doped-polyaniline based sorbents for the simultaneous removal of heavy metals and dyes from water: unravelling the role of synthesis method and doping agent. Chemosphere 286:131941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131941
Nor NM, Hadibarata T, Zubir MMFA, Lazim ZM, Adnan LA, Fulazzaky MA (2015) Mechanism of triphenylmethane cresol red degradation by Trichoderma harzianum M06. Bioproc Biosyst Eng 38:2167–2175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-015-1456-x
Ben Aissa M, Khezami L, Taha K, Elamin N, Mustafa B, Al-Ayed A, Modwi A (2021) Yttrium oxide-doped ZnO for effective adsorption of basic fuchsin dye: equilibrium, kinetics, and mechanism studies. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03816-y
Su M, Li H, He X, Xu Z (2022) Significant enhancement of pesticide and organic dyes degradation by ion-exchange within a metal–organic framework. Polyhedron 215:115651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2022.115651
González-Rodríguez J, Gamallo M, Conde JJ, Vargas-Osorio Z, Vázquez-Vázquez C, Piñeiro Y, Rivas J, Feijoo G, Moreira MT (2021) Exploiting the potential of supported magnetic nanomaterials as Fenton-like catalysts for environmental applications. Nanomaterials 11:2902. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112902
Liang D, Li N, An J, Ma J, Wu Y, Liu H (2021) Fenton-based technologies as efficient advanced oxidation processes for microcystin-LR degradation. Sci Total Environ 753:141809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141809
Zuo S, Jin X, Wang X, Lu Y, Zhu Q, Wang J, Liu W, Du Y, Wang J (2021) Sandwich structure stabilized atomic Fe catalyst for highly efficient Fenton-like reaction at all pH values. Appl Catal B: Environ 282:119551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119551
Wang N, Zheng T, Zhang G, Wang P (2016) A review on Fenton-like processes for organic wastewater treatment. J Environ Chem Eng 4:762–787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2015.12.016
Bokare AD, Choi W (2014) Review of iron-free Fenton-like systems for activating H2O2 in advanced oxidation processes. J Hazard Mater 275:121–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.04.054
Zhou H-C, Long JR and Yaghi OM (2012) Introduction to metal–organic frameworks. ACS Publications, pp. 673–674
Banerjee R, Phan A, Wang B, Knobler C, Furukawa H, O’Keeffe M, Yaghi OM (2008) High-throughput synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks and application to CO2 capture. Science 319:939–943. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1152516
Huang XC, Lin YY, Zhang JP, Chen XM (2006) Ligand-directed strategy for zeolite-type metal–organic frameworks: zinc (II) imidazolates with unusual zeolitic topologies. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 45:1557–1559. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200503778
Sun Y, Zhang N, Yue Y, Xiao J, Huang X, Ishag A (2022) Recent advances in the application of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs) in environmental remediation: a review. Environ Sci Nano 9:4069–4092. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00601D
Duan C, Yu Y, Hu H (2022) Recent progress on synthesis of ZIF-67-based materials and their application to heterogeneous catalysis. Green Energy Environ 7:3–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gee.2020.12.023
Kouser S, Hezam A, Khadri MN, Khanum SA (2022) A review on zeolite imidazole frameworks: synthesis, properties, and applications. J Porous Mater 29:663–681. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-021-01184-z
Nagarjun N, Dhakshinamoorthy A (2019) A Cu-Doped ZIF-8 metal organic framework as a heterogeneous solid catalyst for aerobic oxidation of benzylic hydrocarbons. New J Chem 43:18702–18712. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9nj03698a
Yang X, Zhao J, Cavaco-Paulo A, Su J, Wang H (2023) Encapsulated laccase in bimetallic Cu/Zn ZIFs as stable and reusable biocatalyst for decolorization of dye wastewater. Int J Biol Macromol 233:123410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123410
Anbari AP, Delcheh SR, Heynderickx PM, Chaemcheun S, Zhuiykov S, Verpoort F (2023) Green approach for synthesizing copper-containing ZIFs as efficient catalysts for click chemistry. Catalysts 13:1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13061003
Luong TH, Nguyen TH, Nguyen BV, Nguyen NK, Nguyen TQ, Dang GH (2022) Efficient degradation of methyl orange and methylene blue in aqueous solution using a novel Fenton-like catalyst of CuCo-ZIFs. Green Process Synth 11:71–83. https://doi.org/10.1515/gps-2022-0006
Nguyen TQ, Tran HB, Nguyen NK, Nguyen NM, Dang GH (2023) Removal efficiency of dibenzofuran using CuZn-zeolitic imidazole frameworks as a catalyst and adsorbent. Green Process Synth 12:20228112. https://doi.org/10.1515/gps-2022-8112
Shi J, Zhang L, Sun N, Hu D, Shen Q, Mao F, Gao Q, Wei W (2019) Facile and rapid preparation of Ag@ZIF-8 for carboxylation of terminal alkynes with CO2 in mild conditions. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:28858–28867. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b07991
Goyal S, Shaharun MS, Kait CF and Abdullah B (2018) Effect of monometallic copper on zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 synthesized by hydrothermal method. J Phys: Conf Ser, IOP Publishing, pp. 012062
Hodges BC, Cates EL, Kim J-H (2018) Challenges and prospects of advanced oxidation water treatment processes using catalytic nanomaterials. Nat Nanotechnol 13:642–650. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-018-0216-x
Wei L, Zhang Y, Chen S, Zhu L, Liu X, Kong L, Wang L (2019) Synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes-FePO4 composite from phosphate residue and its application as effective Fenton-like catalyst for dye degradation. J Environ Sci 76:188–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2018.04.024
Bhattacharjee S, Jang M-S, Kwon H-J, Ahn W-S (2014) Zeolitic imidazolate frameworks: synthesis, functionalization, and catalytic/adsorption applications. Catal Surv Asia 18:101–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10563-014-9169-8
Carvalho SS, Carvalho NM (2017) Dye degradation by green heterogeneous Fenton catalysts prepared in presence of Camellia sinensis. J Environ Manage 187:82–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.11.032
Wei H, Hu D, Su J, Li K (2015) Intensification of levofloxacin sono-degradation in a US/H2O2 system with Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. Chin J Chem Eng 23:296–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2014.11.011
Mahmud N, Benamor A, Nasser MS, Ba-Abbad MM, El-Naas MH, Mohammad AW (2021) Effective heterogeneous fenton-like degradation of malachite green dye using the core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 nano-catalyst. ChemistrySelect 6:865–875. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.202003937
Siddique M, Farooq R, Price GJ (2014) Synergistic effects of combining ultrasound with the Fenton process in the degradation of Reactive Blue 19. Ultrason Sonochem 21:1206–1212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2013.12.016
Jaafarzadeh N, Takdastan A, Jorfi S, Ghanbari F, Ahmadi M, Barzegar G (2018) The performance study on ultrasonic/Fe3O4/H2O2 for degradation of azo dye and real textile wastewater treatment. J Mol Liq 256:462–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.02.047
Yang Z, Yang Y, Zhu X, Chen G, Zhang W (2014) An outward coating route to CuO/MnO2 nanorod array films and their efficient catalytic oxidation of acid fuchsin dye. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:9608–9615. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie500358p
Ahmed HR, Aziz KHH, Agha NN, Mustafa FS, Hinder SJ (2023) Iron-loaded carbon black prepared via chemical vapor deposition as an efficient peroxydisulfate activator for the removal of rhodamine B from water. RSC Adv 13:26252–26266
Goebel J, Ault BS, Del Bene JE (2000) Matrix isolation and ab initio study of the hydrogen-bonded complex between H2O2 and (CH3)2O. J Phys Chem A 104:2033–2037
Bienert GP, Schjoerring JK, Jahn TP (2006) Membrane transport of hydrogen peroxide. Biochimica et Biophys Acta (BBA)-Biomembranes 1758:994–1003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.02.015
Dang GH, Le TT, Ta AK, Ho TN, Pham TV, Doan TV, Luong TH (2020) Removal of Congo red and malachite green from aqueous solution using heterogeneous Ag/ZnCo-ZIF catalyst in the presence of hydrogen peroxide. Green Process Synth 9:567–577. https://doi.org/10.1515/gps-2020-0060
Funding
This research was supported by B2023-TCT-22 project funding from the Ministry of Education and Training, Vietnam.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dang, H.G., Tran, T.V.H., Tran, B.H. et al. Combination of Cu and Zn on ZIF structure for efficient degradation of basic fuchsin in aqueous solution. Reac Kinet Mech Cat (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-024-02653-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-024-02653-7