Abstract
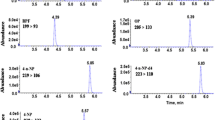
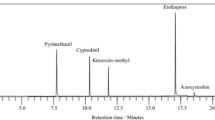
The aim of this study was to develop a kinetic-spectrophotometric method for 2-methyl-4-chlorophenoxy acetic acid (MCPA) determination and apply it for pesticide determination in baby tea and baby food samples, using solid-phase extraction (SPE) followed by the kinetic-spectrophotometric method and the high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method. This method is based on the inhibited effect of MCPA on the oxidation of sulfanilic acid (SA) by hydrogen peroxide in the presence of Co2+ ion as catalyst in alkaline medium. The reaction was monitored spectrophotometrically by measuring the increase in absorbance with time of the reaction product at 368 nm. Under the experimental conditions used, MCPA showed a linear dynamic range of 0.14 to 2.0 μg mL−1, and from 2.0 to 20.00 μg mL−1 with relative standard deviations (RSD) from 1.07 to 4.35%. The limit of detection and the limit of quantification were 0.052 and 0.107 μg mL−1. The method was successfully applied to determination of MCPA residues in baby tea and baby food samples. Solid-phase extraction (SPE) was used for extraction of MCPA from samples using Chromabond® C18 cartridges. The HPLC method was used as a comparative method to verify the results of kinetic method. The results obtained by two different methods showed good agreement. The proposed method is highly sensitive, simple, easy, requires cheap reagents, and leads to good recovery levels. It is linear, precise, and accurate. It can be successfully used for the routine analysis of MCPA in baby tea samples, and baby food samples.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carroquino MJ, Posada M, Landrigan PJ (2012) Environmental toxicology: children at risk. Environ Toxicol 4:239–291. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-5764-0_11
Tudi M, Li H, Li H, Wang L, Lyu J, Yang L, Tong S, Yu QJ, Ruan HD, Atabila A, Phung DT, Sadler R, Connell D (2022) Exposure routes and health risks associated with pesticide application. Toxics 10(6):335. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10060335
Johnen BG (1999) Herbicides and food quality a misfit? In Proceedings of Brighton Conference Weeds, 3rd edn. British Crop Protection Council, London
Manahan SE (2000) Environmental chemistry, 7th edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Olsvik PA, Samuelsen OB, Erdal A, Holmelid B, Lunestad BT (2013) Toxicological assessment of the anti-salmon lice drug difubenzuron on Atlantic cod Gadus morhua. Dis Aquat Org 105:27–43. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao02613
Wang H, Hu L, Li W, Lu R, Zhang S, Zhou W, Gao H (2016) A rapid and simple pretreatment method for benzoylurea insecticides in honey samples using in-syringe dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on the direct solidification of ionic liquids. J Chromatogr A 1471:60–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2016.10.027
Hammami B, Bahri M, Hassine SB, Driss MR (2017) Development of liquid chromatography separation and a solid-phase extraction method for phenoxy alkanoic acid herbicides in water. Mod Chem Appl 5:1000241. https://doi.org/10.4172/2329-6798.1000241
Yang F, Yang Bian Z (2013) Determination of chlorinated phenoxy acid herbicides in tobacco by modified QuEChERS extraction and highperformance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. J AOAC Int 96:1134–1137. https://doi.org/10.5740/jaoacint.12-467
Thorstensen CW, Lode O, Christiansen AL (2000) Development of a solid-phase extraction method for phenoxy acids and bentazone in water and comparison to a liquid-liquid extraction method. J Agric Food Chem 48:5829–5833. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0000124
Wu J, Ee KH, Kee Lee H (2005) Automated dynamic liquid–liquid–liquid microextraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet detection for the determination of phenoxy acid herbicides in environmental waters. J Chromatogr A 1082:121–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2005.05.077
Guo T, Wang X, Wang H, Hu Y, Zhang S, Zhao R (2019) Determination of phenoxy acid herbicides in cereals using high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Food Prot 82:1160–1165. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-18-558
Liu JF, Toräng L, Mayer P, Jönsson JÅ (2007) Passive extraction and clean-up of phenoxy acid herbicides in samples from a groundwater plume using hollow fiber supported liquid membranes. J Chromatogr 1160:56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2007.04.010
Wu J, Kim HE, Hian KL (2005) Automated dynamic liquid-liquid-liquid microextraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet detection for the determination of phenoxy acid herbicides in environmental waters. J Chromatogr A 1082:121–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2005.05.077
Biancolillo A, Maggi AM, Bassi S, Marini F, D’Archivio AA (2020) Retention modelling of phenoxy acid herbicides in reversed-phase HPLC under gradient elution. Molecules 25:1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061262
Wu CC (2017) Multiresidue method for the determination of pesticides in Oolong tea using QuEChERS by gas chromatography-triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry (QuEChERS, GC/MS/MS. Food Chem 229:580–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.02.081
Jahanmard E, Ansari F, Feizi M (2016) Evaluation of quechers sample preparation and gc mass spectrometry method for the determination of 15 pesticide residues in tomatoes used in salad production plants. Iran J Public Health 45:230–238. https://ijph.tums.ac.ir/index.php/ijph/article/view/6108
Anastassiades M, Lehotay SJ (2003) Fast and easy multiresidue method employing acetonitrile extraction/partitioningand “dispersive solid-phaseextraction” for the determination of pesticide residues in produce. J AOAC Int 86:412–431. https://doi.org/10.1093/jaoac/86.2.412
Saraji M, Farajmand B (2008) Application of single-drop microextraction combined with in-microvial derivatization for determination of acidic herbicides in water samples by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1178:17–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2007.11.056
Steinborn A, Alder L, Spitzke M, Dörk D, Anastassiades M (2017) Development of a QuEChERS-based method for the simultaneous determination of acidic pesticides, their esters, and conjugates following alkaline hydrolysis. J Agric Food Chem 65:1296–1305. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.6b05407
Geerdink RB, Kooistra-Sijpersma A, Tiesnitsch J, Kienhuis PGM, Brinkman UAT (1999) Determination of polar pesticides with atmospheric pressure chemical ionisation mass spectrometry–mass spectrometry using methanol and/or acetonitrile for solid-phase desorption and gradient liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 863:147–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(99)00898-5
Tölgyesi A, Korozs G, Tóth E, Bálint M, Ma X, Sharma VK (2022) Automation in quantifying phenoxy herbicides and bentazon in surface water and groundwater using novel solid phase extraction and liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 286:131927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131927
Diez C, Traag W, Zommer P, Marinero P, Atienza J (2006) Comparison of an acetonitrile extraction/partitioning and “dispersive solid-phase extraction” method with classical multi-residue methods for the extraction of herbicide. J Chromatogr A 1131:11–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2006.07.046
Laganà A, Bacaloni A, De Leva I, Faberi A, Fago G, Marino A (2002) Occurrence and determination of herbicides and their major transformation products in environmental waters. Anal Chim Acta 462:87–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(02)00351-3
Koesukwiwat U, Sanguankaew K, Leepipatpiboon N (2008) Rapid determination of phenoxy acid residues in rice by modified QuEChERS extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 626:10–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2008.07.034
Min ZW, Hong S-M, Yang I-C, Kwon H-Y, Kim T-K, Kim D-H (2012) Analysis of Pesticide residues in brown rice using modified QuEChERS multiresidue method combined with electrospray ionization-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometric detection. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem 55:769–775. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13765-012-2153-y
Kaczyński P, Łozowicka B (2017) One-step QuEChERS-based approach to extraction and cleanup in multiresidue analysis of sulfonylurea herbicides in cereals by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Anal Method 10:147–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-016-0564-9
Lee Y-J, Rahman MdM, Abd El-Aty AM, Choi J-H, Chung H, Kim S-W, Abdel-Aty A, Shin H-C, Shim J (2017) Detection of three herbicide, and one metabolite, residues in brown rice and rice straw using various versions of the QuEChERS method and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem 210:442–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.05.005
Rodil R, Quintana JB, López-Mahía P, Muniategui-Lorenzo S, Prada-Rodríguez D (2009) Multi-residue analytical method for the determination of emerging pollutants in water by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1216:2958–2969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2008.09.041
Ji Z, Cheng J, Song C, Hu N, Zhou W, Suo Y, Sun Z, You J (2019) A highly sensitive and selective method for determination of phenoxy carboxylic acids from environmental water samples by dispersive solid-phase extraction coupled with ultra high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 191:313–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.08.055
McManus SL, Moloney M, Richards KG, Coxon CE, Danaher M (2014) Determination and occurrence of phenoxyacetic acid herbicides and their transformation products in groundwater using ultra high performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. Molecules 19:20627–20649. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191220627
Xuefeng J, Shuang L, Gege W, Lin Z, Jiping M (2021) Determination of seven phenoxy acid herbicides in water by dispersive solid phase extraction-ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry based on cationic metal-organic framework mixed matrix membrane. Chin J Chromatogr 39:896–904. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1123.2021.01006
Smarzewska S, Jasińska A, Ciesielski W, Guziejewski D (2016) First electroanalytical studies of profluralin with square wave voltammetry using glassy carbon electrode. Electroanalysis 28:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201600562
Skrzypczyńska K, Kuśmierek K, Świątkowski A (2016) Carbon paste electrodes modified with various carbonaceous materials for the determination of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by differential pulse voltammetry. J Electroanal Chem 766:8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2016.01.025
Liu H, Chen M, Lin Y, Liu Y (2017) Electrochemical study of the herbicide paraquat based on a graphene-zinc oxide nanocomposite. Int J Electrochem Sci 12:8599–8608. https://doi.org/10.20964/2017.09.15
Djurdjić S, Vukojević V, Jevtić S, Pergal MV, Petković BB, Stanković DM (2018) Herbicide clomazone detection using electroanalytical approach using boron doped diamond electrode. Int J Electrochem Sci 13:2791–2799. https://doi.org/10.20964/2018.03.39
Białek A, Skrzypczyńska K, Kuśmierek K, Świątkowski A (2019) Voltammetric determination of MCPA, 4-chloro-o-cresol and o-cresol in water using a modified carbon paste electrode. Int J Electrochem Sci 14:228–237. https://doi.org/10.20964/2019.01.2037
Farhadi K, Matin AA, Hashemi P (2009) LC determination of trace amounts of phenoxyacetic acid herbicides in water after dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. Chromatography 69:45–49. https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-008-0815-z
Pecev-Marinković E, Miletić A, Tošić S, Pavlović A, Kostić D, Rašić Mišić I, Dekić V (2019) Optimization and validation of the kinetic spectrophotometric method for quantitative determination of the pesticide atrazine and its application in infant formulae and cereal-based baby food. J Sci Food Agric 99:5424–5431. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.9803
Sailani R, Pareek D, Jangid K, Khandelwal CL, Sharma PD (2014) Kinetics and mechanism of electron transfer reactions: oxidation of sulfanilic acid by peroxomonosulfate in aqueous acidic medium. Chem Sci Rev Lett 3:166–177
Kolthoff MI, Sandell BE (1963) Textbook of quantitative inorganic analysis, 3d edn. Macmillan, New York
Luruye YY (1989) Spravochnik po Analiticheskoi Khimi. Moskva, Khimiya
Wang CC, Jing HP, Zhang YQ, Wang P, Gao SJ (2015) Three coordination compounds of cobalt with organic carboxylic acids and 1,10-phenanthroline as ligands: syntheses, structures and photocatalytic properties. Transition Met Chem 40:573–584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11243-015-9950-1
Jacimirskii KB (1967) Kinetic methods in analysis. Chimia, Moskva
Müller H, Otto M (1980) Katalytische Methoden in Der Spuren Analyse. Akademische Verlagsgesellschaft, Leipzig
Miller JN (1991) Basic statistical methods for analytical chemistry. Part 2. Calibration and regression methods. Analyst 116:3–14. https://doi.org/10.1039/AN9911600003
Bendito DP, Silva M (1988) Kinetic methods in analytical chemistry. Ellis Horwood, Chichester
Mottola HA (1988) Kinetic aspects of analytical chemistry. Wiley, New York
Prichard E, Barwick V (2007) Quality assurance in analytical chemistry. Wiley, Teddington
Hartmann C, Verbeke JS, Penninckx W, Heyden YV, Vankeerberghen P, Massart DL (1995) Reappraisal of hypothesis testing for method validation: detection of systematic error by comparing the means of two methods or of two laboratories. Anal Chem 67:4491–4499. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac00120a011
Skoog DA, West DM, James Holler F, Crouch SR (2013) Fundamentals of analytical chemistry, 9th edn. Brooks Cole, Belmont
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Serbian Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development (Agreement number 451-03-47/2023-01/200124). The authors are grateful for the financial support provided by this Ministry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EP-M: Conceptualization, Investigation, Formal analysis, Writing—original draft. AMĆ: Investigation, data curation. AP: Validation, Writing—review & editing. IRM: Partly experimental supervision, methodology, Writing—review & editing. JM: Investigation, resources. ES: visualization, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
We declare that this manuscript is original, has not been published before and is not currently being considered for publication elsewhere. We confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pecev-Marinković, E., Miletić Ćirić, A., Pavlović, A. et al. Development and validation of a kinetic-spectrophotometric method for the trace determination of 2-methyl-4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid in baby teas and baby food samples using solid phase extraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 137, 699–717 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-023-02562-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-023-02562-1