Abstract
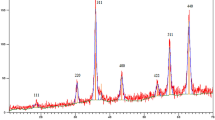
In this research, nanofibrous copper (0) was utilized as an efficient nanostructured catalyst in Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition reaction, reduction of nitrobenzenes to anilines and reduction of aromatic aldehydes to benzyl alcohols. Nanofibrous copper was prepared via dealloying of Cu–Zn powder and was characterized by SEM, TEM, XRD, BET and EDS analyses. This catalyst produced very good results including high product yield, short reaction time and recyclability.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Slater AG, Cooper AI (2015) Porous materials Function-led design of new porous materials. Science 348:e8075
Gottardi G, Galli E 2012 Natural zeolites (Vol. 18). Springer Science, Business Media.
Liu Y, O’Keeffe M, Treacy MM, Yaghi OM (2018) The geometry of periodic knots, polycatenanes and weaving from a chemical perspective: a library for reticular chemistry. Chem Soc Rev 47:4642
Zhao D, Feng J, Huo Q, Melosh N, Fredrickson GH, Chmelka BF, Stucky GD (1998) Triblock copolymer syntheses of mesoporous silica with periodic 50 to 300 angstrom pores. Science 279:548
Zhao XS, Lu GQ, Millar GJ (1996) Advances in mesoporous molecular sieve MCM-41. Ind Eng Chem Res 35:2075
Cote AP, Benin AI, Ockwig NW, O’Keeffe M, Matzger AJ, Yaghi OM (2005) Porous, crystalline, covalent organic frameworks. Science 310:1166
Abbas A, Abbas S, Wang X (2016) Nanoporous copper: fabrication techniques and advanced electrochemical applications. Corros Rev 34:249
Zhang J, Li CM (2012) Nanoporous metals: fabrication strategies and advanced electrochemical applications in catalysis, sensing and energy systems. Chem Soc Rev 41:7016
Chen LY, Yu JS, Fujita T, Chen MW (2009) Nanoporous copper with tunable nanoporosity for SERS applications. Adv Func Mater 19:1221
Erlebacher J, Aziz MJ, Karma A, Dimitrov N, Sieradzki K (2001) Evolution of nanoporosity in dealloying. Nature 410:450
Solanki V, Krupanidhi SB, Nanda KK (2017) Sequential elemental dealloying approach for the fabrication of porous metal oxides and chemiresistive sensors thereof for electronic listening. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:41428
Hayes JR, Hodge AM, Biener J, Hamza AV, Sieradzki K (2006) Monolithic nanoporous copper by dealloying Mn–Cu. J Mater Res 21:2611
Lu HB, Li Y, Wang FH (2007) Synthesis of porous copper from nanocrystalline two-phase Cu–Zr film by dealloying. Scripta Mater 56:165
Zhao C, Qi Z, Wang X, Zhang Z (2009) Fabrication and characterization of monolithic nanoporous copper through chemical dealloying of Mg–Cu alloys. Corros Sci 51:2120
Liu WB, Zhang SC, Li N, Zheng JW, Xing YL (2011) A facile one-pot route to fabricate nanoporous copper with controlled hierarchical pore size distributions through chemical dealloying of Al–Cu alloy in an alkaline solution. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 138:1
Dan Z, Qin F, Sugawara Y, Muto I, Hara N (2012) Fabrication of nanoporous copper by dealloying amorphous binary Ti–Cu alloys in hydrofluoric acid solutions. Intermetallics 29:14
Aburada T, Fitz-Gerald JM, Scully JR (2011) Synthesis of nanoporous copper by dealloying of Al-Cu-Mg amorphous alloys in acidic solution: The effect of nickel. Corros Sci 53:1627
Dan Z, Qin F, Makino A, Sugawara Y, Muto I, Hara N (2014) Fabrication of nanoporous copper by dealloying of amorphous Ti–Cu–Ag alloys. J Alloy Compd 586:S134
Tornøe CW, Christensen C, Meldal M (2002) Peptidotriazoles on solid phase:[1,2,3]-triazoles by regiospecific copper (I)-catalyzed 1, 3-dipolar cycloadditions of terminal alkynes to azides. J Org Chem 67:3057
Appukkuttan P, Dehaen W, Fokin VV, Van der Eycken E (2004) A microwave-assisted click chemistry synthesis of 1, 4-disubstituted 1, 2, 3-triazoles via a copper (I)-catalyzed three-component reaction. Org Lett 6:4223
Feldman AK, Colasson B, Fokin VV (2004) One-pot synthesis of 1, 4-disubstituted 1, 2, 3-triazoles from in situ generated azides. Org Lett 6:3897
Spiteri C, Moses JE (2010) Copper-catalyzed azide–alkyne cycloaddition: regioselective synthesis of 1, 4, 5-trisubstituted 1, 2, 3-triazoles. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:31
Alonso F, Moglie Y, Radivoy G, Yus M (2011) Multicomponent click synthesis of 1, 2, 3-triazoles from epoxides in water catalyzed by copper nanoparticles on activated carbon. J Org Chem 76:8394
Tafesh AM, Weiguny J (1996) A review of the selective catalytic reduction of aromatic nitro compounds into aromatic amines, isocyanates, carbamates, and ureas using CO. Chem Rev 96:2035
Herves P, Pérez-Lorenzo M, Liz-Marzán LM, Dzubiella J, Lu Y, Ballauff M (2012) Catalysis by metallic nanoparticles in aqueous solution: model reactions. Chem Soc Rev 41:5577
Burge HD, Collins DJ, Davis BH (1980) Intermediates in the Raney nickel catalyzed hydrogenation of nitrobenzene to aniline. Ind Eng Chem Prod Res Dev 19:389
Spencer J, Anjum N, Patel H, Rathnam RP, Verma J (2007) Molybdenum hexacarbonyl and DBU reduction of nitro compounds under microwave irradiation. Synlett 2007:2557
Skupiń J, Zukowska A, Chajewski A (2001) Reduction of nitrobenzene to aniline with carbon monoxide and water in the presence of the PdCl2/Fe/I2 system. React Kinet Catal Lett 72:21
Makarova OV, Rajh T, Thurnauer MC, Martin A, Kemme PA, Cropek D (2000) Surface modification of TiO2 nanoparticles for photochemical reduction of nitrobenzene. Environ Sci Technol 34:4797
Subramanian T, Pitchumani K (2012) Selective reduction of nitroarenes by using zeolite-supported copper nanoparticles with 2-propanol as a sustainable reducing agent. ChemCatChem 4:1917
Roy P, Periasamy AP, Liang CT, Chang HT (2013) Synthesis of graphene-ZnO-Au nanocomposites for efficient photocatalytic reduction of nitrobenzene. Environ Sci Technol 47:6688
Nasab MJ, Kiasat AR (2016) Multifunctional Fe 3 O 4@ n SiO 2@ m SiO 2/Pr-Imi-NH 2· Ag core–shell microspheres as highly efficient catalysts in the aqueous reduction of nitroarenes: improved catalytic activity and facile catalyst recovery. RSC Adv 6:41871
Gholinejad M, Zareh F, Nájera C (2018) Nitro group reduction and Suzuki reaction catalysed by palladium supported on magnetic nanoparticles modified with carbon quantum dots generated from glycerol and urea. Appl Organomet Chem 32:e3984
Mullangi D, Chakraborty D, Pradeep A, Koshti V, Vinod CP, Panja S, Vaidhyanathan R (2018) Heterogenous Catalysts: highly stable cof-supported Co/Co (OH) 2 nanoparticles heterogeneous catalyst for reduction of nitrile/nitro compounds under mild conditions. Small 14:1870169
Cantillo D, Moghaddam MM, Kappe CO (2013) Hydrazine-mediated reduction of nitro and azide functionalities catalyzed by highly active and reusable magnetic iron oxide nanocrystals. J Org Chem 78:4530
Ghonchepour E, Islami MR, Bananezhad B, Mostafavi H, Tikdari AM (2019) Synthesis of recoverable palladium composite as an efficient catalyst for the reduction of nitroarene compounds and Suzuki cross-coupling reactions using sepiolite clay and magnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4@ sepiolite-Pd2+). C R Chim 22:84
Zhu H, Ke X, Yang X, Sarina S, Liu H (2010) Reduction of nitroaromatic compounds on supported gold nanoparticles by visible and ultraviolet light. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:9657
Chakraborty S, Bhattacharya P, Dai H, Guan H (2015) Nickel and iron pincer complexes as catalysts for the reduction of carbonyl compounds. Acc Chem Res 48:1995
Kidwai M, Bansal V, Saxena A, Shankar R, Mozumdar S (2006) Ni-nanoparticles: an efficient green catalyst for chemoselective reduction of aldehydes. Tetrahedron Lett 47:4161
Subramanian T, Pitchumani K (2012) Transfer hydrogenation of carbonyl compounds and carbon–carbon multiple bonds by zeolite supported Cu nanoparticles. Catal Sci Technol 2:296
Rayhan U, Do JH, Arimura T, Yamato T (2015) Reduction of carbonyl compounds by Raney Ni–Al alloy and Al powder in the presence of noble metal catalysts in water. C R Chim 18:685
Naimi-Jamal MR, Mokhtari J, Dekamin MG, Kaupp G (2009) Sodium tetraalkoxyborates: intermediates for the quantitative reduction of aldehydes and ketones to alcohols through ball milling with NaBH4. Eur J Org Chem 2009:3567
Sayyahi S, Saghanezhad SJ (2019) Copper-Based Bulk and Nano-Catalysts for the One-Pot Propargylamine Synthesis. Mini-Rev Org Chem 16:361
Tappan BC, Steiner SA III, Luther EP (2010) Nanoporous metal foams. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:4544
Gao W, Hood ZD, Chi M (2017) Interfaces in heterogeneous catalysts: advancing mechanistic understanding through atomic-scale measurements. Acc Chem Res 50:787
Salamatmanesh A, Miraki MK, Yazdani E, Heydari A (2018) Copper (I)–caffeine complex immobilized on silica-coated magnetite nanoparticles: a recyclable and eco-friendly catalyst for click chemistry from organic halides and epoxides. Catal Lett 148:3257
Scott SL (2018) A Matter of life (time) and death. ACS Catal 8:e8597
Dell’Anna MM, Intini S, Romanazzi G, Rizzuti A, Leonelli C, Piccinni F, Mastrorilli P (2014) Polymer supported palladium nanocrystals as efficient and recyclable catalyst for the reduction of nitroarenes to anilines under mild conditions in water. J Mol Catal A: Chem 395:307
Davarpanah J, Kiasat AR (2013) Catalytic application of silver nanoparticles immobilized to rice husk-SiO2-aminopropylsilane composite as recyclable catalyst in the aqueous reduction of nitroarenes. Catal Commun 41:6
Keshipour S, Adak K (2018) Reduction of Nitroaromatics to Amines with Cellulose Supported Bimetallic Pd/Co Nanoparticles. Iran J Chem Chem Eng 37:23
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Mahshahr Branch, Islamic Azad University, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saghanezhad, S.J., Buhamidi, M.M., Ebadi, S. et al. Entangled nanofibrous copper: an efficient and high performance nanostructured catalyst in azide-alkyne cycloaddition reaction and reduction of nitroarenes and aromatic aldehydes. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 133, 897–911 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-021-02011-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-021-02011-x