Abstract
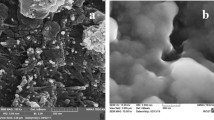
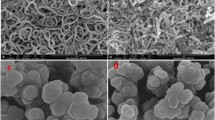
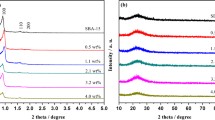
An effective catalyst with high activity and stability is required to produce hydrogen from the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride (NaBH4) for the portable fuel cell applications. In this study, the synthesis of highly effective, stable and reusable polypyrrole (PPy) supported ruthenium nanoparticles (NPs) is presented. PPy powders with porous structure were prepared by the chemical oxidative polymerization, followed by the deposition of Ru NPs using the wet impregnation—reduction method. Due to the synergistic effect of Ru NPs with PPy, the as-synthesized catalyst exerts good catalytic activity, with the hydrogen release rate of 22.74 ± 0.84 L min−1 g −1Ru and activation energy of 39.08 ± 1.69 kJ mol−1, which is lower than most of the reported activation energy values. This novel Ru/PPy catalyst is a promising candidate for small portable hydrogen generators by NaBH4 hydrolysis. Structural, morphological and textural properties of the catalysts were investigated by analytical techniques. Moreover, the effects of reaction temperature, NaOH and NaBH4 concentrations on catalytic activity were also investigated.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wilberforce T, Alaswad A, Palumbo A, Dassisti M, Olabi AG (2016) Advances in stationary and portable fuel cell applications. Int J Hydrog Energy 41:16509–16522
Kirubakaran A, Jain S, Nema RK (2009) A review on fuel cell technologies and power electronic interface. Renew Sust Energy Rev 13:2430–2440
Faur Ghenciu A (2002) Review of fuel processing catalysts for hydrogen production in PEM fuel cell systems. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 6:389–399
Patel N, Fernandes R, Miotello A (2009) Hydrogen generation by hydrolysis of NaBH4 with efficient Co–P–B catalyst: a kinetic study. J Power Sources 188:411–420
Turco M, Ausiello A, Micoli L (2016) Fuel cells operating and structural features of MCFCs and SOFCs, treatment of biogas for feeding high temperature fuel cells: removal of harmful compounds by adsorption processes. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 31–76
Jena P (2011) Materials for hydrogen storage: past, present, and future. J Phys Chem Lett 2:206–211
Ross DK (2006) Hydrogen storage: the major technological barrier to the development of hydrogen fuel cell cars. Vacuum 80:1084–1089
Coşkuner B, Kantürk Figen A, Pişkin S (2013) Solid state preparation and reaction kinetics for Co/B as a catalytic/acidic accelerator for NaBH4 hydrolysis. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 109:375–392
Metin Ö, Özkar S (2009) Hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of ammonia-borane and sodium borohydride using water-soluble polymer-stabilized cobalt(0) nanoclusters catalyst. Energy Fuels 23:3517–3526
Demirci UB, Garin F (2008) Ru-based bimetallic alloys for hydrogen generation by hydrolysis of sodium tetrahydroborate. J Alloy Compd 463:107–111
Kojima Y, Haga T (2003) Recycling process of sodium metaborate to sodium borohydride. Int J Hydrog Energy 28:989–993
Baydaroglu F, Özdemir E, Hasimoglu A (2014) An effective synthesis route for improving the catalytic activity of carbon-supported Co–B catalyst for hydrogen generation through hydrolysis of NaBH4. Int J Hydrog Energy 39:1516–1522
Metin Ö, Koçak E, Özkan S (2011) Effect of stabilizer type on the activity and stability of water-dispersible cobalt(0) nanocluster catalysts in hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 103:325–340
Shih Y-J, Su C-C, Huang Y-H, Lu M-C (2013) SiO2-supported ferromagnetic catalysts for hydrogen generation from alkaline NaBH4 (sodium borohydride) solution. Energy 54:263–270
Liang Y, Dai H-B, Ma L-P, Wang P, Cheng H-M (2010) Hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride solution using a ruthenium supported on graphite catalyst. Int J Hydrog Energy 35:3023–3028
Zou YC, Nie M, Huang YM, Wang JQ, Liu HL (2011) Kinetics of NaBH4 hydrolysis on carbon-supported ruthenium catalysts. Int J Hydrog Energy 36:12343–12351
Kasisomayajula SV, Qi X, Vetter C, Croes K, Pavlacky D, Gelling VJ (2010) A structural and morphological comparative study between chemically synthesized and photopolymerized poly(pyrrole). J Coat Technol Res 7:145–158
Ozkazanc E, Zor S, Ozkazanc H, Gumus S (2013) Preparation and characterization of polypyrrole/selenium composites. Polym Eng Sci 53:1131–1137
Wang T, Zhong W, Ning X, Wang Y, Yang W (2009) Facile route to hierarchical conducting polymer nanostructure: synthesis of layered polypyrrole network plates. J Appl Polym Sci 114:3855–3862
Xiang C, Jiang D, Zou Y, Chu H, Qiu S, Zhang H, Xu F, Sun L, Zheng L (2015) Ammonia sensor based on polypyrrole-graphene nanocomposite decorated with titania nanoparticles. Ceram Int 41:6432–6438
Navale ST, Chougule MA, Patil VB, Mane AT (2014) Highly sensitive, reproducible, selective and stable CSA-polypyrrole NO2 sensor. Synth Met 189:111–118
Kreevoy MM, Jacobson RW (1979) The rate of decomposition of sodium borohydride in basic aqueous solutions. Ventron Alembic 15:2–3
Zhu J, Li R, Niu W, Wu Y, Gou X (2013) Fast hydrogen generation from NaBH4 hydrolysis catalyzed by carbon aerogels supported cobalt nanoparticles. Int J Hydrog Energy 38:10864–10870
Zhu J, Li R, Niu W, Wu Y, Gou X (2012) Facile hydrogen generation using colloidal carbon supported cobalt to catalyze hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. J Power Sources 211:33–39
Li X, Fan G, Zeng C (2014) Synthesis of ruthenium nanoparticles deposited on graphene-like transition metal carbide as an effective catalyst for the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int J Hydrog Energy 39:14927–14934
Amendola SC, Sharp-Goldman SL, Janjua MS, Spencer NC, Kelly MT, Petillo PJ, Binder M (2000) A safe, portable, hydrogen gas generator using aqueous borohydride solution and Ru catalyst. Int J Hydrog Energy 25:969–975
Blasdale WC, Slansky CM (1939) The solubility curves of boric acid and the borates of sodium. J Am Chem Soc 61:917–920
Marrero-Alfonso EY, Beaird AM, Davis TA, Matthews MA (2009) Hydrogen generation from chemical hydrides. Ind Eng Chem Res 48:3703–3712
Lente G (2015) Deterministic kinetics in chemistry and systems biology. The dynamics of complex reaction networks. Springer, Berlin, pp 52–58
Li Y, Zhang Q, Zhang N, Zhu L, Zheng J, Chen BH (2013) Ru-RuO2/C as an efficient catalyst for the sodium borohydride hydrolysis to hydrogen. Int J Hydrog Energy 38:13360–13367
Amendola SC, Sharp-Goldman SL, Janjua MS, Kelly MT, Petillo PJ, Binder M (2000) An ultrasafe hydrogen generator: aqueous, alkaline borohydride solutions and Ru catalyst. J Power Sources 85:186–189
Walter JC, Zurawski A, Montgomery D, Thornburg M, Revankar S (2008) Sodium borohydride hydrolysis kinetics comparison for nickel, cobalt, and ruthenium boride catalysts. J Power Sources 179:335–339
Su C-C, Lu M-C, Wang S-L, Huang Y-H (2012) Ruthenium immobilized on Al2O3 pellets as a catalyst for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis and methanolysis of sodium borohydride. RSC Adv 2:2073–2079
Zahmakiran M, Özkar S (2009) Zeolite-confined ruthenium(0) nanoclusters catalyst: record catalytic activity, reusability, and lifetime in hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Langmuir 25:2667–2678
Liu Z, Guo B, Chan SH, Tang EH, Hong L (2008) Pt and Ru dispersed on LiCoO2 for hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride solutions. J Power Sources 176:306–311
Hsueh C-L, Chen C-Y, Ku J-R, Tsai S-F, Hsu Y-Y, Tsau F, Jeng M-S (2008) Simple and fast fabrication of polymer template-Ru composite as a catalyst for hydrogen generation from alkaline NaBH4 solution. J Power Sources 177:485–492
Sahiner N, Ozay O, Inger E, Aktas N (2011) Controllable hydrogen generation by use smart hydrogel reactor containing Ru nano catalyst and magnetic iron nanoparticles. J Power Sources 196:10105–10111
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. A. Yürüm and A. Tasdemir, Sabanci University, for access to surface area analysis facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baydaroglu, F.O., Özdemir, E. & Gürek, A.G. Ruthenium nanoparticles immobilized on surfactant-directed polypyrrole as an effective and reusable catalyst for hydrogen generation. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 122, 575–591 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-017-1222-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-017-1222-y