Abstract
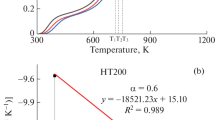
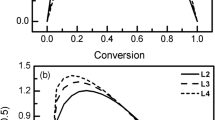
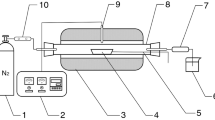
For a better understanding of the devolatilization characteristics of lignite, a highly volatile lignite was devolatilized at four different heating rates in a thermogravimetric analyzer in this study. The results showed that the lignite pyrolysis process was strongly affected by the heating rate. As the heating rate increased, the differential thermogravimetry peak shifted toward higher temperature. Based on thermal analysis and kinetic equations, the effects of the heating rate on the pyrolysis characteristics has been studied and the information about the linkage between the activation energy (E), pre-exponential factor (A) and weight loss of each heating rate has been analyzed simultaneously. In the pyrolysis of lignite, the activation energies of the samples were found to increase with decreasing heating rate for each temperature stages.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singh S, Wu C, Williams PT (2012) J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 94:99
Park SS, Seo DK, Lee SH, Yu T-U, Hwang J (2012) J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 97:29
Jiménez F, Mondragón F, López D (2012) J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 95:164
Puja Khare P, Baruah BP, Rao PG (2011) Fuel 90:3299
Vejahati F, Xu Z, Gupta R (2010) Fuel 89:904
Kok MV (2001) Thermochim Acta 369:149
Iordanidis A, Georgakopoulos A, Markova K (2001) Thermochim Acta 371:137
Alonso MJG, Borrego AG, Alvarez D, Kalkreuth W, Menéndez R (2001) Fuel 80:1857
Pan YG, Enrique V, Luis PJ (1996) Fuel 75:412
Garcia-Perez M, Chaala A, Yang J, Roy C (2001) Fuel 80:1245
Mansaray KG, Ghaly AE (1999) Energy Sources 21:773
Teng HS, Lin HC, Ho JA (1997) Ind Eng Chem Res 36:3974
Enrico B, Federica L, Luigi P, Leonardo T (2002) Fuel 81:1041
Vuthaluru HB (2003) Fuel Process Technol 85:141
Cai JQ, Wang YP, Zhou LM, Huang QW (2008) Fuel Process Technol 89:21
Esteban M, Ariño C, Cruz JM (2006) Trends Anal Chem 25:86
Kök MV (2008) J Therm Anal Calorim 91:763
Du Z, Sarofim AF, Longwell JP (1990) Energy Fuels 4:296
Zhou L, Luo T, Huang Q (2009) Eng Convers Manag 50:705
Zhang C, Jiang X, Wei L, Wang H (2007) Eng Convers Manag 48:797
Shao J (2009) Shenhua Technol 7:17
Xiu J, Chu Z, Che Y (2002) Fuel 81:793
Arenillas A, Rubiera F, Pevida C, Pis JJ (2001) J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 58–59:685
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2012CB723105), National Science & Technology Pillar Program (Grant No. 2012BAA04B03), Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21006066, 51274147) and Shanxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 2011021009-2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y. et al. Thermogravimetric study of the kinetics and characteristics of the pyrolysis of lignite. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 110, 225–235 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-013-0586-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-013-0586-x