Abstract
Purpose
Most economic evaluations of health care programmes do not consider the effects of informal care, while this could lead to suboptimal policy decisions. This study investigates the construct validity of the CarerQol instrument, which measures and values carer effects, in a new population of informal caregivers.
Methods
A questionnaire was distributed by mail (n = 1,100, net response rate = 21%) to regional informal care support centers throughout the Netherlands. Two types of construct validity, i.e., convergent and clinical validity, have been analyzed. Convergent validity was assessed with Spearman’s correlation coefficients and multivariate correlation between the burden dimensions (CarerQol-7D) and the valuation component (CarerQol-VAS) of the CarerQol. Additionally, convergent validity was analyzed with Spearman’s correlation coefficients between the CarerQol and other measures of subjective caregiver burden (SRB, PU). Clinical validity was evaluated with multivariate correlation between CarerQol-VAS and CarerQol-7D, characteristics of caregivers, care recipients and care situation among the whole sample of caregivers and subgroups.
Results
The positive (negative) dimensions of CarerQol-7D were positively (negatively) related to CarerQol-VAS, and almost all had moderate strength of convergent validity. CarerQol-VAS was positively associated with PU and negatively with SRB. The CarerQol-VAS reflects differences in important background characteristics of informal care: type of relationship, age of the care recipient and duration of care giving were associated with higher CarerQol-VAS scores. These results confirmed earlier tests of the construct validity of the CarerQol. Furthermore, the dimensions of CarerQol-7D significantly explained differences in CarerQol-VAS scores among subgroups of carers.
Conclusion
Notwithstanding the limitations of our study, such as the low response rate, this study shows that the CarerQol provides a valid means to measure carer effects for use in economic evaluations. Future research should derive a valuation set for the CarerQol and further address the instrument’s content validity, sensitivity and reliability.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Ill or disabled persons often largely rely on care provided by family or friends, typically non-paid. In the Netherlands, for instance, approximately 23 percent of the total population provides informal care [1]. Informal carers often do so over a long period of time, and they spend a substantial amount of time per week on performing diverse activities which may be fairly demanding and unpleasant to perform. Consequently, informal care can be straining and has a profound impact on caregivers’ lives. For example, informal care may result in problems to perform other activities, such as paid work or leisure activities. It can also lead to social isolation or financial strain, deterioration of a carer’s physical and mental health and even increased mortality risk [2–4]. Nevertheless, many caregivers consider the provision of informal care to their loved ones as a natural part of life or as a simple obligation within a family relationship [5]. Moreover, informal care may have a positive impact on the well-being of carers. Many caregivers prefer to provide care to their ill or disabled loved ones themselves, rather than handing over care to someone else [6]. In addition, care giving may enhance the quality of the relationship between caregiver and care recipient, increase the appreciation of everyday life and stimulate the development of new skills [7], such as management skills to control the care situation.
The attention for informal care in economic evaluations of health care interventions seems to increase. Including informal care in such evaluations is particularly important if an economic evaluation claims to adopt the commonly advocated societal perspective, which entails the inclusion of all relevant costs and effects of an intervention, regardless of where these fall in society [8–11]. Obviously, this includes the full impact of informal care. Health care interventions may not only affect patients, but may simultaneously influence their caregivers, either positively or negatively. For example, early discharge of patients from a hospital may save formal health care costs, but increase caregiver burden and, therefore, costs [12]. This increased burden moreover may in turn lead to more pressure on the health care budget when the health of the caregivers themselves deteriorates due to caring. In general, the exclusion of informal care in economic evaluations of health care interventions in which caregivers play a substantial role may thus lead to suboptimal policy recommendations. Even from a narrower health care perspective, as adopted in some jurisdictions e.g. [13], it can be argued that at least some elements of informal care are relevant, such as the health effects in carers [14].
To date, economic evaluations have usually failed to consider informal care [15]. When it is included, the methods used often vary strongly between studies [16]. Typically, the opportunity costs or shadow price methods are used, which express the value of informal care in monetary terms by multiplying the number of care giving hours with some value per hour [17, 18]. The resulting cost estimate can easily be included in an economic evaluation, i.e., on the cost-side of a cost-effectiveness ratio. A downside, however, is that such valuations do not necessarily reflect the preferences of caregivers [17], for example by not distinguishing between the first or the fiftieth hour of care giving.
Consequently, other monetary valuation methods have been proposed and applied, such as the contingent valuation method [19, 20], conjoint analysis e.g. [21] and the well-being method [22]. These methods supposedly are more sensitive to caregiver preferences, without losing the straightforward manner to include the results in common cost-effectiveness studies.
In addition, non-monetary methods, traditionally mostly subjective burden measures, have been proposed to capture the impact of informal care e.g. [23, 24]. Subjective burden measures indicate the burden experienced by caregivers. However, while informative, such measures cannot be seen as valuation instruments in an economic sense; they are mainly descriptive. It has also been argued that, perhaps in addition to monetary valuation of time, the effects of informal care on health may be directly included in economic evaluations in terms of quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) using validated questionnaires such as the EuroQol-instrument [25]. Changes in health-related quality of life of caregivers could then be combined with changes in patient health and included in the ‘denominator’ of a cost-effectiveness ratio [26]. Still, such an approach only comprises a partial valuation of informal care, i.e., it only captures the health effects of informal care. Hence, there is still the need for instruments that combine the information density of subjective burden measures with a comprehensive valuation method [27, 28]. This need gave rise to the development of the CarerQol instrument, acronym for care-related quality of life [27]. The CarerQol, which will be further discussed in the “Methods” section, comprises two parts (see Fig. 1): a description of the care situation on seven burden dimensions (CarerQol-7D) and a valuation component in terms of general quality of life using a Visual Analogue Scale (CarerQol-VAS).
First test of the CarerQol instrument
Some psychometric properties of the CarerQol, in specific feasibility as well as construct validity, have been previously tested in a heterogeneous population of caregivers identified via regional informal care support centers in the Netherlands (n = 175, [27]). Other psychometric properties of the CarerQol, such as reliability and sensitivity to changes, have not yet been established.
The first results of the psychometric properties of the CarerQol showed that it is a clear, easy to use and comprehensible instrument, of which the feasibility and construct validity, including the convergent and clinical validity, were good [27]. Increased burden measured in terms of the dimensions of the CarerQol-7D was associated with increased burden measured with other burden instruments, such as the Caregiver Strain Index (CSI, [29]) and the Self-rated Burden scale (SRB, [30]). Furthermore, CarerQol-VAS scores correlated well with the CarerQol-7D. More problems on CarerQol-7D dimensions led to lower CarerQol-VAS scores, while all effects were statistically significant except for one dimension (‘support’; see “Methods” section for specific CarerQol-7D dimensions). Regarding the clinical validity of the instrument, the instrument discriminated well between groups [27]. Specifically, different characteristics of the caregiver, care recipient and care situation were related with CarerQol-VAS in the expected direction, e.g., carers having a partner, those in good health, those caring for their parent and carers who care for persons who do not use professional day care had higher CarerQol-VAS scores.
Objectives and hypotheses
The central aim of this paper is to further investigate the construct validity of the CarerQol using a new, but quite similar, population of caregivers. To achieve this aim, we use comparable methods to test convergent and clinical validity as [27]. Convergent validity of the CarerQol is measured as its correlation with other instruments measuring the construct of subjective burden of informal care. Clinical validity concerns the extent to which differences in background characteristics, such as caregiver variables, are reflected in CarerQol-VAS scores. We further study the clinical validity of the CarerQol by performing subgroup analyses, highlighting the differences in CarerQol-VAS scores between groups of carers.
Given the similarities in study samples, we expect that our results on convergent and clinical validity resemble those in [27], i.e., that CarerQol-VAS scores are negatively related to increased burden measured with the CarerQol-7D and other subjective burden instruments. Likewise, a positive association between CarerQol-7D and these other instruments is expected. Concerning the clinical validity, we expect that CarerQol-VAS reflects differences in important background characteristics of informal care, such as the relationship between the caregiver and care recipient. Moreover, certain variables may have a different relationship with the CarerQol-VAS score in different subgroups of caregivers.
Methods
Population
Data were collected with written questionnaires distributed by mail in a heterogeneous population of informal caregivers contacted through regional support centers for informal caregivers throughout the Netherlands (n = 1,100). A regional support center provides support to caregivers, e.g., by organizing self-help groups. The response rate was 25% (n = 275), which is comparable to similar studies e.g. [22]. In total, 230 cases were analyzed; two cases were not suitable for further analysis, 43 were excluded due to missing items on the CarerQol or other important variables (net response rate = 21%). More information on the dataset can be found in [31].
Measures
The CarerQol instrument was included in the written questionnaire (see Fig. 1). The development of the CarerQol instrument was based on the approach used for the EuroQol-instrument [28]. The CarerQol-7D consists of seven dimensions describing the burden experienced by caregivers. These dimensions were selected based on a literature review of validated burden instruments, and the completeness and clarity of this list was evaluated and confirmed in a small pilot study with a convenience sample of informal caregivers [27]. The CarerQol-7D includes (± indicating positive/negative dimension) fulfillment of care giving (+), relational problems (−), mental health problems (−), problems with combining daily activities (−), financial problems (−), social support (+) and physical health problems (−) [27]. Respondents can indicate to what extent they experience problems in these dimensions in their care situation, range in possible answers: no, some, a lot. In total, 2,187 (=37) different care situations can be distinguished.
The valuation component of the instrument (CarerQol-VAS) consists of a Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) measuring general quality of life in terms of happiness (see Fig. 1); a broad measure of well-being or utility increasingly used in the field of (health) economics [32, 33]. Happiness scores are seen as ‘the degree to which an individual judges the overall quality of his life-as-a-whole favorably’ [34]. The CarerQol-VAS consists of a horizontal VAS indicating current happiness ranging from ‘completely unhappy’ (0) to ‘completely happy’ (10), with numeric anchors equally spaced between these two extreme levels. Previous research in the field of informal care showed that such a VAS is feasible and informative [35, 6] with results comparable to a five-point verbal description of happiness [22]. This broad outcome measure makes the instrument sensitive to the variety of consequences informal caregivers may experience, e.g., health or financial problems. A disadvantage is that other not care-related aspects of life may also influence the happiness of a caregiver, e.g., income level and type of work.
The outcomes of the CarerQol can be included at the ‘denominator side’ in a multi-criteria or cost-consequence analysis. One can also view the instrument as a useful tool to perform a cost-utility analysis, if an intervention targeted specifically at caregivers is to be evaluated. For more detailed information on the development of the instrument, we refer to [27].
In addition, the questionnaire included questions on background characteristics of caregivers, care recipients, and the care situation, including objective and subjective burden and process utility. Objective burden consisted of the duration of care in years and months, the intensity of care in days per week and hours per day, the type of care activities distinguishing activities of daily living (ADL), instrumental activities of daily living (IADL), household activities of daily living (HDL), the care recipients’ need for constant surveillance, the use of professional home care and the need and use of respite care. Respite care is a generic term for different informal care support interventions, e.g., day-care programs or support groups.
Subjective burden was measured with a horizontal VAS (Self-Rated Burden scale, SRB) ranging from ‘not straining at all’ (0) to ‘much too straining’ (10) [30].
Process utility (PU) is the utility derived from the process of care giving [6]. PU is computed by the difference in happiness between the current situation and a hypothetical situation in which all care giving tasks would be taken over by a person selected by the care recipient and caregiver, in the home of the care recipient, free of charge.
Statistical analyses
Convergent validity
To test the convergent validity, the associations between CarerQol-7D and CarerQol-VAS were analyzed using Spearman’s correlation coefficients (Table 1). Further, to assess the relation between the two parts of the CarerQol instrument, CarerQol-VAS scores were predicted on the basis of the CarerQol-7D dimensions with the use of multiple linear regression analysis (Table 3). As discussed in the introduction, happiness is a broad outcome measure and therefore CarerQol-VAS may be influenced by variables not necessarily related to caring. To investigate this, we related the CarerQol-7D to a less broad outcome measure, i.e., subjective burden (SRB), also with the use of multiple linear regression analysis (Table 3). The CarerQol-7D dimensions were analyzed as continuous variables in both models as additional analyses (not shown) showed that treating CarerQol-7D as a continuous or categorical variable produced similar results.
In addition, the convergent validity was tested by the association between CarerQol-VAS and the two other measures of caregiver burden, SRB and PU, with Spearman’s correlation coefficients (Table 2). Moreover, the same associations were tested for the CarerQol-7D (Table 2).
Different guidelines exist to assess the strength of correlation coefficients e.g., [36, 37]. In this study, the strength of the Spearman’s correlation coefficients is indicated by the guideline of Hopkins [38]: <0.1 trivial; 0.1–0.3 small; 0.3–0.5 moderate; 0.5–0.7 high; 0.7–0.9 very high; >0.9 nearly perfect, which largely agrees with the other classifications. Correlation of small to moderate strength would be seen as a sign of validity, because happiness is a broad outcome measure and the CarerQol-VAS score may be influenced by more than the effects of care giving alone, for instance by the ‘mere’ fact that a loved one is ill, i.e., ‘family effect’ [26, 39] and by other effects of life in general.
Clinical validity
Descriptive analyses of all variables were performed in means/percentages. The bivariate relation between CarerQol-VAS and characteristics of caregivers, care recipients and care situation was assessed with one-way ANOVA tests (Table 1). Furthermore, the clinical validity of the CarerQol was tested in a combined dataset of our respondents and the respondents of the first test [27]. Using multiple linear regression analysis, the CarerQol-VAS scores were first only related to the CarerQol-7D (as in Table 3) and subsequently, besides to the CarerQol-7D scores to additional variables describing caregiver, care recipient and care situation characteristics (Table 4). The same multiple linear model was then applied in subgroups of carers to further test clinical validity (Table 4). These subgroups consisted of carers with low or high SRB and carers with low or high PU (low SRB/PU: 33rd percentile, high SRB/PU: 66th percentile and higher). When using dummies, the reference categories of these variables were those with the highest CarerQol-VAS score. The CarerQol-7D dimensions were treated all as continuous in the regression models.
Statistical significance was based on an alpha error of 0.05, except in Tables 3 and 4 where an alpha error of 0.10 was used due to a small number of respondents when analyzing cases within categories of variables. Statistical analyses were performed using Stata version 10.0 (Statistics/Data Analysis).
Results
Table 1 presents the characteristics of our sample (n = 230). Caregivers were 59 years, on average, and most of them were women. The majority had a middle or higher educational level and approximately 28% was employed. Most caregivers provided care to a partner or a parent (in-law), and more than half shared a household with the care recipient, then often being their partner or child, not presented in table. Although the majority of caregivers were in good health, approximately 45% rated their health as reasonable or bad. On average, caregivers scored 5.2 on SRB. Mean PU was positive, meaning carers would become less happy when handing over all care giving duties to someone else. Nonetheless, nearly 43% of all caregivers indicated that their well-being would increase in that case.
Care recipients were predominantly women and, on average, 9 years older than the caregiver. Most had a poor health status and one out of three required permanent surveillance.
On average, caregivers had provided informal care for almost 9 years. Currently, they provided care approximately 42 h a week. Most time was spent on household activities, followed by assisting the care recipient with personal care, e.g., eating and dressing, and support with practical issues, e.g., visiting friends and administrative tasks. Two out of three care recipients received professional home care and 20% used day-care facilities. Respite care was used by more than one-third of the caregivers and desired by approximately half of the other carers.
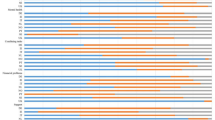
CarerQol-7D
Almost all caregivers experienced fulfillment from caring, and the majority received support with their care tasks (Fig. 2). Many carers had at least some relational problems with the care recipient or problems with combining care giving with other activities. Almost two-thirds reported physical and/or mental health problems. Although the majority did not have financial problems, one in four caregivers indicated having at least some financial problems due to care giving.
CarerQol-VAS score
The mean CarerQol-VAS score was 6.3. Further, considering the bivariate relations (Table 1), it seems that happiness was highest among those caring for distant family or friends and lowest among those caring for their child. The scores were also higher when the health of the caregiver was good, when they felt less burdened and when their process utility was positive.
Caregivers providing care to female care recipients, in relatively good health, and who do not need permanent surveillance, had significantly higher CarerQol-VAS scores, as did those who provided care less than 42 h per week. Caregivers who did not need or use respite care reported higher happiness scores than those using or wanting to use respite care.
Convergent validity
The Spearman’s correlation coefficients of CarerQol-VAS, SRB, PU and CarerQol-7D are shown in Table 2. CarerQol-VAS was negatively associated with caregiver burden (SRB score) and the CarerQol-7D dimensions relational problems, mental health problems, problems with daily activities, financial problems and physical health problems (range absolute values correlation coefficients 0.19–0.56).
A positive association was observed with PU and the CarerQol-7D dimensions fulfillment and receiving support, although the latter was not statistically significant (range absolute values correlation coefficients 0.04–0.58). SRB and PU were associated with the CarerQol-7D dimensions in the expected way (range absolute values correlation coefficients 0.03–0.55).
Association of CarerQol-VAS and SRB
Table 3 presents models to explain CarerQol-VAS and SRB, both on the basis of the CarerQol-7D scores. The CarerQol-VAS model shows that problems with mental and physical health and with performing daily activities were negatively associated with the CarerQol-VAS, and fulfillment positively. This model accounted for 38% of the variance in CarerQol-VAS scores.
The model explaining SRB showed similar results; mental health problems and problems with daily activities were positively related to caregiver burden, while fulfillment was negatively related to SRB and the model accounted for 38% of the variance in SRB.
Clinical validity
The results of the multivariate analysis between CarerQol-VAS and background characteristics are presented in Table 4 (first column; analyses performed in combined dataset). These results were largely in agreement with the correlation coefficients presented in Table 2, with the exception of the CarerQol-7D dimension financial problems. Furthermore, caring for a child, compared to caring for distant family or friends, significantly decreased CarerQol-VAS. In addition, the CarerQol-VAS was negatively related to the age of the care recipient and positively to the number of years caring.
Subgroups
The CarerQol-VAS of caregivers who experience little or no burden from caring, see “Appendix 1” for subgroup characteristics, was positively associated with fulfillment derived from caring and negatively with mental or physical health problems and problems with combining activities (analyses performed in combined dataset). In addition, a high educational level compared to a middle educational level significantly increased the score among these less burdened carers.
In the subgroup of carers with a high SRB score, the CarerQol-7D dimensions’ mental and physical health were also negatively associated with CarerQol-VAS scores. Furthermore, relational problems were negatively related to this score. The CarerQol-7D dimension combining activities was not associated with the CarerQol-VAS in this group, probably because most carers experienced these problems (not presented). CarerQol-VAS scores were also higher for those caring for their partner and those providing long-term care, while not having a paid job and intensity of care, were negatively associated with CarerQol-VAS. Lastly, a low educational level compared to a middle educational level was positively related to this score. This same relationship was also observed among the less burdened carers but, probably due to the small number of respondents with a low educational level, this difference did not reach statistical significance.
The same analyses were performed for two other subgroups of carers; carers with little or no PU and carers with high PU. The results, not presented here, were similar and thus in support of the clinical validity of the CarerQol.
Discussion
There is increasing consensus that economic evaluations of health care interventions should include the impact on informal carers whenever informal care potentially plays an important role in order to arrive at optimal policy decisions. The CarerQol is intended to measure and value those carer outcomes. Our study investigated the convergent and clinical validity of this instrument in a heterogeneous population of caregivers.
Convergent validity
As expected, the CarerQol-VAS was negatively associated with SRB and the negative dimensions of the CarerQol-7D, and positively with PU and the positive dimensions of the CarerQol-7D. Most of these correlations had moderate strength albeit the dimensions relational problems, financial problems and support had low convergent validity and the support dimension was not statistically significantly related to CarerQol-VAS. We also found evidence for the validity of the CarerQol-7D. The positive items of CarerQol-7D were positively associated to PU and negatively to SRB, while the reverse was true for the negative items of CarerQol-7D. These results are nearly identical to those reported by Brouwer et al. [27]. Overall, the results of our study suggest that the CarerQol shows moderate, but not unsatisfactory, convergent validity, given the broad outcome measure of happiness. Still, the CarerQol-7D explained the variation in CarerQol-VAS, and the narrower concept of burden measured with SRB more or less equally well and both were not fully explained by it (explained variance 38%). It would be worthwhile to investigate whether a more targeted valuation component, for instance measuring ‘care-related quality of life’—in analogy to health-related quality of life, could be meaningfully formulated and useful in this context to avoid too much influence of non-care giving related variables.
Initially, the analyses to test the convergent validity were performed using both parametric and non-parametric tests (not presented) in order to adjust for the fact that, although VAS scores are generally considered as interval variables, they must be regarded as ordinal e.g. [40]. The results of these tests are comparable, legitimizing the use of parametric tests in this study. This finding is confirmed by research on the methodological assumptions of the concept of happiness [33].
Clinical validity
The CarerQol-VAS reflects differences in important background characteristics of informal care; the relationship between caregiver and care recipient, age of care recipients and the duration of care giving were significantly associated with CarerQol-VAS. Brouwer et al. [27] showed comparable results. In addition, they found other factors related to happiness: partner and health status of the caregiver and the use of day care by the care recipient. However, their model differed somewhat from ours. Using a model resembling theirs the results become more similar. For example, the health of the caregiver was also positively associated with CarerQol-VAS (results not shown).
The dimensions of CarerQol-7D significantly explained the difference in CarerQol-VAS scores among subgroups of carers. Specifically, CarerQol-VAS was positively associated with fulfillment among carers with low subjective burden and negatively with relational problems among those with a high subjective burden.
Limitations of the CarerQol
An important limitation of the CarerQol is the difficulty of including its results in economic evaluations. The CarerQol outcomes cannot be summed with patient outcomes, however, can be included next to patient effects in cost-consequence analyses or as a separate item in a multi-criteria analysis. Standard (utility) scores for ‘care profiles’ defined by the CarerQol-7D are not (yet) available, but would facilitate the use of the CarerQol in economic evaluations. Future research will focus on deriving such utility scores, i.e., ‘tariffs’, potentially using care-related quality of life as relevant measure, in analogy to the tariffs available for the EuroQol-5D [41, 42].
In addition, the non-significant relation of the support dimension of the CarerQol-7D deserves attention. This non-significant relation may be due to a lack of power, but may also imply that support is less relevant in this context, that it measures different aspects, e.g., professional support or informal support, or that support is already indirectly captured in other CarerQol-7D dimensions. This issue of content validity deserves attention in future research.
This study, like the first test [27], was cross-sectional. Especially in the context of economic evaluations, it is important to test the sensitivity of the instrument to changes in the care giving situation, which requires a longitudinal study setup. Moreover, the reliability of the CarerQol instrument needs to be investigated as well.
Limitations of the study design
Some limitations of our study deserve mentioning. First, our results cannot be straightforwardly generalized, because our sample is not necessarily representative of the population of Dutch informal caregivers. Respondents were contacted via regional support centers and therefore are expected to be relatively burdened [43]. Indeed, the mean SRB score of 5.2 and the mean CarerQol-VAS score of 6.3 indicate that although carers in our sample were fairly happy, they still experienced substantial care giving burden. As a reference, the mean SRB in a population of carers of stroke patients was 3.0 [44], and 5.8 in a heterogeneous sample of Dutch carers, very similar to the current sample [6]. Moreover, the average happiness of the general population in the Netherlands, measured on a comparable scale, was 7.8 [45]. The relatively high burden among caregivers in our sample may have influenced the results. Nevertheless, we argue that for the purpose of this study, which was testing the psychometric properties of the CarerQol, such a bias seems unproblematic.
In addition, the external validity may be relatively low, because the non-response rate was relatively high. Possible reasons for a relatively high non-response are lack of time or energy to complete the questionnaire among caregivers due to the high strain placed on them by the care situation. Additionally, some informal caregivers may not regard their activities as ‘informal care’ and therefore do not feel the need to participate in research on this subject.
To overcome these biases, the convergent and clinical validity of the CarerQol should also be tested in samples of caregivers not selected via support centers. It may also be worthwhile to test the validity among a specific population of caregivers, e.g., carers of persons with a specific disease.
Conclusion
Our study confirmed results of the first test of the convergent and clinical validity of the CarerQol. Overall, the CarerQol provides a good description of the impact of care giving on informal caregivers and therefore can be seen as a useful instrument to include this effect in economic evaluations. To improve its use (fullness) to measure and value the effects of care giving, future research should further investigate its content validity, reliability and sensitivity and the development of utility scores for the ‘care profiles’. Ultimately, the aim is to adequately inform policy makers about the effects of interventions on caregivers and, as such, support informed decisions in the field of health care.
References
Schellingerhout, R. (2003). The informal caregiver. In J. Timmermans (Ed.), Informal care. Care of and to informal carers (pp. 33–57). The Hague: SCP.
Schulz, R., & Beach, S. R. (1999). Caregiving as a risk factor for mortality: The caregiver health effects study. Journal of the American Medical Association, 282(23), 2215–2219.
Broese van Groenou, M., & De Boer, A. (2009). Findings: Burden of informal carers. In A. De Boer, M. Broese, J. van Groenou, & J. Timmermans (Eds.), Informal care. An overview of the support given by and to informal carers in 2007 (pp. 144–165). The Hague: SCP.
Schellingerhout, R. (2003). Extra expenses and loss of income. In J. Timmermans (Ed.), Informal care. Care of and to informal carers (pp. 163–206). The Hague: SCP.
Hoefman, R. (2009). Care providers. In A. De Boer, M. Broese, J. van Groenou, & J. Timmermans (Eds.), Informal care. An overview of the support given by and to informal carers in 2007 (pp. 29–44). The Hague: SCP.
Brouwer, W. B., van Exel, N. J., van den Berg, B., van den Bos, G. A., & Koopmanschap, M. A. (2005). Process utility from providing informal care: The benefit of caring. Health Policy, 74(1), 85–99.
Broese van Groenou, M., & De Boer, A. (2009). Findings: Positive experiences. In A. De Boer, M. Broese, J. van Groenou, & J. Timmermans (Eds.), Informal care. An overview of the support given by and to informal carers in 2007 (pp. 167–183). The Hague: SCP.
Gold, M. R., Siegel, J. E., Russell, L. B., & Weinstein, M. (1996). Cost-effectiveness in health and medicine. New York: Oxford University Press.
Drummond, M. F., Sculpher, M. J., Torrance, G. W., O’Brien, B. J., & Stoddart, G. L. (2005). Methods for the economic evaluation of health care programmes. New York: Oxford University Press.
Jacobs, P., Ohinmaa, A., & Brady, B. (2005). Providing systematic guidance in pharmacoeconomic guidelines for analysing costs. PharmacoEconomics, 23(2), 143–153.
College voor Zorgverzekeringen (CVZ). (2005). Guidelines for pharmaco-economic research; evaluation and actualisation [richtlijnen voor farmaco-economisch onderzoek; evaluatie en actualisatie]. Diemen: CVZ.
van Exel, J., Koopmanschap, M., & Brouwer, W. (2003). Kostbaar ontslag. Korte verpleegduur brengt mantelzorgers in de problemen. Medisch Contact, 58(34), 1272–1274.
National Institute for Clinical Excellence. (2008). Guide to the methods of technology appraisal. London: NICE.
National Institute for Clinical Excellence. (2009). NICE technology appraisal guidance 111. Donepezil, galantamine, rivastigmine (review) and memantine for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease (amended). London: NICE.
Stone, P. W., Chapman, R. H., Sandberg, E. A., Liljas, B., & Neumann, P. J. (2000). Measuring costs in cost-utility analyses. Variations in the literature. International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care, 16(1), 111–124.
van den Berg, B., Brouwer, W. B., & Koopmanschap, M. A. (2004). Economic valuation of informal care. An overview of methods and applications. The European Journal of Health Economics, 5(1), 36–45.
van den Berg, B., Brouwer, W., van Exel, J., Koopmanschap, M., van den Bos, G. A., & Rutten, F. (2006). Economic valuation of informal care: Lessons from the application of the opportunity costs and proxy good methods. Social Science and Medicine, 62(4), 835–845.
Koopmanschap, M. A., van Exel, J. N., van den Berg, B., & Brouwer, W. B. (2008). An overview of methods and applications to value informal care in economic evaluations of healthcare. PharmacoEconomics, 26(4), 269–280.
van den Berg, B., Bleichrodt, H., & Eeckhoudt, L. (2005). The economic value of informal care: A study of informal caregivers’ and patients’ willingness to pay and willingness to accept for informal care. Health Economics, 14(4), 363–376.
de Meijer, C., Brouwer, W., Koopmanschap, M., van den Berg, B., & van Exel, J. (2009). The value of informal care-a further investigation of the feasibility of contingent valuation in informal caregivers. Health Economics, 19, 755–771.
van den Berg, B., Al, M., van Exel, J., Koopmanschap, M., & Brouwer, W. (2008). Economic valuation of informal care: Conjoint analysis applied in a heterogeneous population of informal caregivers. Value in Health, 11(7), 1041–1050.
van den Berg, B., & Ferrer-I-Carbonell, A. (2007). Monetary valuation of informal care: The well-being valuation method. Health Economics, 16(11), 1227–1244.
Vernooij-Dassen, M. J., Persoon, J. M., & Felling, A. J. (1996). Predictors of sense of competence in caregivers of demented persons. Social Science and Medicine, 43(1), 41–49.
Scholte op Reimer, W. J., de Haan, R. J., Pijnenborg, J. M., Limburg, M., & van den Bos, G. A. (1998). Assessment of burden in partners of stroke patients with the sense of competence questionnaire. Stroke, 29(2), 373–379.
EuroQol Group. (1990). EuroQol—a new facility for the measurement of health-related quality of life. Health Policy, 16(3), 199–208.
Brouwer, W. B. F., Van Exel, N. J. A., & Tilford, M. J. (2010). Incorporating caregiver and family effects in economic evaluations of child health. In W. J. Ungar (Ed.), Economic evaluation in child health. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Brouwer, W. B., van Exel, N. J., van Gorp, B., & Redekop, W. K. (2006). The CarerQol instrument: A new instrument to measure care-related quality of life of informal caregivers for use in economic evaluations. Quality of Life Research, 15(6), 1005–1021.
Al-Janabi, H., Coast, J., & Flynn, T. N. (2008). What do people value when they provide unpaid care for an older person? A meta-ethnography with interview follow-up. Social Science and Medicine, 67(1), 111–121.
Robinson, B. C. (1983). Validation of a caregiver strain index. Journal of Gerontology, 38(3), 344–348.
van Exel, N. J., Scholte op Reimer, W. J., Brouwer, W. B., van den Berg, B., Koopmanschap, M. A., & van den Bos, G. A. (2004). Instruments for assessing the burden of informal caregiving for stroke patients in clinical practice: A comparison of CSI, CRA, SCQ and self-rated burden. Clinical Rehabilitation, 18(2), 203–214.
van Exel, J., de Graaf, G., & Brouwer, W. (2008). Give me a break! Informal caregiver attitudes towards respite care. Health Policy, 88(1), 73–87.
Frey, B. S., & Stutzer, A. (2002). What can economists learn from happiness research? Journal of Economic Literature, 40, 402–435.
Ferrer-i-Carbonell, A., & Frijters, P. (2004). How important is methodology for the estimates of the determinants of happiness? The Economic Journal, 114, 641–659.
Veenhoven, R. (1984). Conditions of happiness. Dordrecht: Kluwer.
van Exel, N. J., Brouwer, W. B., van den Berg, B., Koopmanschap, M. A., & van den Bos, G. A. (2004). What really matters: An inquiry into the relative importance of dimensions of informal caregiver burden. Clinical Rehabilitation, 18(6), 683–693.
De Vaus, D. A. (2002). Surveys in social research. St. Leonards: Allen & Unwin.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Hopkins, W. G. (2002). A new view of statistics: Effect magnitudes. http://www.sportsci.org/resource/stats/effectmag.html.
Bobinac, A., van Exel, N. J., Rutten, F. F., & Brouwer, W. B. (2010). Caring for and caring about: Disentangling the caregiver effect and the family effect. Journal of Health Economics, 29, 549–556.
Svensson, E. (2000). Comparison of the quality of assessments using continuous and discrete ordinal rating scales. Biometrical Journal, 4, 417–434.
Lamers, L. M., McDonnell, J., Stalmeier, P. F., Krabbe, P. F., & Busschbach, J. J. (2006). The Dutch tariff: Results and arguments for an effective design for national EQ-5D valuation studies. Health Economics, 15(10), 1121–1132.
Dolan, P. (1997). Modeling valuations for EuroQol health states. Medical Care, 35(11), 1095–1108.
van Exel, J., Moree, M., Koopmanschap, M., Goedheijt, T. S., & Brouwer, W. (2006). Respite care—an explorative study of demand and use in Dutch informal caregivers. Health Policy, 78(2–3), 194–208.
van Exel, N. J., Koopmanschap, M. A., van den Berg, B., Brouwer, W. B., & van den Bos, G. A. (2005). Burden of informal caregiving for stroke patients. Identification of caregivers at risk of adverse health effects. Cerebrovascular Diseases, 19(1), 11–17.
Veenhoven, R. (2009). World database of happiness, distributional findings in nations. http://worlddatabaseofhappiness.eur.nl.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by Zorgonderzoek Nederland (ZonMW), Netherlands Organisation for Health Research and Development. A draft of this paper was presented at the ISPOR 12th Annual European Congress, France, Paris, and at the first lowlands Health Economists’ Study Group (lolaHESG), the Netherlands. We thank the participants, in specific Elske van den Akker, PhD, for useful comments and discussion points.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/2.0), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
About this article
Cite this article
Hoefman, R.J., van Exel, N.J.A., Looren de Jong, S. et al. A new test of the construct validity of the CarerQol instrument: measuring the impact of informal care giving. Qual Life Res 20, 875–887 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-010-9829-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-010-9829-8