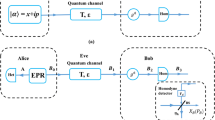
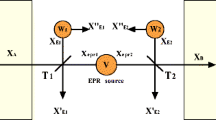
Abstract
The distinguishing of coherent states with minimum error is one of the fundamental tasks in continuous-variable quantum key distribution (CV-QKD). Homodyne detector, which is also a common element in current telecommunication, is considered as the simplest setup for such tasks due to it relying only on Gaussian operations. However, a practical homodyne detector has a finite linearity domain, thus eavesdroppers can open secure loopholes by displacing its operation into the nonlinearity domain, e.g., saturation attack and homodyne-detector-blinding attack. Here, we propose a counteracting strategy using mean-restricted unary linear regression to defend against such attacks caused by finite linearity domain problem. This strategy, which relies only on local operations plus classical communication (LOCC) processing, can estimate the displacements from the eavesdropper and then recover the attacked data. To show its practical utility in CV-QKD, we discuss two potential applications under composable security: (1) against saturation attack with one average to limit the line fitted, (2) against homodyne-detector-blinding attack with various averages to limit the line fitted. Numerical analysis shows that the estimated displacements have acceptable accuracy compared with the real displacements caused by the eavesdropper.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Xu, F., Ma, X., Zhang, Q., Lo, H.-K., Pan, J.-W.: Secure quantum key distribution with realistic devices. Rev. Mod. Phys. 92(2), 025002 (2020)
Lucamarini, M., Yuan, Z.L., Dynes, J.F., Shields, A.J.: Overcoming the rate-distance limit of quantum key distribution without quantum repeaters. Nature 557(7705), 400–403 (2018)
Zhang, W., Leent, T., Redeker, K., Garthoff, R., Schwonnek, R., Fertig, F., Eppelt, S., Rosenfeld, W., Scarani, V., Lim, C.C.-W., et al.: A device-independent quantum key distribution system for distant users. Nature 607(7920), 687–691 (2022)
Weedbrook, C., Pirandola, S., García-Patrón, R., Cerf, N.J., Ralph, T.C., Shapiro, J.H., Lloyd, S.: Gaussian quantum information. Rev. Mod. Phys. 84(2), 621 (2012)
Braunstein, S.L., Van Loock, P.: Quantum information with continuous variables. Rev. Mod. Phys. 77(2), 513 (2005)
Grosshans, F., Van Assche, G., Wenger, J., Brouri, R., Cerf, N.J., Grangier, P.: Quantum key distribution using gaussian-modulated coherent states. Nature 421(6920), 238–241 (2003)
Laudenbach, F., Pacher, C., Fung, C.-H.F., Poppe, A., Peev, M., Schrenk, B., Hentschel, M., Walther, P., Hübel, H.: Continuous-variable quantum key distribution with gaussian modulation—The theory of practical implementations. Adv. Quantum Technol. 1(1), 1800011 (2018)
Pirandola, S., Andersen, U.L., Banchi, L., Berta, M., Bunandar, D., Colbeck, R., Englund, D., Gehring, T., Lupo, C., Ottaviani, C., et al.: Advances in quantum cryptography. Adv. Opt. Photon. 12(4), 1012–1236 (2020)
Jouguet, P., Kunz-Jacques, S., Leverrier, A., Grangier, P., Diamanti, E.: Experimental demonstration of long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Nat. Photon. 7(5), 378–381 (2013)
Ma, X.-C., Sun, S.-H., Jiang, M.-S., Liang, L.-M.: Wavelength attack on practical continuous-variable quantum-key-distribution system with a heterodyne protocol. Phys. Rev. A 87(5), 052309 (2013)
Tan, X., Guo, Y., Zhang, L., Huang, J., Shi, J., Huang, D.: Wavelength attack on atmospheric continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 103(1), 012417 (2021)
Ma, X.-C., Sun, S.-H., Jiang, M.-S., Liang, L.-M.: Local oscillator fluctuation opens a loophole for eve in practical continuous-variable quantum-key-distribution systems. Phys. Rev. A 88(2), 022339 (2013)
Jouguet, P., Kunz-Jacques, S., Diamanti, E.: Preventing calibration attacks on the local oscillator in continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 87, 062313 (2013)
Qi, B., Lougovski, P., Pooser, R., Grice, W., Bobrek, M.: Generating the local oscillator “locally’’ in continuous-variable quantum key distribution based on coherent detection. Phys. Rev. X 5, 041009 (2015)
Soh, D.B., Brif, C., Coles, P.J., Lütkenhaus, N., Camacho, R.M., Urayama, J., Sarovar, M.: Self-referenced continuous-variable quantum key distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. X 5(4), 041010 (2015)
Wang, T., Zuo, Z., Li, L., Huang, P., Guo, Y., Zeng, G.: Continuous-variable quantum key distribution without synchronized clocks. Phys. Rev. Appl. 18(1), 014064 (2022)
Qin, H., Kumar, R., Alléaume, R.: Quantum hacking: saturation attack on practical continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 94(1), 012325 (2016)
Qin, H., Kumar, R., Makarov, V., Alléaume, R.: Homodyne-detector-blinding attack in continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 98, 012312 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.98.012312
Wang, T., Huang, P., Zhou, Y., Liu, W., Ma, H., Wang, S., Zeng, G.: High key rate continuous-variable quantum key distribution with a real local oscillator. Opt. Express 26(3), 2794–2806 (2018)
Huo, M., Qin, J., Cheng, J., Yan, Z., Qin, Z., Su, X., Jia, X., Xie, C., Peng, K.: Deterministic quantum teleportation through fiber channels. Sci. Adv. 4(10), 9401 (2018)
Zuo, Z., Wang, Y., Liao, Q., Guo, Y.: Overcoming the uplink limit of satellite-based quantum communication with deterministic quantum teleportation. Phys. Rev. A 104(2), 022615 (2021)
Zhao, H., Li, H., Xu, Y., Huang, P., Wang, T., Zeng, G.: Simple continuous-variable quantum key distribution scheme using a SAGNAC-based Gaussian modulator. Opt. Lett. 47(12), 2939–2942 (2022)
Lodewyck, J., Debuisschert, T., García-Patrón, R., Tualle-Brouri, R., Cerf, N.J., Grangier, P.: Experimental implementation of non-gaussian attacks on a continuous-variable quantum-key-distribution system. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 030503 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.98.030503
Jouguet, P., Kunz-Jacques, S., Leverrier, A.: Long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution with a Gaussian modulation. Phys. Rev. A 84, 062317 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.84.062317
Shao, Y., Wang, H., Pi, Y., Huang, W., Li, Y., Liu, J., Yang, J., Zhang, Y., Xu, B.: Phase noise model for continuous-variable quantum key distribution using a local local oscillator. Phys. Rev. A 104(3), 032608 (2021)
Wang, T., Huang, P., Zhou, Y., Liu, W., Zeng, G.: Pilot-multiplexed continuous-variable quantum key distribution with a real local oscillator. Phys. Rev. A 97, 012310 (2018)
Pirandola, S.: Composable security for continuous variable quantum key distribution: trust levels and practical key rates in wired and wireless networks. Phys. Rev. Res. 3, 043014 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevResearch.3.043014
Pirandola, S.: Limits and security of free-space quantum communications. Phys. Rev. Res. 3, 013279 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevResearch.3.013279
Zuo, Z., Wang, Y., Huang, D., Guo, Y.: Atmospheric effects on satellite-mediated continuous-variable quantum key distribution. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 53(46), 465302 (2020)
Zuo, Z., Wang, Y., Mao, Y., Ruan, X., Guo, Y.: Security of quantum communications in oceanic turbulence. Phys. Rev. A 104(5), 052613 (2021)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61871407, 61801522)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are not any possible conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, W., Li, J., Jin, D. et al. Withstanding detector attacks in continuous-variable quantum key distribution via mean-restricted unary linear regression. Quantum Inf Process 23, 59 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-024-04266-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-024-04266-4