Abstract
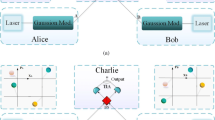
Continuous variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution (CV MDI-QKD) where legitimate communication parties, Alice and Bob, do not connect to each other directly but to an untrusted relay where the detection is performed can defend attacks that aim at measurement devices. It was recently shown that the preparation noise, although being trusted, was breaking the security of CV QKD. Hence, we study the security of continuous variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution based on noisy modulation of coherent states and investigate how the preparation noise influences the maximum transmission distance of the system. We propose a scheme of using a variable attenuator to attenuate decoder’s (Bob’s) mode to purify the coherent states he sends out under two-mode coherent attack. The simulation results show that when taking preparation noise into consideration the maximum transmission distance decreases seriously and our scheme can effectively compensate the detrimental effect of the preparation noise and improve the maximum transmission distance.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnett, S.M., Phoenix, S.J.: Information-theoretic limits to quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. A 48, R5–R8 (1993)
Filip, R.: Continuous-variable quantum key distribution with noisy coherent states. Phys. Rev. A 77, 022310–022314 (2008)
Grosshans, F., Assche, G.V., Wenger, J., Brouri-Tualle, R., Cerf, N.J., Grangier, P.: Quantum key distribution using gaussian-modulated coherent states. Nature 421, 238–241 (2003)
Häseler, H.H., Moroder, T., Lütkenhaus, N.: Testing quantum devices: practical entanglement verification in bipartite optical systems. Phys. Rev. A 77, 032303–032314 (2008)
Huang, J.Z., Weedbrook, C., Yin, Z.Q., Wang, S., Li, H.W., Guo, G., Han, Z.F.: Quantum hacking of a continuous-variable quantum-key-distribution system using a wavelength attack. Phys. Rev. A 87, 062329–062337 (2013)
Jouguet, P., Kunz-Jacques, S., Leverrier, A., Grangier, P., Diamanti, E.: Experimental demonstration of long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Nat. Photonics 7, 378–381 (2013a)
Jouguet, P., Kunz-Jacques, S., Diamanti, E.: Preventing calibration attacks on the local oscillator in continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 87, 062313–062319 (2013b)
Leverrier, A., Grangier, P.: Continuous-variable quantum-key-distribution with a non-Gaussian modulation. Phys. Rev. A 83, 042312–042328 (2011)
Li, Z., Zhang, Y.C., Xu, F., Peng, X., Guo, H.: Continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 89, 052301–052309 (2014)
Lodewyck, J., Bloch, M., Garcia-Patron, R., Fossier, S., Karpov, E., Diamanti, E., Debuisschert, T., Cerf, N.J., Brouri-Tualle, R., McLaughlin, S.W., Grangier, P.: Quantum key distribution over 25 km with an all-fiber continuous-variable systems. Phys. Rev. A 76, 042305–042315 (2007)
Ma, X.C., Sun, S.H., Jiang, M.S., Liang, L.M.: Local oscillator fluctuation opens a loophole for Eve in practical continuous-variable quantum key-distribution systems. Phys. Rev. A 88, 022339–022346 (2013a)
Ma, X.C., Sun, S.H., Jiang, M.S., Liang, L.M.: Wavelength attack on practical continuous-variable quantum-key-distribution system with a heterodyne protocol. Phys. Rev. A 87, 052309–052314 (2013b)
Ma, X.C., Sun, S.H., Jiang, M.S., Gui, M., Liang, L.M.: Gaussian-modulated coherent-state measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 89, 4089–4091 (2013c)
Ottaviani, C., Spedalieri, G., Braunstein, S.L., Pirandola, S.: Continuous-variable quantum cryptography with an untrusted relay: detailed security analysis of the symmetric configuration. Nat. Photonics 9, 397–402 (2015)
Pirandola, S.: Entanglement reactivation in separable environments. New J. Phys. 15, 1633–1691 (2013)
Pirandola, S., Serafini, A., Lloyd, S.: Correlation matrices of two-mode bosonic systems. Phys. Rev. A 79, 1744–1747 (2009)
Pirandola, S., Ottaviani, C., Spedalieri, G., Weedbrook, C., Braunstein, S. L., Lloyd, S., Gehring, T., Jacobsen, C. S., Andersen, U. L.: preprint arXiv:1312.4104 (2013)
Qin, H., Kumar, R., Alléaume, R.: Saturation attack on continuous-variable quantum key distribution system. SPIE Security + Defense International Society for Optics and Photonics 8899, 717–718 (2013)
Ralph, T.C.: Continuous variable quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. A 61, 010303–010310 (1999)
Serafini, A.: Multimode uncertainty relations and separability of continuous variable states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 110402–110405 (2006)
Shen, Y., Peng, X., Yang, J., Guo, H.: Continuous-variable quantum key distribution with Gaussian source noise. Phys. Rev. A 83(86), 10017–10028 (2011)
Spedalieri, G., Ottaviani, C., Pirandola, S.: Covariance matrices under Bell-like detections. Open Syst. Inf. Dyn. 20, 112–121 (2012)
Usenko, V.C., Filip, R.: Feasibility of continuous-variable quantum key distribution with noisy coherent states. Phys. Rev. A 81, 022318–022327 (2010)
Wang, T., Yu, S., Zhang, Y.C., Gu, W., Guo, H.: Improving the maximum transmission distance of continuous-variable quantum key distribution with noisy coherent states using a noiseless amplifier. Phys. Rev. A 1633, 113–115 (2014)
Weedbrook, C., Pirandola, S., Garcia-Patron, R., Cerf, N.J., Ralph, T.C., Shapiro, J.H., Lloyd, S.: Gaussian quantum information. Rev. Mod. Phys. 84, 621–669 (2012)
Wilde, M.M.: From classical to quantum Shannon theory. arXiv:1106.1445 (2011)
Wootters, W.K., Zurek, W.H.: A single quantum cannot be cloned. Nature 299, 802–803 (1982)
Zhang, Y.C., Li, Z., Yu, S., Gu, W., Peng, X., Guo, H.: Continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution using squeezed states. Phys. Rev. A 90, 052325–052331 (2014)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61177072). We thank Xuejin Wang for the useful help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, C., Wang, X. CV MDI-QKD with noisy coherent states. Opt Quant Electron 48, 430 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-016-0697-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-016-0697-5