Abstract
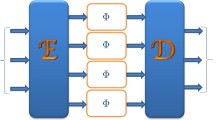
We introduce a general method of gluing multi-partite states and show that entanglement swapping is a special class of a wider range of gluing operations. The gluing operation of two m and n qudit states consists of an entangling operation on two given qudits of the two states followed by operations of measurements of the two qudits in the computational basis. Depending on how many qudits (two, one or zero) we measure, we have three classes of gluing operation, resulting respectively in \(m+n-2\), \(m+n-1\), or \(m+n\) qudit states. Entanglement swapping belongs to the first class and has been widely studied, while the other two classes are presented and studied here. In particular, we study how larger GHZ and W states can be constructed when we glue the smaller GHZ and W states by the second method. Finally we prove that when we glue two states by the third method, the k-uniformity of the states is preserved. That is when a k-uniform state of m qudits is glued to a \(k'\)-uniform state of n qudits, the resulting state will be a \(\hbox {min}(k,k')\)-uniform of \(m+n\) qudits.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raussendorf, R., Briegel, H.J.: A one-way quantum computer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 5188 (2001)
Aolita, L., Chaves, R., Cavalcanti, D., Acín, A., Davidovich, L.: Scaling laws for the decay of multiqubit entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 080501 (2008)
Barreiro, J.T., Schindler, P., Gühne, O., Monz, T., Chwalla, M., Roos, C.F., Hennrich, M., Blatt, R.: Experimental multiparticle entanglement dynamics induced by decoherence. Nat. Phys. 6, 943 (2010)
Benjamin, S.C., Browne, D.E., Fitzsimons, J., Morton, J.J.L.: Brokered graph-state quantum computation. New J. Phys. 8, 141 (2006)
Briegel, H.J., Browne, D.E., Dür, W., Raussendorf, R., van den Nest, M.: Measurement-based quantum computation. Nat. Phys. 5, 19 (2009)
Scott, A.J.: Multipartite entanglement, quantum-error-correcting codes, and entangling power of quantum evolutions. Phys. Rev. A 69, 052330 (2004)
Calderbank, A.R., Shor, P.W.: Good quantum error-correcting codes exist. Phys. Rev. A 54, 1098 (1996)
Steane, A.M.: Multiple particle interference and quantum error correction. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 452, 2551 (1996)
Cleve, R., Gottesman, D., Lo, Hoi-Kwong: How to share a quantum secret. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 648 (1999)
Hillery, M., Buzek, V., Berthiaume, A.: Quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 59, 1829 (1999)
Karlsson, A., Bourennane, M.: Quantum teleportation using three-particle entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 58, 4394 (1998)
Dür, W., Cirac, J.I.: Multiparty teleportation. J. Mod. Opt. 47, 247–255 (2000)
Cirac, J.I., Zoller, P., Kimble, H.J., Mabuchi, H.: Quantum state transfer and entanglement distribution among distant nodes in a quantum network. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 3221 (1997)
Kimble, H.J.: The quantum internet. Nature 452, 1023 (2008)
Facchi, P., Florio, G., Parisi, G., Pascazio, S.: Maximally multipartite entangled states. Phys. Rev. A 77, 060304 (2008)
Facchi, P.: Multipartite entanglement in qubit systems. Rend. Lincei Mat. Appl. 20, 25 (2009)
Helwig, W., Cui, W., Latorre, J.I., Riera, A., Lo, H.-K.: Absolute maximal entanglement and quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 86, 052335 (2012)
Arnaud, L., Cerf, N.J.: Exploring pure quantum states with maximally mixed reductions. Phys. Rev. A 87, 012319 (2013)
Goyenche, D., Życzkowski, K.: Genuinely multipartite entangled states and orthogonal arrays. Phys. Rev. A 90, 022316 (2014)
Jennewein, T., Weihs, G., Pan, J.W., Zeilinger, A.: Experimental nonlocality proof of quantum teleportation and entanglement swapping. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 017903 (2001)
Sciarrino, F., Lombardi, E., Milani, G., De Martini, F.: Delayed-choice entanglement swapping with vacuum-one-photon quantum states. Phys. Rev. A 66, 024309 (2002)
Jennewein, T., Aspelmeyer, M., Brukner, Č., Zeilinger, A.: Experimental proposal of switched delayed-choice for entanglement swapping. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 3, 73 (2005)
Ma, X.S., Zotter, S., Ko er, J., Ursin, R., Jennewein, T., Brukner, Č., Zeilinger, A.: Experimental delayed-choice entanglement swapping. Nat. Phys. 8, 480 (2012)
Su, X., Tian, C., Deng, X., Li, Q., Xie, Changde, Peng, Kunchi: Quantum entanglement swapping between two multipartite entangled states Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 240503 (2016)
Dür, W., Vidal, G., Cirac, J.I.: Three qubits can be entangled in two inequivalent ways. Phys. Rev. A 62, 062314 (2000)
Greenberger, D.M., Horne, M.A., Shimony, A.: Bell theorem without inequalities. Am. J. Phys. 58, 1131 (1990)
Gisin, N., Bechmann-Pasquinucci, H.: Bell inequality, Bell states and maximally entangled states for n qubits. Phys. Lett. A 246, 1 (1998)
Gour, G., Wallach, N.R.: All maximally entangled four qubits states. J. Math. Phys. 51, 112201 (2010)
Laflamme, R., Miquel, C., Paz, J.P., Zurek, W.H.: Perfect quantum error correcting code. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 198 (1996)
Borras, A., Plastino, A.R., Batle, J., Zander, C., Casas, M., Plastino, A.: Multi-qubit systems: highly entangled states and entanglement distribution. J. Phys. A 40, 13407 (2007)
Huber, F., Gühne, O., Siewert, J.: Absolutely maximally entangled states of seven qubits do not exist. arXiv:1608.06228v1 [quant-ph]
Agrawal, P., Pati, A.: Perfect teleportation and superdense coding with W states. Phys. Rev. A 74, 062320 (2006)
Yildiz, A.: Optimal distillation of three-qubit W states. Phys. Rev. A 82, 012317 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raissi, Z., Karimipour, V. Creating maximally entangled states by gluing. Quantum Inf Process 16, 81 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1535-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1535-9