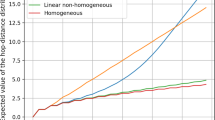
Abstract
The connection between coined and continuous-time quantum walk models has been addressed in a number of papers. In most of those studies, the continuous-time model is derived from coined quantum walks by employing dimensional reduction and taking appropriate limits. In this work, we produce the evolution of a coined quantum walk on a generic graph using a continuous-time quantum walk on a larger graph. In addition to expanding the underlying structure, we also have to switch on and off edges during the continuous-time evolution to accommodate the alternation between the shift and coin operators from the coined model. In one particular case, the connection is very natural, and the continuous-time quantum walk that simulates the coined quantum walk is driven by the graph Laplacian on the dynamically changing expanded graph.



Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Let \(n_t\) be a Poisson random variable and denote the expected value by \(\langle \,\cdot \,\rangle \). For the continuous-time transition matrix \(M_{\mathrm{CT}}(t)\) and the discrete-time transition matrix \(M_{\mathrm{DT}}(k)\) of the RW, we have
$$\begin{aligned} M_{\mathrm{CT}}(t) = \langle M_{\mathrm{DT}}(n_t) \rangle = \sum _{k=0}^\infty P(n_t=k)M_{\mathrm{DT}}(k) = \text {exp}[t(M_{\mathrm{DT}}-I)] . \end{aligned}$$.
In order to write down a matrix representation of C or S, one first has to decide how to list the basis elements \(|v,j\rangle \). Arranging them with respect to v yields a matrix representation of C that is in block diagonal form. The representation of S can be made block diagonal by ordering in the j-component.
References
Aharonov, Y., Davidovich, L., Zagury, N.: Quantum random walks. Phys. Rev. A 48, 1687–1690 (1993)
Aharonov, D., Ambainis, A., Kempe, J., Vazirani, U.: Quantum walks on graphs. In: Proceedings of the Thirty-third Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, STOC ’01, pp. 50–59. ACM, New York (2001)
Farhi, E., Gutmann, S.: Quantum computation and decision trees. Phys. Rev. A 58, 915–928 (1998)
Kempe, J.: Quantum random walks: an introductory overview. Contemp. Phys. 44(4), 307–327 (2003)
Hillery, M., Bergou, J., Feldman, E.: Quantum walks based on an interferometric analogy. Phys. Rev. A 68, 032314 (2003)
Hughes, B.D.: Random Walks and Random Environments: Random walks, vol. 1. Clarendon Press, Oxford (1995)
Lawler, G.F., Limic, V.: Random Walk: A Modern Introduction. Cambridge Studies in Advanced Mathematics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2010)
Ambainis, A.: Quantum walks and their algorithmic applications. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 01(04), 507–518 (2003)
Grover, L.K.: A fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-eighth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, STOC ’96, pp. 212–219. ACM, New York (1996)
Childs, A.M., Goldstone, J.: Spatial search by quantum walk. Phys. Rev. A 70, 022314 (2004)
Ambainis, A., Kempe, J., Rivosh, A.: Coins make quantum walks faster. In: Proceedings of the Sixteenth Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, SODA ’05, pp. 1099–1108. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Philadelphia (2005)
Wong, T.G.: Faster quantum walk search on a weighted graph. Phys. Rev. A 92, 032320 (2015)
Chakraborty, S., Novo, L., Ambainis, A., Omar, Y.: Spatial search by quantum walk is optimal for almost all graphs. Phys. Rev. Lett. 116, 100501 (2016)
Childs, A.M.: On the relationship between continuous- and discrete-time quantum walk. Commun. Math. Phys. 294(2), 581–603 (2009)
Paparo, G.D., Müller, M., Francesc, C., Martin-Delgado, M.A.: Quantum google in a complex network. Sci. Rep. 3, 2773 (2013)
Mallick, A., Mandal, S., Chandrashekar, C.M.: Simulation of neutrino oscillations using discrete-time quantum walk. ArXiv e-prints, April (2016)
Meyer, D.A.: On the absence of homogeneous scalar unitary cellular automata. Phys. Lett. A 223(5), 337–340 (1996)
Portugal, R., Santos, R.A.M., Fernandes, T.D., Gonçalves, D.N.: The staggered quantum walk model. Quantum Inf. Process. 15(1), 85–101 (2016)
Portugal, R.: Staggered quantum walks on graphs. Phys. Rev. A 93, 062335 (2016)
Strauch, F.W.: Connecting the discrete- and continuous-time quantum walks. Phys. Rev. A 74, 030301 (2006)
D’Alessandro, D.: Connection between continuous and discrete time quantum walks. From D-dimensional lattices to general graphs. Rep. Math. Phys. 66(1), 85–102 (2010)
di Molfetta, G., Debbasch, F.: Discrete-time quantum walks: continuous limit and symmetries. J. Math. Phys. 53(12), 123302 (2012)
Dheeraj, M.N., Brun, T.A.: Continuous limit of discrete quantum walks. Phys. Rev. A 91, 062304 (2015)
Szegedy, M.: Quantum speed-up of Markov chain based algorithms. In: 45th Annual IEEE symposium on foundations of computer science, 2004. Proceedings, pp. 32–41, Oct (2004)
Romanelli, A., Siri, R., Abal, G., Auyuanet, A., Donangelo, R.: Decoherence in the quantum walk on the line. Phys. A 347(C), 137–152 (2005)
Oliveira, A.C., Portugal, R., Donangelo, R.: Decoherence in two-dimensional quantum walks. Phys. Rev. A 74(012312), 012312 (2006)
Kollár, B., Kiss, T., Novotný, J., Jex, I.: Asymptotic dynamics of coined quantum walks on percolation graphs. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 230505 (2012)
Mülken, O., Pernice, V., Blumen, A.: Quantum transport on small-world networks: a continuous-time quantum walk approach. Phys. Rev. E 76, 051125 (2007)
Anishchenko, A., Blumen, A., Mülken, O.: Enhancing the spreading of quantum walks on star graphs by additional bonds. Quantum Inf. Process. 11(5), 1273–1286 (2012)
Darázs, Z., Kiss, T.: Time evolution of continuous-time quantum walks on dynamical percolation graphs. J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 46(37), 375305 (2013)
Portugal, R.: Establishing the equivalence between Szegedy’s and coined quantum walks using the staggered model. Quantum Inf. Process. 15(4), 1387–1409 (2016)
Shapir, Y., Aharony, A., Harris, A.B.: Localization and quantum percolation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 49, 486–489 (1982)
Santos, R.A.M., Portugal, R., Fragoso, M.D.: Decoherence in quantum Markov chains. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(2), 559–572 (2014)
Acknowledgements
P.P. would like to thank CNPq for its financial support (Grant Nos. 400216/2014-0 and 150726/2015-5). R.P. acknowledges financial support from Faperj (Grant No. E-26/102.350/2013) and CNPq (Grant Nos. 303406/2015-1 and 474143/2013-9).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Philipp, P., Portugal, R. Exact simulation of coined quantum walks with the continuous-time model. Quantum Inf Process 16, 14 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-016-1475-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-016-1475-9