Abstract
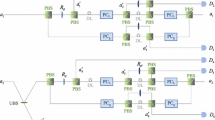
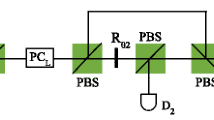
In this scheme, based on the weak cross-Kerr nonlinearity, an hyperconcentration protocol for the arbitrary partially hyperentangled N-particle Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger (GHZ) state is presented. Considering the N photons initially in the nonmaximally hyperentangled GHZ state in which photons are entangled simultaneously in the polarization and the spatial-mode degrees of freedom, we can obtain the maximally hyperentangled N-particle GHZ state by the projection measurements on the additional photons. Numerical simulation demonstrates that by iterating the entanglement concentration process, we can improve the success probability of the scheme. Furthermore, we discuss the feasibility of the setups of the protocol, concluding that the present protocol is feasible with existing experimental technology. All these advantages make this scheme more efficient and more convenient in quantum communication.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gisin, N., Ribordy, G., Tittel, W., Zbinden, H.: Quantum cryptography. Rev. Mod. Phys. 74, 145 (2002)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Crépeau, C., Jozsa, R., Peres, A., Wootters, W.K.: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1895 (1993)
Bennett, C.H., Wiesner, S.J.: Communication via one- and two-particle operators on Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 69, 2881 (1992)
Liu, X.S., Long, G.L., Tong, D.M., Li, F.: General scheme for superdense coding between multiparties. Phys. Rev. A 65, 022304 (2002)
Hillery, M., Bužek, V., Berthiaume, A.: Quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 59, 1829 (1999)
Xiao, L., Long, G.L., Deng, F.G., Pan, J.W.: Efficient multiparty quantum-secret-sharing schemes. Phys. Rev. A 69, 052307 (2004)
Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum-key-distribution scheme. Phys. Rev. A 65, 032302 (2002)
Zhu, Z.C., Hu, A.Q., Fu, A.M.: Cryptanalysis and improvement of the controlled quantum secure direct communication by using four particle cluster states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 53, 1495 (2014)
Yabushita, A., Kobayashi, T.: Spectroscopy by frequency-entangled photon pairs. Phys. Rev. A 69, 013806 (2004)
Xiao, L., Wang, C., Zhang, W., Huang, Y.D., Peng, J.D., Long, G.L.: Efficient strategy for sharing entanglement via noisy channels with doubly entangled photon pairs. Phys. Rev. A 77, 042315 (2008)
Barbieri, M., Vallone, G., Mataloni, P., De Martini, F.: Complete and deterministic discrimination of polarization Bell states assisted by momentum entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 75, 042317 (2007)
Schuck, C., Huber, G., Kurtsiefer, C., Weinfurter, H.: Complete deterministic linear optics Bell state analysis. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 190501 (2006)
Barreiro, J.T., Wei, T.C., Kwiat, P.G.: Beating the channel capacity limit for linear photonic superdense coding. Nat. Phys. 4, 282 (2008)
Wang, C., Deng, F.G., Li, Y.S., Liu, X.S., Long, G.L.: Quantum secure direct communication with high-dimension quantum superdense coding. Phys. Rev. A 71, 044305 (2005)
Wilde, M.M., Uskov, D.B.: Linear-optical hyperentanglement-assisted quantum error-correcting code. Phys. Rev. A 79, 022305 (2009)
Bruss, D., Macchiavello, C.: Optimal eavesdropping in cryptography with Three-dimensional quantum states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 127901 (2002)
Cerf, N.J., Bourennane, M., Karlsson, A., Gisin, N.: Security of quantum key distribution using \(d\)-level systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 127902 (2002)
Zou, X.F., Qiu, D.W.: Three-step semiquantum secure direct communication protocol. Sci. China Phys. Mech. 57, 1696 (2014)
Zheng, C., Long, G.F.: Quantum secure direct dialogue using Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen pairs. Sci. China Phys. Mech. 57, 1238 (2014)
Chang, Y., Xu, C.X., Zhang, S.B., Yan, L.L.: Controlled quantum secure direct communication and authentication protocol based on five-particle cluster state and quantum one-time pad. Chin. Sci. Bull. 88, 2541 (2014)
Krenn, M., Huber, M., Fickler, R., Lapkiewics, R., Ramelow, S., Zeilinger, A.: Generation and confirmation of a (100\(\times \)100)-dimensional entangled quantum system. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 111, 6243 (2014)
Barreiro, J.T., Langford, N.K., Peters, N.A., Kwiat, P.G.: Generation of hyperentangled photon pairs. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 260501 (2005)
Cao, D.Y., Liu, B.H., Wang, Z., Huang, Y.F., Li, C.F., Guo, G.C.: Multiuser-to-multiuser entanglement distribution based on 1550 nm polarization-entangled photons. Sci. Bull. 60, 1128 (2015)
Heilmann, R., Gräfe, M., Nolte, S., Szameit, A.: A novel integrated quantum circuit for high-order W-state generation and its highly precise characterization. Sci. Bull. 60, 96 (2015)
Sheng, Y.B., Deng, F.G., Long, G.L.: Complete hyperentangled-Bell-state analysis for quantum communication. Phys. Rev. A 82, 032318 (2010)
Wang, X.L., Cai, X.D., Su, Z.E., Chen, M.C., Wu, D., Li, L., Liu, N.L., Lu, C.Y., Pan, J.W.: Quantum teleportation of multiple degrees of freedom of a single photon. Nature 518, 516 (2015)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Popescu, S., Schumacher, B., Smolin, J.A., Wootters, W.K.: Purification of noisy entanglement and faithful teleportation via noisy channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 722 (1996)
Deutsch, D., Ekert, A., Jozsa, R., Macchiavello, C., Popescu, S., Sanpera, A.: Quantum privacy amplification and the security of quantum cryptography over noisy channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 2818 (1996)
Pan, J.W., Simon, C., Zellinger, A.: Entanglement purification for quantum communication. Nature 410, 1067 (2001)
Simon, C., Pan, J.W.: Polarization entanglement purification using spatial entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 257901 (2002)
Pan, J.W., Gasparonl, S., Ursin, R., Weihs, G., Zellinger, A.: Experimental entanglement purification of arbitrary unknown states. Nature (London) 423, 417 (2003)
Sheng, Y.B., Zhou, L.: Deterministic entanglement distillation for secure double-server blind quantum computation. Sci. Rep. 15, 7815 (2015)
Sheng, Y.B., Deng, F.G.: Deterministic entanglement purification and complete nonlocal Bell-state analysis with hyperentanglement. Phys. Rev. A 81, 032307 (2010)
Sheng, Y.B., Zhou, L., Long, G.L.: Hybrid entanglement purification for quantum repeaters. Phys. Rev. A 88, 022302 (2013)
Li, X.H.: Deterministic polarization-entanglement purification using spatial entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 82, 044304 (2010)
Deng, F.G.: One step error correction for multipartite polarization entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 83, 062316 (2011)
Deng, F.G.: Efficient multipartite entanglement purification with the entanglement link from a subspace. Phys. Rev. A 84, 052312 (2011)
Sheng, Y.B., Zhou, L.: Deterministic polarization entanglement purification using time-bin entanglement. Laser Phys. Lett. 11, 085203 (2014)
Ren, B.C., Deng, F.G.: Hyperentanglement purification and concentration assisted by diamond NV centers inside photonic crystal cavities. Laser phys. Lett. 10, 115201 (2013)
Ren, B.C., Du, F.F., Deng, F.G.: Two-step hyperentanglement purification with the quantum-state-joining method. Phys. Rev. A 90, 052309 (2014)
Fan, L.L., Xia, Y., Song, J.: Complete hyperentanglement-assisted multi-photon Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger states analysis with cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Opt. Commun. 317, 102 (2014)
Bennett, C.H., Bernstein, H.J., Popescu, S., Schumacher, B.: Concentrating partial entanglement by local operations. Phys. Rev. A 53, 2046 (1996)
Bose, S., Vedral, V., Knight, P.L.: Purification via entanglement swapping and conserved entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 60, 194 (1999)
Shi, B.S., Jiang, Y.K., Guo, G.C.: Optimal entanglement purification via entanglement swapping. Phys. Rev. A 62, 054301 (2000)
Yamamoto, T., Koashi, M., Imoto, N.: Concentration and purification scheme for two partially entangled photon pairs. Phys. Rev. A 64, 012304 (2001)
Sheng, Y.B., Deng, F.G., Zhou, H.Y.: Nonlocal entanglement concentration scheme for partially entangled multipartite systems with nonlinear optics. Phys. Rev. A 77, 062325 (2008)
Deng, F.G.: Optimal nonlocal multipartite entanglement concentration based on projection measurements. Phys. Rev. A 85, 022311 (2012)
Sheng, Y.B., Zhou, L., Zhou, S.M.: Efficient two-step entanglement concentration for arbitrary W states. Phys. Rev. A 85, 042302 (2012)
Zhou, L., Sheng, Y.B., Cheng, Wen W., Gong, L.Y., Zhao, S.Mei: Efficient entanglement concentration for arbitrary less-entangled NOON states. Quantum Inf. Process. 12, 1307 (2013)
Wang, C.: Efficient entanglement concentration for partially entangled electrons using a quantum-dot and microcavity coupled system. Phys. Rev. A 86, 012323 (2012)
Ren, B.C., Du, F.F., Deng, F.G.: Hyperentanglement concentration for two-photon four-qubit systems with linear optics. Phys. Rev. A 88, 012302 (2013)
Li, X.H., Ghose, S.: Hyperconcentration for multipartite entanglement via linear optics. Laser phys. Lett. 11, 125201 (2014)
Fan, L.L., Xia, Y., Song, J.: Efficient entanglement concentration for arbitrary less-hyperentanglement multi-photon W states with linear optics. Quantum Inf. Process. 13, 1967 (2014)
Ren, B.C., Long, G.L.: General hyperentanglement concentration for photon systems assisted by quantum-dot spins inside optical microcavities. Opt. Express 22, 6547 (2014)
Du, F.F., Deng, F.G.: Heralded entanglement concentration for photon systems with linear-optical elements. Sci. China Phys. Mech. 58, 040303 (2015)
Cao, C., Ding, H., Li, Y., Wang, T.J., Mi, S.C., Zhang, R., Wang, C.: Efficient multipartite entanglement concentration protocol for nitrogen-vacancy center and microresonator coupled systems. Quantum Inf. Process. 14, 1265 (2015)
Wang, G.Y., Li, T., Deng, F.G.: High-efficiency atomic entanglement concentration for quantum communication network assisted by cavity QED. Quantum Inf. Process. 14, 1305 (2015)
Sheng, Y.B., Zhou, L.: Two-step complete polarization logic Bell-state analysis. Sci. Rep. 5, 13453 (2015)
Nemoto, K., Munro, W.J.: Nearly deterministic linear optical controlled-not gate. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 250502 (2004)
Bartkowiak, M., Miranowicz, A.: Linear-optical implementations of the iSWAP and controlled NOT gates based on conventional detectors. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 27, 2369 (2010)
Kok, P., Munro, W.J., Nemoto, K.: Linear optical quantum computing with photonic qubits. Rev. Mod. Phys 79, 135 (2007)
Kok, P., Lee, H., Dowling, J.P.: Single-photon quantum-nondemolition detectors constructed with linear optics and projective measurements. Phys. Rev. A 66, 063814 (2002)
Shapiro, J.H.: Single-photon Kerr nonlinearities do not help quantum computation. Phys. Rev. A 73, 062305 (2006)
Wittmann, C., Andersen, U.L., Takeoka, M., Sych, D., Leuchs, G.: Discrimination of binary coherent states using a homodyne detector and a photon number resolving detector. Phys. Rev. A 81, 062338 (2010)
He, B., Lin, Q., Simon, C.: Cross-Kerr nonlinearity between continuous-mode coherent states and single photons. Phys. Rev. A 83, 053826 (2011)
Feizpour, A., Xing, X.X., Steinberg, A.M.: Amplifying single-photon nonlinearity using weak measurements. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 133603 (2011)
Zhu, C., Huang, G.: Giant Kerr nonlinearity, controlled entangled photons and polarization phase gates in coupled quantum-well structures. Opt. Express 19, 23364 (2011)
Lin, Q., Li, J.: Quantum control gates with weak cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Phys. Rev. A 79, 022301 (2009)
Li, Y.M., Zhang, K.S., Peng, K.C.: Generation of qudits and entangled qudits. Phys. Rev. A 77, 015802 (2008)
Jeong, H., An, N.B.: Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger-type and W-type entangled coherent states: Generation and Bell-type inequality tests without photon counting. Phys. Rev. A 74, 022104 (2006)
Jin, G.S., Lin, Y., Wu, B.: Generating multiphoton Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger states with weak cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Phys. Rev. A 75, 054302 (2007)
Guo, Q., Bai, J., Cheng, L.Y., Shao, X.Q., Wang, H.F., Zhang, S.: Simplified optical quantum-information processing via weak cross-Kerr nonlinearities. Phys. Rev. A 83, 054303 (2011)
Lin, Q., He, B.: Addendum to Single-photon logic gates using minimum resources. Phys. Rev. A. 82, 064303 (2010)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 11575045 and 11374054, the Foundation of Ministry of Education of China under Grant No. 212085, and the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China under Grant No. 2012CB921601.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, HJ., Xia, Y. & Song, J. Efficient hyperentanglement concentration for N-particle Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger state assisted by weak cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Quantum Inf Process 15, 2033–2052 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-016-1258-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-016-1258-3