Abstract
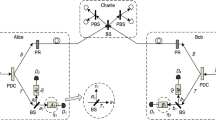
Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution (MDI-QKD) is immune to all the detection attacks. Based on decoy-state method, MDI-QKD can be implemented with nonperfect single-photon sources. In this paper, the performance of three-intensity decoy-state MDI-QKD under asymmetric channel transmittance efficiency is considered and compared with the results under the symmetric choice scenario. The relation between security key generation rate and the total transmission loss is shown with exchanged ratio of the two distances between Alice to the untrusted third party and Bob to the third party. Based on the relationship, an optimal intensity method is proposed to improve the key rate for a fixed distance ratio, which will provide important parameters for practical experiment.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennet, C.H., Brassard, G.: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference Computers, Systems and Signal Processing. IEEE, New York, pp. 175–179 (1984)
Shor, P.W.: J. Preskill. Simple proof of security of the BB84 quantum key distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 441 (2000)
Mayers, D.: Unconditional security in quantum cryptography. J. ACM. 48, 351 (2001)
Gottesman, D., Lo, H.K., Lutkenhaus, N., Preskill, J.: Security of quantum key distribution with imperfect devices. Quantum Inf. Comput. 4, 325–360 (2004)
Braunstein, S.L., Pirandola, S.: Side-channel-free quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 130502 (2012)
Brassard, G., Lutkenhaus, N., Mor, T., Sanders, B.C.: Limitations on practical quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 1330–1333 (2000)
Sun, S.H., Liang, L.M.: Experimental demonstration of an active phase randomization and monitor module for quantum key distribution. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 071107 (2012)
Makarov, V.: Faked states attack using detector efficiency mismatch on SARG04, phase-time, DPSK, and Ekert protocols. J. Skaar. Quantum. Inf. Comput. 86, 0622–0635 (2008)
Zhao, Y., Fung, C.H.F., Qi, B., Chen, C., Lo, H.K.: Quantum hacking: experimental demonstration of time-shift attack against practical quantum-key-distribution systems. Phys. Rev. A 78, 042333 (2008)
Makarov, V.: Controlling passively quenched single photon detectors by bright light. New J. Mod. Opt. 11, 065003 (2009)
Mayers, D., Yao, A.C-C.: Proceedings of the 39th Annual Symposium on Foundation of Computer Science. IEEE Computer Society, Washington DC, p. 503 (1998)
Gisin, N., Pironio, S., Sangouard, N.: Proposal for implementing device-independent quantum key distribution based on a heralded qubit amplifier. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 70501 (2010)
Curty, M., Moroder, T.: Heralded-qubit amplifiers for practical device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 84, 010304 (2011)
Pironio, S., Acín, A., Brunner, N., Gisin, N., Massar, S., Scarani, V.: Device-independent quantum key distribution secure against collective attacks. New J. Phys. 11, 045021 (2009)
Lo, H.K., Curty, M., Qi, B.: Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys Rev. Lett. 108, 130503 (2012)
Hwang, W.Y.: Quantum key distribution with high loss: toward global secure communication. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 057901 (2003)
Ma, X.F., Fung, C.H.F., Razavi, M.: Statistical fluctuation analysis for measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 86, 052305 (2012)
Curty, M., Xu, F.H., Cui, W., Lim, C.C.W., Tamaki, K., Lo, H.K.: Finite-key analysis for measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Nat. Commun. 5, 3732 (2014)
Wang, X.B.: Three-intensity decoy state method for device-independent quantum key distribution with basis-dependent errors. Phys. Rev. A 87, 012320 (2013)
Sun, S.H., Gao, M., Li, C.Y., Liang, L.M.: Practical decoy-state measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 87, 052329 (2013)
Xu, F.H., Curty, M., Qi, B., Lo, H.K.: Practical measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. New J. Phys. 15, 113007 (2013)
Liu, Y., et al.: Experimental measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 130502 (2013)
Tang, Z., Liao, Z., Xu, F., Qi, B., Qian, L., Lo, H.K.: Experimental demonstration of polarization encoding measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 190503 (2014)
Rubenok, A., Slater, J.A., Chan, P., Martinez, I.L., Tittel, W.: Real-world two-photon interference and proof-of-principle quantum key distribution immune to detector attacks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 130501 (2013)
Sasaki, M., et al.: Field test of quantum key distribution in the Tokyo QKD network. Opt. Express 19, 10387 (2011)
Ma, X.F., Razavi, M.: Alternative schemes for measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 86, 062319 (2012)
Acknowledgments
The authors thank S.H. Sun for many helps. This work is partially supported by the NSFC Grant No. 6110606
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, D., Shang-Hong, Z., Wei-Hu, Z. et al. Analysis of measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution under asymmetric channel transmittance efficiency. Quantum Inf Process 13, 2525–2534 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-014-0806-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-014-0806-y