Abstract
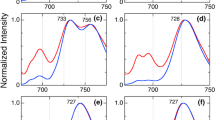
In this work, we applied Stark fluorescence spectroscopy to an iron-stressed cyanobacterial membrane to reveal key insights about the electronic structures and excited state dynamics of the two important pigment-protein complexes, IsiA and PSII, both of which prevail simultaneously within the membrane during iron deficiency and whose fluorescence spectra are highly overlapped and hence often hardly resolved by conventional fluorescence spectroscopy. Thanks to the ability of Stark fluorescence spectroscopy, the fluorescence signatures of the two complexes could be plausibly recognized and disentangled. The systematic analysis of the SF spectra, carried out by employing standard Liptay formalism with a realistic spectral deconvolution protocol, revealed that the IsiA in an intact membrane retains almost identical excited state electronic structures and dynamics as compared to the isolated IsiA we reported in our earlier study. Moreover, the analysis uncovered that the excited state of the PSII subunit of the intact membrane possesses a significantly large CT character. The observed notably large magnitude of the excited state CT character may signify the supplementary role of PSII in regulative energy dissipation during iron deficiency.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akita F et al (2020) Structure of a cyanobacterial photosystem I surrounded by octadecameric IsiA antenna proteins. Commun Biology 3(1):232
Albertsson P-Å (2001) A quantitative model of the domain structure of the photosynthetic membrane. Trends Plant Sci 6(8):349–354
Ara AM et al (2006) External electric field effects on fluorescence of pyrene butyric acid in a polymer film: concentration dependence and temperature dependence. J Phys Chem B 110(47):23669–23677
Ara AM et al (2020) Stark fluorescence spectroscopy on peridinin–chlorophyll–protein complex of dinoflagellate, Amphidinium carterae. Photosynth Res 143:233–239
Ara AM et al (2021) Absence of far-red emission band in aggregated core antenna complexes. Biophys J 120(9):1680–1691
Berera R et al (2009) A mechanism of energy dissipation in cyanobacteria. Biophys J 96(6):2261–2267
Bibby TS, Nield J, Barber J (2001) Iron deficiency induces the formation of an antenna ring around trimeric photosystem I in cyanobacteria. Nature 412(6848):743–745
Boehm M et al (2011) Investigating the early stages of photosystem II assembly in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803: isolation of CP47 and CP43 complexes. J Biol Chem 286(17):14812–14819
Boekema E et al (1987) Evidence for a trimeric organization of the photosystem I complex from the thermophilic cyanobacterium Synechococcus Sp. FEBS Lett 217(2):283–286
Boekema E et al (2001) A giant chlorophyll–protein complex induced by iron deficiency in cyanobacteria. Nature 412(6848):745–748
Braver Y, Valkunas L, Gelzinis A (2021) Stark absorption and Stark fluorescence spectroscopies: Theory and simulations The Journal of Chemical Physics, 155(24)
Campbell D et al (1998) Chlorophyll fluorescence analysis of cyanobacterial photosynthesis and acclimation. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62(3):667–683
Fraser JM et al (2013) Photophysiological and photosynthetic complex changes during iron starvation in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 and Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942. PLoS ONE 8(3):e59861
Gobets B, Van Grondelle R (2001) Energy transfer and trapping in photosystem I, Biochimica et Biophysica Acta BBA-Bioenergetics. 1507(1–3):80–99.
Gottfried DS, Stocker JW, Boxer SG (1991) Stark effect spectroscopy of bacteriochlorophyll in light-harvesting complexes from photosynthetic bacteria. Biochim et Biophys Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics 1059(1):63–75
Grossman AR et al (1994) The responses of cyanobacteria to environmental conditions: light and nutrients, in the molecular biology of cyanobacteria. Springer, pp 641–675
Guikema JA, Sherman LA (1983) Organization and function of chlorophyll in membranes of cyanobacteria during iron starvation. Plant Physiol 73(2):250–256
Havaux M et al (2005) The chlorophyll-binding protein IsiA is inducible by high light and protects the cyanobacterium Synechocystis PCC6803 from photooxidative stress. FEBS Lett 579(11):2289–2293
Herranen M et al (2004) Towards functional proteomics of membrane protein complexes in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Plant Physiol 134(1):470–481
Horton P, Ruban A, Walters R (1996) Regulation of light harvesting in green plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 47(1):655–684
Huang G et al (2021) Structural insights into a dimeric Psb27-photosystem II complex from a cyanobacterium Thermosynechococcus Vulcanus. Proc Natl Acad Sci 118(5):pe2018053118
Ihalainen JA et al (2005) Aggregates of the chlorophyll-binding protein IsiA (CP43 ‘) dissipate energy in cyanobacteria. Biochemistry 44(32):10846–10853
Ivanov AG et al (2006) Iron deficiency in cyanobacteria causes monomerization of photosystem I trimers and reduces the capacity for state transitions and the effective absorption cross section of photosystem I in vivo. Plant Physiol 141(4):1436–1445
Johnson VM et al (2022) Psb27, a photosystem II assembly protein, enables quenching of excess light energy during its participation in the PSII lifecycle. Photosynth Res 152(3):297–304
Karapetyan NV (2008) Protective dissipation of excess absorbed energy by photosynthetic apparatus of cyanobacteria: role of antenna terminal emitters. Photosynth Res 97:195–204
Lamb JJ, Røkke G, Hohmann-Marriott MF (2018) Chlorophyll fluorescence emission spectroscopy of oxygenic organisms at 77 K. Photosynthetica 56(1):105–124
Laudenbach DE, Straus NA (1988) Characterization of a cyanobacterial iron stress-induced gene similar to psbC. J Bacteriol 170(11):5018–5026
Legaspi CM et al (2018) Rigidity and polarity effects on the electronic properties of two deep blue delayed fluorescence emitters. J Phys Chem C 122(22):11961–11972
Lockhart DJ, Boxer SG (1988) Electric field modulation of the fluorescence from Rhodobacter sphaeroides reaction centers. Chem Phys Lett 144(3):243–250
Mimuro M et al (2007) Delayed fluorescence observed in the nanosecond time region at 77 K originates directly from the photosystem II reaction center. Biochim et Biophys Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics 1767(4):327–334
Moore LJ, Zhou H, Boxer SG (1999) Excited-state electronic asymmetry of the special pair in photosynthetic reaction center mutants: absorption and Stark spectroscopy. Biochemistry 38(37):11949–11960
Murray JW, Duncan J, Barber J (2006) CP43-like chlorophyll binding proteins: structural and evolutionary implications. Trends Plant Sci 11(3):152–158
Nakabayashi T, Wahadoszamen M, Ohta N (2005) External electric field effects on state energy and photoexcitation dynamics of diphenylpolyenes. J Am Chem Soc 127(19):7041–7052
Nakatani H et al (1984) Identity of the photosystem II reaction center polypeptide Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics. 765(3):347–352
Novoderezhkin VI (2023) Excitonic interactions and Stark fluorescence spectra. J Chem Phys, 159(5)
Novoderezhkin VI, Dekker JP, Van Grondelle R (2007) Mixing of exciton and charge-transfer states in photosystem II reaction centers: modeling of stark spectra with modified redfield theory. Biophys J 93(4):1293–1311
Odom WR et al (1993) Characterization of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 in iron-supplied and iron-deficient media. Plant Mol Biol 23:1255–1264
Pakrasi HB, Goldenberg A, Sherman LA (1985) Membrane development in the cyanobacterium, Anacystis nidulans, during recovery from iron starvation. Plant Physiol 79(1):290–295
Romero E et al (2009) The origin of the low-energy form of photosystem I light-harvesting complex Lhca4: mixing of the lowest exciton with a charge-transfer state. Biophys J 96(5):L35–L37
Sandström S et al (2001) CP43′, the isiA Gene product, functions as an Excitation Energy Dissipator in the Cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. PCC 7942¶. Photochem Photobiol 74(3):431–437
Sarcina M, Mullineaux CW (2004) Mobility of the IsiA chlorophyll-binding protein in cyanobacterial thylakoid membranes. J Biol Chem 279(35):36514–36518
Somsen OJ et al (1998) Excitonic interactions and Stark spectroscopy of light harvesting systems. J Phys Chem B 102(44):8893–8908
Toporik H et al (2019) The structure of the stress-induced photosystem I–IsiA antenna supercomplex. Nat Struct Mol Biol 26(6):443–449
van der Weij-de CD et al (2007) Fluorescence quenching of IsiA in early stage of iron deficiency and at cryogenic temperatures. Biochim et Biophys Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics 1767(12):1393–1400
van Grondelle R et al (1994) Energy transfer and trapping in photosynthesis. Biochim et Biophys Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics 1187(1):1–65
Vinnemeier J, Hagemann M (1999) Identification of salt-regulated genes in the genome of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 by subtractive RNA hybridization. Arch Microbiol 172:377–386
Wahadoszamen M et al (2006) External electric field effects on absorption and fluorescence spectra of a fullerene derivative and its mixture with zinc-tetraphenylporphyrin doped in a PMMA film. J Phys Chem B 110(41):20354–20361
Wahadoszamen M et al (2012) Identification of two emitting sites in the dissipative state of the major light harvesting antenna. Phys Chem Chem Phys 14(2):759–766
Wahadoszamen M et al (2014a) Stark fluorescence spectroscopy reveals two emitting sites in the dissipative state of FCP antennas. Biochim et Biophys Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics 1837(1):193–200
Wahadoszamen M et al (2014b) The role of charge-transfer states in energy transfer and dissipation within natural and artificial bacteriochlorophyll proteins. Nat Commun 5(1):5287
Wahadoszamen M et al (2015) Identification of common motifs in the regulation of light harvesting: the case of cyanobacteria IsiA, vol 1847. BBA)-Bioenergetics, pp 486–492. 4–5Biochimica et Biophysica Acta
Wahadoszamen M et al (2016) Identification and characterization of multiple emissive species in aggregated minor antenna complexes. Biochim et Biophys Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics 1857(12):1917–1924
Wahadoszamen M et al (2020) Charge transfer states in phycobilisomes. Biochim et Biophys Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics 1861(7):148187
Walters KA, Gaal DA, Hupp JT (2002) Interfacial charge transfer and colloidal semiconductor dye-sensitization: mechanism assessment via Stark emission spectroscopy. J Phys Chem B 106(20):5139–5142
Yeremenko N et al (2004) Supramolecular organization and dual function of the IsiA chlorophyll-binding protein in cyanobacteria. Biochemistry 43(32):10308–10313
Zabret J et al (2021) Structural insights into photosystem II assembly. Nat Plants 7(4):524–538
Zhao L-S et al (2022) Native architecture and acclimation of photosynthetic membranes in a fast-growing cyanobacterium. Plant Physiol 190(3):1883–1895
Acknowledgements
The authors thankfully acknowledge the contribution of Jos Thieme for his technical assistance. Md. W., A. M. A. and R. v. G. were supported by the VU University Amsterdam, the Laserlab-Europe Consortium and the advanced investigator grant (267333, PHOTPROT) from the European Research Council. Md. W. and R. v. G. were supported further by the TOP grant (700.58.305) from the Foundation of Chemical Sciences part of NWO.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Md. W., A. M. A., and R. v. G. designed experiment. S.D prepared IsiA membrane. A. M. A, S. D., and Md. W. prepared Stark samples. Md. W. and A. M. A. carried out Stark experiments. A. M. A. and Md. W. performed Stark data analysis. A. M. A., S. D., R. v. G., and Md. W. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ara, A.M., D’Haene, S., van Grondelle, R. et al. Unveiling large charge transfer character of PSII in an iron-deficient cyanobacterial membrane: A Stark fluorescence spectroscopy study. Photosynth Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-024-01099-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-024-01099-1