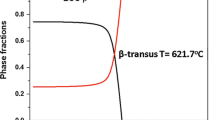
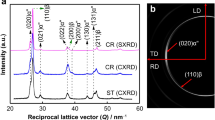
The strain-induced martensitic transformation in a medical alloy from the ternary Ti–Nb–Mo system was studied. The low-doped Ti92.5Nb5Mo2.5 alloy was produced by arc remelting, followed by annealing, rolling at room temperature, reannealing, and water quenching. X-ray diffraction analysis showed that thermomechanical processing resulted in the alloy primarily consisting of orthorhombic martensite (αʺ) with a small amount of the β-titanium phase. Hysteresis loops were recorded in loading–unloading cycles with 1% strain increments up to a total strain of 4% under compression testing, employing a precision strain gauge. Young’s modulus under loading varied from 51.2 GPa at the initial section to 39.7 GPa after a 2% residual strain. Young’s modulus remains unchanged, within 74.3 GPa, during unloading. Elastic, pseudoelastic, and plastic strains were found to significantly depend on the previous strain within the first three loading–unloading cycles. To examine the impact of higher strains (up to 23.4%) on structural rearrangements and phase transformations, the samples were compressed without a precision strain gauge. X-ray diffraction analysis revealed that only the crystalline texture of the alloy changed after compression. Strains exceeding 23.4% were achieved by rolling at room temperature. After rolling to a strain of 64%, the diffraction patterns indicated an increased amount of the β-phase, as evidenced by the (200) diffraction peak, not observed previously. The increased amount of the β-phase suggests that strain prompted the reverse martensitic transformation (αʺ → β).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Guo, K. Georgarakis, Y. Yokoyama, and A.R. Yavari, “On the mechanical properties of TiNb based alloys,” J. Alloys Compd., 571, 25–30 (2013).
S. Banumathy, R.K. Mandal, and A.K. Singh, “Structure of orthorhombic martensitic phase in binary Ti–Nb alloys,” J. Appl. Phys., 106, Issue 9, 093518 (2009).
R. Davis, H.M. Flower, and D.R.F. West, “Martensitic transformations in Ti–Mo alloys,” J. Mater. Sci., 14, 712–722 (1979).
M. Li, X. Min, K. Yao, and F. Ye, “Novel insight into the formation of αʺ-martensite and ω-phase with cluster structure in metastable Ti–Mo alloys,” Acta Mater., 164, 322–333 (2019).
M. Bönisch, M. Calin, J. van Humbeeck, W. Skrotzki, and J. Eckert, “Factors influencing the elastic moduli, reversible strains and hysteresis loops in martensitic Ti–Nb alloys,” Mater. Sci. Eng.: C, 48, 511–520 (2015).
O.M. Myslyvchenko, Y.M. Podrezov, A.A. Bondar, P.M. Romanko, N.M. Marchenko, and I.A. Poliakov, “Phase transformations in the Ti92.5Nb5Mo2.5 alloy under tensile strain,” J. Surf. Invest. X-ray, Synchrotron Neutron Tech., 15, No. 6, 1357–1360 (2021).
S. Cai, J.E. Schaffer, Y. Ren, and C. Yu, “Texture evolution during nitinol martensite detwinning and phase transformation,” Appl. Phys. Lett., 103, 241909 (2013).
M.J. Szczerba and R. Chulist, “Detwinning of a non-modulated Ni–Mn–Ga martensite: From selfaccommodated microstructure to single crystal,” Acta Mater., 85, 67–73 (2015).
P. Castany, T. Gloriant, F. Sun, and F. Prima, “Design of strain-transformable titanium alloys,” C. R. Phys., 19, Issue 8, 710–720 (2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Poroshkova Metallurgiya, Vol. 61, Nos. 11–12 (548), pp. 142–149, 2022.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Myslyvchenko, O.M., Podrezov, Y.M., Bondar, A.A. et al. The Influence of Strain on Texture Changes and Phase Transformations in the Quenched Ti92.5Nb5Mo2.5 Alloy. Powder Metall Met Ceram 61, 748–753 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-023-00361-w
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-023-00361-w