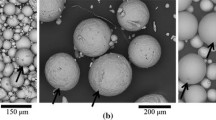
316L stainless steel parts are manufactured via selective laser melting. The investigation into the main characteristics and metallurgical mechanisms of selective laser melting process are highlighted in this work. The morphologies, microstructures and elemental compositions of as received scan tracks and samples are detected through optical microscope, SEM and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy respectively. The morphology of melted track exhibits scaly figures from top view, which is similar to welding process. The central zone of melted track shows a cellular microstructure while the edge zone of molten pool represents a columnar structure, which is caused by the heat transfer process. The surface morphology of SLM part in low magnification can show multi-lined feature, and the surface morphology in high magnification can reflect the solidification and crystallization process. Moreover, a little amount of oxide and splash with balling effect can also be found on the SLM part surface. The microstructure of SLM part is extremely fine coupled with multiple crystal directions. The very fine crystal structure is caused by the extraordinarily rapid cooling and the multiple crystal directions are due to the variable heat transfer direction. The element distribution is homogeneous and no elemental aggregations can be found. The metallurgical mechanisms for the above characteristics are also addressed.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. P. Kruth, L. Froyen, J. Van Vaerenbergh, et al., “Selective laser melting of iron-based powder, “J. Materials Processing Technology, 149, Issue 1–3, 616–622 (2004).
E. C. Santos, K. Osakada, M. Shiomi, et al., “Microstructure and mechanical properties of pure titanium models fabricated by selective laser melting, “J. Mech. Eng. Sci., 218, Issue 7, 711–719 (2004).
K. Osakada and M. Shiomi, “Flexible manufacturing of metallic products by selective laser melting of powder, “Internat. J. Machine Tools & Manufacture, 46, Issue 11, 1188–1193 (2006).
I. Yadroitsev, I. Shishkovsky, P. Bertrand, and I. Smurov, “Manufacturing of fine-structured 3D porous filter elements by selective laser melting, “Applied Surface Science, 255, Issue 10, 5523–5527 (2009).
J. H. Liu, Y. S. Shi, K. H. Chen, and S. H. Huang, “Research on manufacturing Cu matrix Fe–Cu–Ni–C alloy composite parts by indirect selective laser sintering, “Internat. J. Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 33, No. 7–8, 693–697 (2007).
W. X. Zhang, Y. S. Shi, B. Liu, et al., “Consecutive sub-sector scan mode with adjustable scan lengths for selective laser melting technology, “Internat. J. Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 41, No. 7–8, 706–713 (2009).
J. P. Kruth, P. Mercelis, J. Van Vaerenbergh, and T. Craeghs, “Feedback control of selective laser melting, “Virtual and Rapid Manufacturing, 849, 521–527 (2008).
D. D. Gu, Y. F. Shen, J. L. Yang, and Y. Wang, “Effects of processing parameters on direct laser sintering of multicomponent Cu based metal powder, “Materials Science and Technology, 22, No. 12, 1449–1455 (2006).
I. Yadroitsev, P. Bertrand, and I. Smurov, “Parametric analysis of the selective laser melting process, “Applied Surface Science, 253, Issue 19, 8064–8069 (2007).
H. Meier and C. Haberland, “Experimental studies on selective laser melting of metallic parts, “Materialwissenschaft und Werkstofftechnik, 39, No. 9, 665–670 (2008).
F. Abe, E. C. Santos, Y. Kitamura, et al., “Influence of forming conditions on the titanium model in rapid prototyping with the selective laser melting process, “J. Mechanical Engineering Science, 217, Issue 1, 119–126 (2003).
D. D. Gu and Y. F. Shen, “Development and characterisation of direct laser sintering multicomponent Cu based metal powder, “Powder Metallurgy, 49, Issue 3, 258–264 (2006).
D. D. Gu, Y. F. Shen, P. Dai, and M. C. Yang, “Microstructure and property of sub-micro WC–10% Co particulate reinforced Cu matrix composites prepared by selective laser sintering, “Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 16, No. 2, 357–362 (2006).
A. Simchi and D. Godlinski, “Effect of SiC particles on the laser sintering of Al–7Si–0.3Mg alloy,“ Scripta Materialia, 2(59), 199–202 (2008).
A. Simchi and H. Pohl, “Direct laser sintering of iron-graphite powder mixture, “Materials Science and Engineering. A: Structural Materials Properties, Microstructure and Processing, 383, No. 2, 191–200 (2004).
H. H. Zhu, L. Lu, and J. Y. H. Fuh, “Development and characterisation of direct laser sintering Cu-based metal powder, “J. Materials Processing Technology, 140, 314–317 (2003).
D. D. Gu and Y. F. Shen, “Balling phenomena in direct laser sintering of stainless steel powder: Metallurgical mechanisms and control methods, “Materials & Design, 30, No. 8, 2903–2910 (2009).
D. D. Gu and Y. F. Shen, “Balling phenomena during direct laser sintering of multi-component Cu-based metal powder, “J. Alloys and Compounds, 432, No. 1–2, 163–166 (2007).
M. Shiomi, K. Osakada, K. Nakamura, et al., “Residual stress within metallic model made by selective laser melting process, “Cirp Annals-Manufacturing Technology, 53, No. 1, 195–198 (2004).
F. Abe, K. Osakada, M. Shiomi, et al., “The manufacturing of hard tools from metallic powders by selective laser melting, “J. Materials Processing Technology, 111, No. 1–3, 210–213 (2001).
A. Simchi, “Direct laser sintering of metal powders: Mechanism, kinetics and microstructural features, “Materials Science and Engineering. A: Structural Materials Properties, Microstructure and Processing, 428, No. 1–2, 148–158 (2006).
W. X. Zhang, Y. S. Shi, J. H. Liu, et al., “Complex structure micro-parts formed with selective laser melting method, “in: 3rd International Conference on Advanced Research in Virtual and Rapid Prototyping (Leiria, Portugal, 2007), Leiria, 2007, pp. 537–540.
W. X. Zhang, Y. S. Shi, J. H. Liu, et al., “Type HRPM-II machine for selective laser melting process, “in: 3rd International Conference on Advanced Research in Virtual and Rapid Prototyping (Leiria, Portugal, 2007), Leiria, 2007, pp. 541–544.
Weld-Staff, Basis of Welding Metallurgy [in Chinese], China Industrial Press, Beijing (1961).
R. D. Li, J. H. Liu, Y. S. Shi, et al., “316L stainless steel with gradient porosity fabricated by selective laser melting, “J. Materials Engineering and Performance, 19, No. 5, 666–671 (2010).
W. D. Huang, Laser Three-Dimensional Forming [in Chinese], Northwestern Polytechnical University Press, Xi'an (2007).
S. A. David, J. M. Vitek, S. S. Babu, et al., “Welding of nickel base superalloy single crystals, “Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2, No. 2, 79–88 (1997).
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to give thanks to the Chinese Foundation of Nature Science (grant No. 61078078) and National High-Tech Program (863) of China (grant No. 2007AA03Z115).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Poroshkovaya Metallurgiya, Vol. 50, No. 3–4 (478), pp. 23–34, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, R., Shi, Y., Wang, L. et al. The key metallurgical features of selective laser melting of stainless steel powder for building metallic part. Powder Metall Met Ceram 50, 141 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-011-9311-3
Received:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-011-9311-3