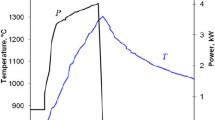
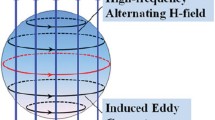
Model experiments for the initial stage of microwave sintering have revealed volume diffusion that can be accompanied by evaporation–condensation and surface diffusion. The volume diffusion is also confirmed by closer distances between the particles. The experimental data show that the mass transfer is intensified during microwave heating.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Agrawal, “Microwave sintering of ceramics, composites, metals, and transparent мaterials,” J. Mat. Ed., 19, No. 4–6, 49–58 (1999).
J. G. Fisher, K. Bai, S. K Woo, et al., “Microwave heated reaction-bonded silicon nitride using an inverse temperature gradient,” Met. Mat. Int., 9, No. 2, 187–191 (2003).
J. Katz, “Microwave sintering of ceramics,” Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci., 22, 153–70 (1992).
P. Yadojib, R. Peelamedua, D. Agrawal, et al., “Microwave sintering of Ni–Zn ferrites: comparison with conventional sintering,” Mat. Sci. Eng. B, 98, 269–278 (2003).
S. S. Panda, V. Singh, A. Upadhyaya, et al., “Sintering response of austenitic (316L) and ferritic (434L) stainless steel consolidated in conventional and microwave furnaces,” Scr. Mat., 54, 2179–2183 (2006).
R. Roy, D. Agrawal, J. Cheng, et al., “Full sintering of powdered-metal bodies in a microwave field,” Nature, 339, 668–670 (1999).
J. Cheng, R. Roy, and D. Agrawal, “Radically different effects on materials by separated microwave electric and magnetic fields,” Mat. Res. Innovat., 5, No. 3-4, 170–170 (2002).
J. Ma, J. F. Diehl, E. J. Johnson, et al., “Systematic study of microwave absorption, heating, and microstructure evolution of porous copper powder metal compacts,” J. Appl. Phys., 101, 1–8 (2007).
D. E. Clark, D. C. Folz, and J. K West, “Processing materials with microwave energy,” Mat. Sci. Eng. A, 287, 153–158 (2000).
E. Pert, Y. Carmel, A. Birnboim, et al., “Temperature measurements during microwave processing: the significance of thermocouple effects,” J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 84, 1981–1986 (2001).
G. C. Kuczynski, “Self-diffusion in sintering of metallic particles,” Metall. Trans. AIME, 185, 169–178 (1949).
Ya. E. Geguzin, Physics of Sintering [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1984), p. 312.
A. M. Gokhale, M. Basavaiah, G. S. Upadhyaya, et al. “Kinetics of neck growth during loose stack sintering,” Met. Mat. Trans. A, 19, No. 9, 2153–2161 (1988).
W. D. Kingery and M. Berg, “Study of initial stages of sintering solids by viscous flow, evaporationcondensation, and self-diffusion,” J. Appl. Phys., 26, No. 10, 1205–1212 (1955).
T. L. Wilson and P. G. Shewmon, “The role of interfacial diffusion in the sintering of copper,” Metall. Trans. AIME, 236, 48–58 (1966).
G. J. R. Rockland, “The determination of the mechanism of sintering,” Acta Met., 15, 277–286 (1967).
K.-S. Hwang, R. M. German, and F. V. Lenel, “Analysis of initial stage sintering through computer simulation,” Powder Met. Int., 23, 86–91 (1991).
K. Saitou, “Microwave sintering of iron, cobalt, nickel, copper and stainless steel powders,” Scripta Mat., 54, 875–879 (2006).
Yu. V. Bykov, K. I. Rybakov, and V. E. Semenov, “High-temperature microwave processing of materials,” J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 34, R55–R75 (2001).
R. Roy, P. D. Peelamedu, L. Hurtt, et al., “Definitive experimental evidence for microwave effects: Radically new effects of separated E and H fields, such as decrystallization of oxides in seconds,” Mat. Res. Innovat., 6, 128–140 (2002).
D. Demirskyi, D. Agrawal, and A. Ragulya, “Neck formation between copper spherical particles under single-mode and multimode microwave sintering,” Mat. Sci. Eng: A, A527, 2142–2145 (2010).
N. Yoshikawa, E. Ishizuka, and K. Mashiko, “Carbon reduction kinetics of NiO by microwave heating of the separated electric and magnetic fields,” Met. Mat. Trans. B, 38, 863–868 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Poroshkovaya Metallurgiya, Vol. 49, No. 3–4 (472), pp. 30–37, 2010.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Demirskii, D.N., Ragulya, A.V. Initial kinetics of microwave sintering of copper. Powder Metall Met Ceram 49, 147–152 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-010-9214-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-010-9214-8