Abstract
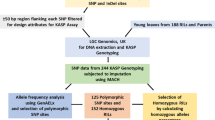
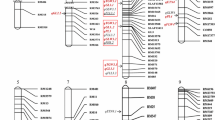
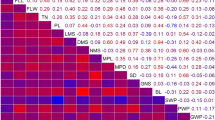
A backcross breeding strategy was used to identify quantitative trait loci (QTLs) associated with 14 traits in a BC2F2 population derived from a cross between MR219, an indica rice cultivar and an accession of Oryza rufipogon (IRGC 105491). A total of 261 lines were genotyped with 96 microsatellite markers and evaluated for plant morphology, yield components and growth period. The genetic linkage map generated for this population with an average interval size of 16.2 cM, spanning 1,553.4 cM (Kosambi) of the rice genome. Thirty-eight QTLs were identified with composite interval mapping (CIM), whereas simple interval mapping (SIM) resulted in 47 QTLs (LOD >3.0). The O. rufipogon allele was favourable for 59% of QTLs detected through CIM. Of 261 BC2F2 families, 26 advanced backcross breeding lines (BC2F5) were used for QTL validation. These lines were selected on the basis of the yield traits potentiality in BC2F3 and BC2F4 generations. The field trial was conducted at three different locations in Malaysia using randomized complete block design with three replications. Trait based marker analysis was done for QTL determination. Twenty-five QTLs were detected in BC2F5 generation whereas 29 QTLs were detected in BC2F2 generation of the same population. Two QTLs (qPL-1 and qSPL-7) were not considered for validation due to their low R 2 values and two QTLs (qPSS-3-2 and qGW-3-2) were not detected in the BC2F5 population. Fifteen QTLs showed the beneficial effect to enhance the trait value of the breeding lines. QTL validation aided to select the promising lines for further utilization.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashkani S, Rafii MY, Rusli I, Sariah M et al (2011) SSRs for marker-assisted selection for blast resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol Biol Rep. doi:10.1007/s11105-011-0315-4 (Online First)
Bhuiyan MAR, Narimah MK, Abdul Rahim H, Abdullah MZ, Wickneswari R (2011) Transgressive variants for red pericarp grain with high yield potential derived from Oryza rufipogon × Oryza sativa: field evaluation, screening for blast disease, QTL validation and background marker analysis for agronomic traits. Field Crop Res 121:232–239
Brar DS, Khush GS (1997) Alien introgression in rice. Plant Mol Biol 35:35–47
Bres-patry C, Lorieux M, Clement G, Bangratz M, Ghesquiere A (2001) Heredity and genetic mapping of domestication-related traits in a temperate japonica weedy rice. Theor Appl Genet 102:118–126
Cai HW, Morishima H (2002) QTL clusters reflect character associations in wild and cultivated rice. Theor Appl Genet 104:1217–1228
Campoy JA, Ruiz D, Egea J et al (2011) Inheritance of flowering time in apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) and analysis of linked quantitative trait loci (QTLs) using simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers. Plant Mol Biol Rep 29:404–410
Chen X, Temnykh S, Xu Y, Cho YG, Mccouch SR (1997) Development of a microsatellite framework map providing genome-wide coverage in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 95:553–567
Cho YG, Kang HJ, Lee JS, Lee YT, Lim SJ, Gauch H, Eun MY, McCouch SR (2007) Identification of quantitative trait loci in rice for yield, yield components, and agronomic traits across years and locations. Crop Sci 47:2403–2417
Churchill GA, Doerge RW (1994) Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138:963–971
Foolad MR, Zhang LP, Lin GY (2001) Identification and validation of QTLs for salt tolerance during vegetative growth in tomato by selective genotyping. Genome 44:444–454
International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) (1996) Standard evaluation system for rice, 4th edn. International Rice Research Institute (IRRI), Manila, Philippines
Joehanes R, Nelson JC (2008) QGene 4.0, an extensible Java QTL-analysis platform. Bioinformatics 24:2788–2789
Kohn JR, Leyva N, Dossey R, Sobral B, Morishima H (1997) Quantitative trait locus analysis of trait variation among annual and perennial ecotypes of Oryza rufipogon. Int Rice Res Notes 22:4–5
Li J, Wang X, Dong R, Yang Y, Zhou J, Yu C, Cheng Y, Yan C, Chen J (2011) Evaluation of high-resolution melting for gene mapping in rice. Plant Mol Biol Rep 29:979–985
Liu R, Zhang H, Zhao P, Zhang Z, Liang W et al (2011) Mining of candidate maize genes for nitrogen use efficiency by integrating gene expression and QTL data. Plant Mol Biol Rep. doi:10.1007/s11105-011-0346-x (Online First)
McCouch SR, Cho YG, Yano M, Paul E, Blinstrub M, Morishima H, Kinoshita T (1997) Report on QTL nomenclature. Rice Genet Newsl 14:11–13
McCouch SR, Teytelman L, Xu Y, Lobos KB, Clare K, Walton M, Fu B, Maghirang R, Li Z et al (2002) Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L). DNA Res 9:199–207
McCouch SR, Sweeney M, Li J, Jiang H, Thomson MJ, Septiningsih EM, Edwards J, Moncada P, Xiao J, Garris A, Tai T, Martinez C, Tohme J, Sugiono M, Mcclung A, Yuan LP, Ahn SN (2007) Through the genetic bottleneck: O. rufipogon as a source of trait-enhancing alleles for O. sativa. Euphytica 154:377–399
Moncada P, Martínez CP, Borrero J, Chatel M, Gauch H Jr, Guimaraes E, Tohme J, Mccouch SR (2001) Quantitative trait loci for yield and yield components in an Oryza sativa × Oryza rufipogon BC2F2 population evaluated in an upland environment. Theor Appl Genet 102:41–52
Monna L, Kitazawa N, Yoshino R, Suzuki J, Masuda H, Maehara Y, Tanji M, Sato M, Nasu S, Minobe Y (2002) Positional cloning of rice semidwarfing gene, sd-1: rice “green revolution gene” encodes a mutant enzyme involved in gibberellin synthesis. DNA Res 9:11–17
Murray M, Thompson MF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Ngu MS, Sabu KK, Lim LS, Abdullah MZ, Wickneswari R (2010) Genetic structure of Oryza rufipogon Griff. natural populations in Malaysia: implications for conservation and genetic introgression of cultivated rice. Tropical Plant Biol 3:227–239
Panaud O, Chen X, McCouch SR (1996) Development of microsatellite markers and characterisation of simple sequence length polymorphism (SSLP) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Genet 252:597–607
Robertson DS (1985) A possible technique for isolating genic DNA for quantitative traits in plants. J Theor Biol 117:1–10
Sabu KK, Abdullah MZ, Lim LS, Wickneswari R (2006) Development and evaluation of advanced backcross families of rice for agronomically important traits. Commun Biom Crop Sci 1:111–123
SAS Institute Inc (2003) SAS procedures guide. Release 9.1.3. SAS Institute Inc, Cary
Sasaki A, Ashikari M, Ueguchi-tanaka M, Itoh H, Nishimura A, Swapan D et al (2002) A mutant gibberellin synthesis gene in rice. Nature 416:701–702
Septiningsih EM, Prasetiyono J, Lubis E, Tai TH, Tjubaryat T, Moeljopawiro S, Mccouch SR (2003) Identification of quantitative trait loci for yield and yield components in an advanced backcross population derived from the Oryza sativa variety IR64 and the wild relative O rufipogon. Theor Appl Genet 107:1419–1432
Shen L, Courtois B, Mcnally KL, Robin S, Li Z (2001) Evaluation of near-isogenic lines of rice introgressed with QTLs for root depth through marker-aided selection. Theor Appl Genet 103:75–83
Stam P, Zeven AC (1981) The theoretical proportion of the donor genome in near-isogenic lines of self-fertilisers bred by backcrossing. Euphytica 30:227–238
Swamy BPM, Sarla N (2011) Meta-analysis of yield QTLs derived from inter-specific crosses of rice reveals consensus regions and candidate genes. Plant Mol Biol Rep 29:663–680
Tanksley SD, McCouch SR (1997) Seed banks and molecular maps: unlocking genetic potential from the wild. Science 277:1063–1066
Tanksley SD, Nelson JC (1996) Advanced backcross QTL analysis: a method for the simultaneous discovery and transfer of valuable QTLs from unadapted germplasm into elite breeding lines. Theor Appl Genet 92:191–203
Temnykh S, Park W, Ayres N, Cartinhour S, Hauck N, Lipovich L, Cho LG, Ishii T, McCouch SR (2000) Mapping and genome organisation of microsatellite sequences in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 100:697–712
Thomson MJ, Tai TH, McClung AM, Lai XH, Hinga ME, Lobos KB, Xu Y, Martinez CP, McCouch SR (2003) Mapping quantitative trait loci for yield, yield components and morphological traits in an advanced backcross population between Oryza rufipogon and the Oryza sativa cultivar Jefferson. Theor Appl Genet 107:479–493
Tian F, Li DJ, Fu Q, Zhu ZF, Fu YC, Wang XK, Sun CQ (2006) Construction of introgression lines carrying wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.) segments in cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) background and characterization of introgressed segments associated with yield-related traits. Theor Appl Genet 112:570–580
Venuprasad R, Shashidhar HE, Hittalmani S (2002) Tagging quantitative trait loci associated with grain yield and root morphological traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under contrasting moisture regimes. Euphytica 128:293–300
Wang B, Changxiang Z, Xu L, Wenying W, Hanfeng et al (2011) Fine Mapping of qHD4-1, a QTL controlling the heading date, to a 20.7-kb DNA fragment in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol Biol Rep 29:702–713
Xiao J, Li J, Grandillo S, Ahn SN, Yuan L, Tanksley SD, McCouch SR (1998) Identification of trait-improving quantitative trait loci alleles from a wild rice relative, Oryza rufipogon. Genetics 150:899–909
Zeng ZB (1994) Precision mapping of quantitative trait loci. Genetics 136:1457–1468
Zhao F, Cai Z, Hu T, Yao H, Wang L, Dong N, Wang B, Ru Z, Zhai W (2010) Genetic analysis and molecular mapping of a novel gene conferring resistance to rice stripe virus. Plant Mol Biol Rep 28:512–518
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation (MOSTI) for research grant of this study under the Project Nos. IRPA 01-03-03-001 BTK/ER/01 and UKM-ABI-NBD0001-2007 and express their gratitude to Malaysian Agricultural Research and Development Institute (MARDI) for the research facilities. Special thanks to Prof. Dr. Susan McCouch from Cornell University for technical advice on the first mapping population development and SSR genotyping.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wickneswari, R., Bhuiyan, M.A.R., Kalluvettankuzhy K., S. et al. Identification and Validation of Quantitative Trait Loci for Agronomic Traits in Advanced Backcross Breeding Lines Derived from Oryza rufipogon × Oryza sativa Cultivar MR219. Plant Mol Biol Rep 30, 929–939 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-011-0404-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-011-0404-4