Abstract
Backgroud
Echinochloa curs-galli (barnyardgrass) is the most prominent weed in rice fields, and its herbicide resistance seriously threatens rice yields. Penoxsulam failed to control an E. crus-galli var. zelayensis population (R) in field. However, the resistance level, cross-resistance pattern and resistance mechanism is not characterized.
Methods
The whole plant method was employed to determine the resistance level to penoxsulam and the cross-resistance pattern in R. Enzyme activity, gene cloning and sequencing, quantative real-time quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) were conducted to determine the target-site resistance mechanisms. Metabolism enzyme inhibitors pretreatment, RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) and qRT-PCR validation were performed to identify the penoxsulam-resistance related metabolism genes.
Results
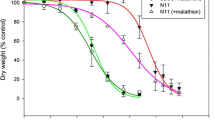
Here we identified an E. crus-galli var. zelayensis population (R) highly resistant to acetolactate synthase (ALS) inhibitor penoxsulam, cross-resistant to bispyribac-sodium and pyribenzoxim, and multiple-resistant to auxin mimics florpyrauxifen, but susceptible to acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase (ACCase) cyhalofop-butyl and the 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (HPPD) inhibitor benzobicyclon. Molecular investigation indicated that the penoxsulam resistance was unrelated to amino acid substitution or overexpression of the target enzyme. The metabolism inhibitors were employed to investigate the non-target site resistance mechanism consequently. P450s inhibitor malathion or GSTs inhibitor 4-chloro-7-nitro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole (NBD-Cl) both significantly decreased the resistance level to penoxsulam in population R. RNA-seq and qRT-PCR validation indicated that 15 P450s and 5 glutathione S-transferase (GST) genes were upregulated by penoxsulam in R plants.
Conclusion
We present an E. crus-galli var. zelayensis population with resistance to penoxsulam and multiple-resistance to auxin mimics. Enhanced herbicide metabolism via P450s and GSTs played a vital role in penoxsulam resistance.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai S, Yin M, Lyu Q, Jiang B, Li L (2022) Cytochrome P450 BsCYP99A44 and BsCYP704A177 confer metabolic resistance to ALS herbicides in Beckmannia syzigachne. Int J Mol Sci 23:12175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012175
Bai S, Zhao Y, Zhou Y, Wang M, Li Y, Luo X, Li L (2020) Identification and expression of main genes involved in non-target site resistance mechanisms to fenoxaprop-p-ethyl in Beckmannia syzigachne. Pest Manag Sci 76:2619–2626. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.5800
Beckie HJ, Tardif RJ (2012) Herbicide cross resistance in weeds. Crop Prot 35:15–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2011.12.018
Benekos K, Kissoudis C, Nianiou-Obeidat I, Labrou N, Madesis P, Kalamaki M, Makris A, Tsaftaris A (2010) Overexpression of a specific soybean GmGSTU4 isoenzyme improves diphenyl ether and chloroacetanilide herbicide tolerance of transgenic tobacco plants. J Biotechnol 150:195–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2010.07.011
Casey A, Dolan L (2023) Genes encoding cytochrome P450 monooxygenases and glutathione S-transferases associated with herbicide resistance evolved before the origin of land plants. PLoS ONE 18:e0273594. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0273594
Chen J, Pei Z, Dai L, Wang B, Liu L, An X, Peng D (2014) Transcriptome profiling using pyrosequencing shows genes associated with bast fiber development in ramie (Boehmeria nivea L). BMC Genomics 15:919. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-919
Chen G, Wang Q, Yao Z, Zhu L, Dong L (2016) Penoxsulam-resistant barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crus-galli) in rice fields in China. Weed Biol Manag 16(1):16–23. https://doi.org/10.1111/wbm.12086
China Minister of Agriculture and Rural Affairs (2021) The annual statistics of planting industry in China (In Chinese). http://zdscxx.moa.gov.cn:8080/nyb/pc/sourceArea.jsp. Accessed 13 Jan 2023
Cicero LL, Catara V, Strano CP, Bella P, Madesis P, Piero ARL (2017) Over-expression of CsGSTU promotes tolerance to the herbicide alachlor and resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv. Tabaci in transgenic tobacco. Biol Plant 61:169–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-016-0659-6
Cicero LL, Madesis P, Tsaftaris A, Lo Piero AR (2015) Tobacco plants over-expressing the sweet orange tau glutathione transferases (CsGSTUs) acquire tolerance to the diphenyl ether herbicide fluorodifen and to salt and drought stresses. Phytochem 116:69–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2015.03.004
Cummins I, Wortley DJ, Sabbadin F, He Z, Coxon CR, Straker HE, Sellars JD, Knight K, Edwards L, Hughes D, Kaundun SS, Hutchings SJ, Steel PG, Edwards R (2013) Key role for a glutathione transferase in multiple-herbicide resistance in grass weeds. P Natl Acad Sci 110(15):5812–5817. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1221179110
Deng W, Yang M, Li Y, Xia Z, Chen Y, Yuan S, Yang Q (2021) Enhanced metabolism confers a high level of cyhalofop-butyl resistance in a Chinese sprangletop (Leptochloa chinensis (L.) Nees) population. Pest Manag Sci 77:2576–2583. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.6297
Dimaano NG, Iwakami S (2021) Cytochrome P450-mediated herbicide metabolism in plants current understanding and prospects. Pest Manag Sci 77:22–32. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.6040
Dimaano NG, Tominaga T, Iwakami S (2022) Thiobencarb resistance mechanism is distinct from CYP81A-based cross-resistance in late watergrass (Echinochloa phyllopogon). Weed Sci 70(2):160–166. https://doi.org/10.1017/wsc.2022.4
Dimaano NG, Yamaguchi T, Fukunishi K, Tominaga T, Iwakami S (2020) Functional characterization of cytochrome P450 CYP81A subfamily to disclose the pattern of cross-resistance in Echinochloa phyllopogon. Plant Mol Biol 102:403–416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-019-00954-3
Dong L, Gao Y, Fang J, Chen G (2018) Research progress on the herbicide-resistance of weeds in rice fields in China. Plant Prot 44(5):69–75. https://doi.org/10.16688/j.zwbh.2018250. (in Chinese)
Estévez IH, Hernández MR (2020) Plant glutathione S-transferases: an overview. Plant Gene 23:100233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plgene.2020.100233
Fang J, Liu T, Zhang Y, Li J, Dong L (2019a) Target site-based penoxsulam resistance in barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crus-galli) from China. Weed Sci 67:281–287. https://doi.org/10.1017/wsc.2019.5
Fang J, Yang D, Zhao Z, Chen J, Dong L (2022) A novel phe-206-Leu mutation in acetolactate synthase confers resistance to penoxsulam in barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crus-galli (L.) P. Beauv). Pest Manag Sci 78(6):2560–2570. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.6887
Fang J, Zhang Y, Liu T, Yan B, Li J, Dong L (2019b) Target-site and metabolic resistance mechanisms to penoxsulam in Barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crus-galli (L.) P. Beauv). J Agric Food Chem 67:8085–8095. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b01641
Gaines TA, Duke SO, Morran S, Rigon CAG, Tranel PJ, Kupper A, Dayan FE (2020) Mechanisms of evolved herbicide resistance. J Biol Chem 295(30):10307–10330. https://doi.org/10.1006/pest.2000.2511
Georgakis N, Poudel N, Papageorgiou AC, Labrou NE (2020) Comparative structural and functional analysis of Phi class glutathione transferases involved in multiple-herbicide resistance of grass weeds and crops. Plant Physiol Biochem 149:266–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.02.012
Gion K, Inui H, Takakuma K, Yamada T, Kambara Y, Nakai S, Fujiwara H, Miyamura T, Imaishi H, Ohkawa H (2014) Molecular mechanisms of herbicide-inducible gene expression of tobacco CYP71AH11 metabolizing the herbicide chlorotoluron. Pestic Biochem Physiol 108:49–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2013.12.003
Guo W, Feng L, Zhang C, Zhang T, Wu D, Tian X (2020) Resistance of barnyard grass Echinochloa crus-galli to penoxsulam in rice fields in Guangdong Province. J Plant Prot 47:1131–1138. https://doi.org/10.13802/j.cnki.zwbhxb.2020.2019190. (in Chinese)
Han H, Yu Q, Beffa R, Gonzalez S, Maiwald F, Wang J, Powles SB (2021) Cytochrome P450 CYP81A10v7 in Lolium rigidum confers metabolic resistance to herbicides across at least five modes of action. Plant J 105(1):79–92. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.15040
Haywood J, Vadlamani G, Stubbs KA, Mylne JS (2021) Antibiotic resistance lessons for the herbicide resistance crisis. Pest Manag Sci 77(9):3807–3814. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.6357
He H, Wang H, Fang C, Lin Z, Yu Z, Lin W (2012) Separation of allelopathy from resource competition using rice/barnyardgrass mixed-cultures. PLoS ONE 7(5):e37201. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0037201
Iwakami S, Uchino A, Kataoka Y, Shibaike H, Watanabe H, Inamura T (2014a) Cytochrome P450 genes induced by bispyribac-sodium treatment in a multiple-herbicide-resistant biotype of Echinochloa phyllopogon. Pest Manag Sci 70(4):549–558. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.3572
Iwakami S, Endo M, Saika H, Okuno J, Nakamura N, Yokoyama M, Watanabe H, Toki S, Uchino A, Inamura T (2014b) Cytochrome P450 CYP81A12 and CYP81A21 are associated with resistance to two acetolactate synthase inhibitors in Echinochloa phyllopogon. Plant Physiol 116:618–629. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.113.232843
Jing W, Fu H, Lu Y, Zhu L, Mao H, Wu K, Yang X (2005) Effect of penoxsulam on weed control in paddy field. Weed Sci (01):36–37. https://doi.org/10.19588/j.issn.1003-935x.2005.01.016. (in Chinese)
Jugulam M, Shyam C (2019) Non-target-site resistance to herbicides recent developments. Plants 8(10):417. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8100417
Labrou NE, Papageorgiou AC, Pavli O, Flemetakis E (2015) Plant GSTome: structure and functional role in xenome network and plant stress response. Curr Opin Biotech 32:186–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2014.12.024
Li X (2018) Main problems and management strategies of weeds in agricultural fields in China in recent years. Plant Prot 44(5):77–84. https://doi.org/10.16688/j.zwbh.2018322protec. (in Chinese)
Li B, Dewey CN (2011) RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics 12:323. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-12-323
Ma G, Bai L, Liu D, Liu X, Tang T, Peng Y (2014) Control of herbicide resistant Echinochloa crusgalli indirect-seed rice crops. Acta Pratacul Sin 23:259–265. https://doi.org/10.11686/cyxb20140631. (in Chinese)
Ma G, Liu D, Peng Y, Zhang S, Li X, Li S, Liu X, Bo L (2021) Resistance detection of field populations of Echinochloa spp. to penoxsulam. Chin J Pestic Sci 23:905–914. https://doi.org/10.16801/j.issn.1008-7303.2021.0127. (in Chinese)
Murphy BP, Tranel PJ (2019) Target-site mutations conferring herbicide resistance. Plants 8(10):382. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8100382
Nakka S, Godar AS, Thompson CR, Peterson DE, Jugulam M (2017) Rapid detoxification via glutathione S-transferase (GST) conjugation confers a high level of atrazine resistance in Plamer Amaranth (Amaranthus palemeri). Pest Manag Sci 73:2236–2243. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.4615
Ohkawa H, Inui H (2015) Metabolism of agrochemicals and related environmental chemicals based on cytochrome P450s in mammals and plants. Pest Manag Sci 71:824–828. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.3871
Pan L, Guo Q, Wang J, Shi L, Yang X, Zhou Y, Yu Q, Bai L (2022) CYP81A68 confers metabolic resistance to ALS and ACCase-inhibiting herbicides and its epigenetic regulation in Echinochloa crus-galli. J Hazard Mater 428:128225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128225
Pan L, Yu Q, Han H, Mao L, Nyporko A, Fan L, Bai L, Powles SB (2019) Aldo-keto reductase metabolizes glyphosate and confers glyphosate resistance in Echinochloa colona. Plant Physiol 181(4):1519–1534. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.19.00979
Pan L, Yu Q, Wang J, Han H, Mao L, Nyporko A, Maguza A, Fan L, Bai L, Powles SB (2021) An ABCC-type transporter endowing glyphosate resistance in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci 118(16):e2100136118. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2100136118
Pan G, Zhang X, Liu K, Zhang J, Wu X, Zhu J, Tu J (2006) Map-based cloning of a novel rice cytochrome P450 gene CYP81A6 that confers resistance to two different classes of herbicides. Plant Mol Biol 61:933–943. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-006-0058-z
Pandian BA, Sathishraj R, Djanaguiraman M, Prasad PVV, Jugulam M (2020) Role of cytochrome p450 enzymes in plant stress response. Antioxidants 9:454. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9050454
Panozzo S, Mascanzoni E, Scarabel L, Milani A, Dalazen G, Merotto AJ, Tranel PJ, Sattin M (2021) Target-site mutations and expression of ALS gene copies vary according to Echinochloa species. Genes 12(11):1841. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12111841
Panozzo S, Scarabel L, Rosan V, Sattin M (2017) A new Ala-122-Asn amino acid change confers decreased fitness to ALS-resistant Echinochloa crus-galli. Front Plant Sci 8:2042. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.02042
Powles SB, Yu Q (2010) Evolution in action: plants resistant to herbicides. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:317–347. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-042809-112119
Preston C, Powles SB (1998) Amitrole inhibits diclofop metabolism and synergises diclofop-methyl in a diclofop-methyl-resistant biotype of Lolium rigidum. Pestic Biochem Physiol 62:179–189. https://doi.org/10.1006/pest.1998.2382
Saika H, Horita J, Taguchi-Shiobara F, Nonaka S, Nishizawa-Yokoi A, Iwakami S, Hori K, Matsumoto T, Tanaka T, Itoh T, Yano M, Kaku K, Shimizu T, Toki S (2014) A novel rice cytochrome P450 gene, CYP73A31, confers tolerance to acetolactate synthase-inhibiting herbicides in rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 166:1232–1240. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.113.231266
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.73
Seefeldt S, Jensen J, Fuerst E (1995) Log-logistic analysis of herbicide dose response relationship. Weed Technol 9:218–227. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0890037X00023253
Thyssen GN, Naoumkina M, McCarty JC, Jenkins JN, Florane C, Li P, Fang DD (2018) The P450 gene CYP749A16 is required for tolerance to the sulfonylurea herbicide trifloxysulfuron sodium in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L). BMC Plant Biol 18:186. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1414-2
Wang M, Liu B, Li Y, Luo X, Li L (2019) Non-target site based resistance to the ALS-inhibiting herbicide mesosulfuron-methyl in American sloughgrass (Beckmannia syzigachne). Weed Sci 67:527–533. https://doi.org/10.1017/wsc.2019.22
Yang Q, Yang X, Zhang Z, Wang J, Fu W, Li Y (2021) Investigating the resistance levels and mechanisms to penoxsulam and cyhalofop-butyl in barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crus-galli) from Ningxia Province China. Weed Sci 69(4):422–429. https://doi.org/10.1017/wsc.2021.37
Ye C, Wu D, Mao L, Jia L, Qiu J, Lao S, Chen M, Jiang B, Tang W, Peng Q et al (2020) The genomes of the allohexaploid Echinochloa crus-galli and its progenitors provide insights into polyploidization-driven adaptation. Mol Plant 13(9):1298–1310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2020.07.001
Yu Q, Friesen L, Zhang X, Powles SB (2004) Tolerance to acetolactate synthase and acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase inhibiting herbicides in Vulpia bromoides is conferred by two co-existing resistance mechanisms. Pestic Biochem Physiol 78:21–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2003.07.004
Yu X, Ge L, Liu L, Li Y (2010) Resistance of barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crus-galli) to multiple herbicides in direct-seeded rice. Jiangsu J Agri Sci 26:1438–1440. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2010.06.060. (in Chinese)
Zia Ul Haq M, Zhang Z, Wei J, Qiang S (2020) Ethylene biosynthesis inhibition combined with cyanide degradation confer resistance to quinclorac in Echinochloa crus-galli var. mitis. Int J Mol Sci 21:1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051573
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Key R&D Program of Shandong Province [2021CXGC010811], Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundations, China [ZR2020QC136], Postgraduate Innovation Program and Undergraduate Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program Project of Qingdao Agricultural University. The authors thank Instrumental Analysis Center of QAU for their assistance in conducting this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lingxu Li, Qinghao Lyu, and Jiang Bo designed this research and wrote the manuscripts. Shuang Bai revised the manuscript. Qinghao Lyu, Jiang Bo, Pengfei He, Shuang Bai and Xiyu Sun performed the experiments. Jinling Liu and Lingxu Li analyzed the data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: M. Iqbal R. Khan.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lyu, Q., Jiang, B., He, P. et al. The non-target site resistance mechanism to Penoxsulam in Echinochloa crus-galli var. zelayensis. Plant Soil (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-024-06716-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-024-06716-5