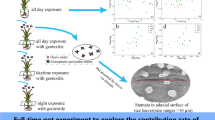
Abstract
Aims
Atmospheric trace metal deposition is an important source in agricultural soils and crops, but a large knowledge gap exists between foliar and root uptake of wet/dry deposition. We aim to distinguish the contribution of dry and wet-deposited trace metals to rice plant via foliar and root uptake and to investigate their accumulations during the full growth season.
Methods
We performed an atmospheric exposure experiment using customized open top chambers (OTCs) to distinguish the impacts of wet and dry deposition contribution to foliar and root uptake and their mobility in soils. The foliar uptake and then translocation was hypothesized the major pathway of trace metal accumulation in rice grains.
Results
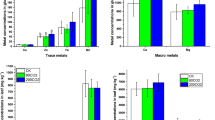
Foliar uptake of wet- and dry-deposited Cu, Zn, and Pb played an important role in their accumulations in rice plant, contributing to 44–47%, 23–25%, and 35–37% in rice grains, respectively. The leaf Cu, Zn, and Pb accumulated from atmospheric deposition can be transported upward to rice grains but nodes seem to restrict them downward translocation. Rice leaves cannot directly take up atmospheric As and the deposited As can only accumulate in rice through the root uptake. The trace metals showed high mobility in atmospheric deposition, which significantly increase the bioavailable trace metal fractions in surface soils and soil solutions.
Conclusions
This study provides a new insight of similar or even higher contributions of foliar uptake than root uptake of trace metals from atmospheric deposition and that reducing the accumulation of atmospheric trace metals due to deposition on leaves can effectively decrease the accumulation of trace metals in crops.
Graphic abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Aarkrog A, Lippert J (1971) Direct contamination of barley with Cr-51, Fe-59, Co-58, Zn-65, Hg-203 and Pb-210. Radiation Bot 11:463. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0033-7560(71)91125-2
Belon E, Boisson M, Deportes IZ, Eglin TK, Feix I, Bispo AO, Galsomies L, Leblond S, Guellier CR (2012) An inventory of trace elements inputs to french agricultural soils. Sci Total Environ 439:87–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.09.011
Cao X, Tan C, Wu L, Luo Y, He Q, Liang Y, Peng B, Christie P (2020) Atmospheric deposition of cadmium in an urbanized region and the effect of simulated wet precipitation on the uptake performance of rice. Sci Total Environ 700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134513
Chabbi I, Bahloul M, Dammak R, Baati H, Azri C (2020) Wet deposition of major ions and trace elements in rural and coastal-urban sites in Monastir Region, Eastern Tunisia. Arab J Geosci 13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-5014-8
Chen Y, Moore KL, Miller AJ, McGrath SP, Ma JF, Zhao F-J (2015) The role of nodes in arsenic storage and distribution in rice. J Exp Bot 66:3717–3724. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv164
Cheng K, Wang Y, Tian H, Gao X, Zhang Y, Wu X, Zhu C, Gao J (2015) Atmospheric emission characteristics and control policies of five precedent-controlled toxic heavy metals from anthropogenic sources in China. Environ Sci Technol 49:1206–1214. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5037332
Colle C, Madoz-Escande C, Leclerc E (2009) Foliar transfer into the biosphere: review of translocation factors to cereal grains. J Environ Radioact 100:683–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2008.10.002
De Temmerman L, Waegeneers N, Ruttens A, Vandermeiren K (2015) Accumulation of atmospheric deposition of as, cd and pb by bush bean plants. Environ Pollut 199:83–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.01.014
Desboeufs K, Nguyen EB, Chevaillier S, Triquet S, Dulac F (2018) Fluxes and sources of nutrient and trace metal atmospheric deposition in the northwestern Mediterranean. Atmos Chem Phys 18:14477–14492. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-18-14477-2018
Faizan M, Sehar S, Rajput VD, Faraz A, Afzal S, Minkina T, Sushkova S, Adil MF, Yu F, Alatar AA, Akhter F, Faisal M (2021) Modulation of cellular redox status and antioxidant defense system after synergistic application of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Salicylic Acid in Rice (Oryza sativa) plant under Arsenic stress. Plants-Basel 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10112254
Heagle AS, Body DE, Heck WW (1973) An open-top field chamber to assess the impact of air pollution on plants. J Environ Qual 2(3):365–368. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1973.00472425000200030014x
Ho MD, Evans GJ (2000) Sequential extraction of metal contaminated soils with radiochemical assessment of readsorption effects. Environ Sci Technol 34:1030–1035. https://doi.org/10.1021/es981251z
Hou Q, Yang Z, Ji J, Yu T, Chen G, Li J, Xia X, Zhang M, Yuan X (2014) Annual net input fluxes of heavy metals of the agro-ecosystem in the Yangtze River delta, China. J Geochem Explor 139:68–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.08.007
Hu Y, Zhou J, Du B, Liu H, Zhang W, Liang J, Zhang W, You L, Zhou J (2019) Health risks to local residents from the exposure of heavy metals around the largest copper smelter in China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 171:329–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.12.073
Huang H, Ji X-B, Cheng L-Y, Zhao F-J, Wang P (2021) Free radicals produced from the oxidation of ferrous sulfides promote the remobilization of cadmium in paddy soils during drainage. Environ Sci Technol 55:9845–9853. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c00576
Huang B-Y, Zhao F-J, Wang P (2022a) The relative contributions of root uptake and remobilization to the loading of cd and as into rice grains: implications in simultaneously controlling grain cd and as accumulation using a segmented water management strategy*. Environ Pollut 293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118497
Huang S, Yamaji N, Ma FJ (2022b) Zinc transport in rice: how to balance optimal plant requirements and human nutrition. J Exp Bot 73:1800–1808. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erab478
Isinkaralar K (2022a) Atmospheric deposition of pb and cd in the Cedrus atlantica for environmental biomonitoring. Landscape Ecol Eng 18:341–350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11355-022-00503-z
Isinkaralar K (2022b) The large-scale period of atmospheric trace metal deposition to urban landscape trees as a biomonitor. Biomass Convers Biorefin. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-02796-4
Isinkaralar K (2022c) Temporal variability of Trace Metal evidence in Cupressus arizonica, Platanus orientalis, and Robinia pseudoacacia as Pollution-Resistant species at an Industrial Site. Water Air Soil Pollut 233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05743-1
Isinkaralar K, Isinkaralar O, Koc I, Ozel HB, Sevik H (2023) Assessing the possibility of airborne bismuth accumulation and spatial distribution in an urban area by tree bark: a case study in Duzce, Turkiye. Biomass Convers Biorefin. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-023-04399-z
Jiang M, Jiang J, Li S, Li M, Tan Y, Song S, Shu Q, Huang J (2020) Glutamate alleviates cadmium toxicity in rice via suppressing cadmium uptake and translocation. J Hazard Mater 384:121319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121319
Kachenko AG, Graefe M, Singh B, Heald SM (2010) Arsenic speciation in tissues of the Hyperaccumulator P. calomelanos var. Austroamericana using X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Environ Sci Technol 44:4735–4740. https://doi.org/10.1021/es1005237
Kaur R, Das S, Bansal S, Singh G, Sardar S, Dhar H, Ram H (2021) Heavy metal stress in rice: uptake, transport, signaling, and tolerance mechanisms. Physiol Plant 173:430–448. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.13491
Kubo K, Kobayashi H, Fujita M, Ota T, Minamiyama Y, Watanabe Y, Nakajima T, Shinano T (2016) Varietal differences in the absorption and partitioning of cadmium in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L). Environ Exp Bot 124:79–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2015.12.007
Larue C, Castillo-Michel H, Sobanska S, Trcera N, Sorieul S, Cecillon L, Ouerdane L, Legros S, Sarret G (2014) Fate of pristine TiO2 nanoparticles and aged paint-containing TiO2 nanoparticles in lettuce crop after foliar exposure. J Hazard Mater 273:17–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.03.014
Lei GJ, Yamaji N, Ma JF (2021) Two metallothionein genes highly expressed in rice nodes are involved in distribution of Zn to the grain. New Phytol 229:1007–1020. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.16860
Li L, Zhang Y, Ippolito JA, Xing W, Qiu K, Wang Y (2020) Cadmium foliar application affects wheat cd, Cu, Pb and Zn accumulation. Environ Pollut 262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114329
Liu H-L, Zhou J, Li M, Hu Y-m, Liu X, Zhou J (2019) Study of the bioavailability of heavy metals from atmospheric deposition on it the soil-pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) system. J Hazard Mater 362:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.09.032
Liu H-L, Zhou J, Li M, Obrist D, Wang X-Z, Zhou J (2021) Chemical speciation of trace metals in atmospheric deposition and impacts on soil geochemistry and vegetable bioaccumulation near a large copper smelter in China. J Hazard Mater 413:125346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125346
Liu H, Zhou J, Li M, Xia R, Wang X, Zhou J (2022) Dynamic behaviors of newly deposited atmospheric heavy metals in the soil-pak choi system. Environ Sci Technol 56:12734–12744. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.2c04062
Luo X, Bing H, Luo Z, Wang Y, Jin L (2019) Impacts of atmospheric particulate matter pollution on environmental biogeochemistry of trace metals in soil-plant system: a review. Environ Pollut 255:113138
Luster J, Goettlein A, Nowack B, Sarret G (2009) Sampling, defining, characterising and modeling the rhizosphere-the soil science tool box. Plant Soil 321:457–482. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9781-3
Meharg AA, Meharg C (2021) The Pedosphere as a Sink, source, and record of anthropogenic and natural Arsenic Atmospheric Deposition. Environ Sci Technol 55:7757–7769. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c00460
Morselli L, Olivieri P, Brusori B, Passarini F (2003) Soluble and insoluble fractions of heavy metals in wet and dry atmospheric depositions in Bologna, Italy. Environ Pollut 124:457–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0269-7491(03)00013-7
Nair R, Varghese SH, Nair BG, Maekawa T, Yoshida Y, Kumar DS (2010) Nanoparticulate material delivery to plants. Plant Sci 179:154–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2010.04.012
Penezic A, Milinkovic A, Alempijevic SB, Zuzul S, Frka S (2021) Atmospheric deposition of biologically relevant trace metals in the eastern Adriatic coastal area. Chemosphere 283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131178
Rai PK, Lee SS, Zhang M, Tsang YF, Kim K-H (2019) Heavy metals in food crops: Health risks, fate, mechanisms, and management. Environ Int 125:365–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.01.067
Reid RJ, Dunbar KR, McLaughlin MJ (2003) Cadmium loading into potato tubers: the roles of the periderm, xylem and phloem. Plant, Cell Environ 26:201–206. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3040.2003.00945.x
Sabin LD, Lim JH, Stolzenbach KD, Schiff KC (2005) Contribution of trace metals from atmospheric deposition to stormwater runoff in a small impervious urban catchment. Water Res 39:3929–3937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2005.07.003
Sanchez-Lopez AS, Carrillo-Gonzalez R, del Carmen Angeles Gonzalez-Chavez M, Hanako Rosas-Saito G, Vangronsveld J (2015) Phytobarriers: plants capture particles containing potentially toxic elements originating from mine tailings in semiarid regions. Environ Pollut 205:33–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.05.010
Schreck E, Dappe V, Sarret G, Sobanska S, Nowak D, Nowak J, Stefaniak EA, Magnin V, Ranieri V, Dumat C (2014) Foliar or root exposures to smelter particles: consequences for lead compartmentalization and speciation in plant leaves. Sci Total Environ 476:667–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.12.089
Shahid M, Dumat C, Khalid S, Niazi NK, Antunes PMC (2017a) Cadmium bioavailability, uptake, toxicity and detoxification in soil-plant system. In: DeVoogt P (ed) Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 241:73–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46945-4
Shahid M, Dumat C, Khalid S, Schreck E, Xiong T, Niazi NK (2017b) Foliar heavy metal uptake, toxicity and detoxification in plants: a comparison of foliar and root metal uptake. J Hazard Mater 325:36–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.11.063
Shahid M, Natasha, Dumat C, Niazi NK, Xiong TT, Farooq ABU, Khalid S (2021) Ecotoxicology of heavy metal(loid)-enriched particulate matter: foliar accumulation by plants and health impacts. In: DeVoogt P (ed) Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 253:65–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-52541-5
Shi T, Ma J, Wu F, Ju T, Gong Y, Zhang Y, Wu X, Hou H, Zhao L, Shi H (2019) Mass balance-based inventory of heavy metals inputs to and outputs from agricultural soils in Zhejiang Province, China. Sci Total Environ 649:1269–1280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.414
Srivastava D, Xu J, Vu TV, Liu D, Li L, Fu P, Hou S, Moreno Palmerola N, Shi Z, Harrison RM (2021) Insight into PM2.5 sources by applying positive matrix factorization (PMF) at urban and rural sites of Beijing. Atmos Chem Phys 21:14703–14724. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-21-14703-2021
Tapia-Gatica J, Gonzalez-Miranda I, Salgado E, Bravo MA, Tessini C, Dovletyarova EA, Paltseva AA, Neaman A (2020) Advanced determination of the spatial gradient of human health risk and ecological risk from exposure to as, Cu, Pb, and Zn in soils near the Ventanas Industrial Complex (Puchuncavi, Chile). Environ Pollut 258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113488
Uchimiya M, Bannon D, Nakanishi H, McBride MB, Williams MA, Yoshihara T (2020) Chemical Speciation, Plant Uptake, and toxicity of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils. J Agric Food Chem 68:12856–12869. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c00183
Uzu G, Sobanska S, Sarret G, Munoz M, Dumat C (2010) Foliar lead uptake by Lettuce exposed to Atmospheric Fallouts. Environ Sci Technol 44:1036–1042. https://doi.org/10.1021/es902190u
Wang H-Y, Wen S-L, Chen P, Zhang L, Cen K, Sun G-X (2016) Mitigation of cadmium and arsenic in rice grain by applying different silicon fertilizers in contaminated fields. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:3781–3788. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5638-5
Werkenthin M, Kluge B, Wessolek G (2014) Metals in european roadside soils and soil solution - A review. Environ Pollut 189:98–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2014.02.025
Wiggenhauser M, Bigalke M, Imseng M, Keller A, Archer C, Wilcke W, Frossard E (2018) Zinc isotope fractionation during grain filling of wheat and a comparison of zinc and cadmium isotope ratios in identical soil-plant systems. New Phytol 219:195–205. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15146
Xia R, Zhou J, Cui H, Liang J, Liu Q, Zhou J (2022) Nodes play a major role in cadmium (cd) storage and redistribution in low-Cd-accumulating rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars. Sci Total Environ 160436–160436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160436
Xiang M, Li Y, Yang J, Lei K, Li Y, Li F, Zheng D, Fang X, Cao Y (2021) Heavy metal contamination risk assessment and correlation analysis of heavy metal contents in soil and crops*. Environ Pollut 278:116911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116911
Xiaosan L, Long C, Xiuzhen H, Lianzhen L, Dongmei Z (2007) In-situ aampling of soil solution and determination of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) with UV absorption method (UVA_(254)). Soils 39:943–947
Xie L, Hao P, Cheng Y, Ahmed IM, Cao F (2018) Effect of combined application of lead, cadmium, chromium and copper on grain, leaf and stem heavy metal contents at different growth stages in rice. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 162:71–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.06.072
Xiong T, Zhang T, Dumat C, Sobanska S, Dappe V, Shahid M, Xian Y, Li X, Li S (2019) Airborne foliar transfer of particular metals in Lactuca sativa L.: translocation, phytotoxicity, and bioaccessibility. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:20064–20078. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3084-x
Xu Z, Zhu Z, Zhao Y, Huang Z, Fei J, Han Y, Wang M, Yu P, Peng J, Huang Y, Fahmy AE (2022) Foliar uptake, accumulation, and distribution of cadmium in rice (Oryza sativa L.) at different stages in wet deposition conditions. Environ Pollut 306:119390–119390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119390. (Barking, Essex: 1987)
Yamaji N, Xia J, Mitani-Ueno N, Yokosho K, Ma JF (2013) Preferential delivery of zinc to developing tissues in Rice is mediated by P-Type heavy metal ATPase OsHMA2. Plant Physiol 162:927–939. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.113.216564
Yan B-F, Nguyen C, Pokrovsky OS, Candaudap F, Coriou C, Bussiere S, Robert T, Cornu JY (2018) Contribution of remobilization to the loading of cadmium in durum wheat grains: impact of post-anthesis nitrogen supply. Plant Soil 424:591–606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3560-6
Yang J-Y, Sun M-Q, Chen Z-L, Xiao Y-T, Wei H, Zhang J-Q, Huang L, Zou Q (2022) Effect of foliage applied chitosan-based silicon nanoparticles on arsenic uptake and translocation in rice (Oryza sativa L). J Hazard Mater 433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128781
Yang X, Wang C, Huang Y, Liu B, Liu Z, Huang Y, Cheng L, Huang Y, Zhang C (2021) Foliar application of the sulfhydryl compound 2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid inhibits cadmium, lead, and arsenic accumulation in rice grains by promoting heavy metal immobilization in flag leaves. Environ Pollut 285:117355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117355
Yi K, Fan W, Chen J, Jiang S, Huang S, Peng L, Zeng Q, Luo S (2018) Annual input and output fluxes of heavy metals to paddy fields in four types of contaminated areas in Hunan Province, China. Sci Total Environ 634:67–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.294
Yu M, Yao J, Liang J, Zeng Z, Cui B, Zhao X, Sun C, Wang Y, Liu G, Cui H (2017) Development of functionalized abamectin poly(lactic acid) nanoparticles with regulatable adhesion to enhance foliar retention. RSC Adv 7:11271–11280. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra27345a
Zhang C, Lu W, Yang Y, Shen Z, Ma JF, Zheng L (2018a) OsYSL16 is required for preferential Cu distribution to Floral Organs in Rice. Plant Cell Physiol 59:2039–2051. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcy124
Zhang Y, Chen K, Zhao F-J, Sun C, Jin C, Shi Y, Sun Y, Li Y, Yang M, Jing X, Luo J, Lian X (2018b) OsATX1 interacts with Heavy Metal P1B-Type ATPases and affects copper transport and distribution. Plant Physiol 178:329–344. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.18.00425
Zhang S, Geng L, Fan L, Zhang M, Zhao Q, Xue P, Liu W (2020) Spraying silicon to decrease inorganic arsenic accumulation in rice grain from arsenic-contaminated paddy soil. Sci Total Environ 704:135239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135239
Zheng L, Yamaji N, Yokosho K, Ma JF (2012) YSL16 is a phloem-localized transporter of the copper-nicotianamine complex that is responsible for copper distribution in Rice. Plant Cell 24:3767–3782. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.103820
Zhong C, Yang Z, Jiang W, Hu B, Hou Q, Yu T, Li J (2016) Ecological geochemical assessment and source identification of trace elements in atmospheric deposition of an emerging industrial area: Beibu Gulf economic zone. Sci Total Environ 573:1519–1526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.08.057
Zhou J, Du B, Liu H, Cui H, Zhang W, Fan X, Cui J, Zhou J (2020) The bioavailability and contribution of the newly deposited heavy metals (copper and lead) from atmosphere to rice (Oryza sativa L). J Hazard Mater 384:121285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121285
Zhou J, Liang J, Hu Y, Zhang W, Liu H, You L, Zhang W, Gao M, Zhou J (2018) Exposure risk of local residents to copper near the largest flash copper smelter in China. Sci Total Environ 630:453–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.211
Zhou J, Zhang C, Du B, Cui H, Fan X, Zhou D, Zhou J (2021) Soil and foliar applications of silicon and selenium effects on cadmium accumulation and plant growth by modulation of antioxidant system and cd translocation: comparison of soft vs. durum wheat varieties. J Hazard Mater 402:123546
Zhu Z, Xu Z, Peng J, Fei J, Yu P, Wang M, Tan Y, Huang Y, Zhran M, Fahmy A (2022) The contribution of atmospheric deposition of cadmium and lead to their accumulation in rice grains. Plant Soil 477:373–387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-022-05429-x
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by Key Scientific Research and Development Projects of Jiangxi Provence (20194ABC28010) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (42177234). We are also acknowledged Mei-Xiang Qiu, Xiao-Hui Zhang, and Man-Ju Zhu for the help in filed management in the experimental site.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. The writing and overall conceptualization were performed by Ruizhi Xia and Jun Zhou. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Ruizhi Xia, Yazhu Mi and Kaixin Hu. Hongbiao Cui, Hailong Liu, Jing Zhou commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Jun Zhou designed the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
All authors have no financial interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Jian Feng Ma.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 12.4 MB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, R., Zhou, J., Mi, Y. et al. Chemical fractions of trace metals in atmospheric wet and dry deposition and contribution to rice root and foliar uptake. Plant Soil 494, 285–299 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-023-06274-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-023-06274-2