Abstract
Aims
Although the influences of coastal embankments on soil physicochemical properties and carbon (C) and nitrogen (N) cycling have been widely reported, the mechanisms of their effects on soil microbial ecologies remain poorly understood. Thus, the aim of this study was to investigate the variations in the diversity and composition of soil bacterial and archaeal communities between natural and embanked saltmarshes, as well as the determinants that drive these variations.
Methods
16S rRNA gene sequence analysis was performed to assess the impacts of coastal embankments on the bacterial and archaeal communities of native Suaeda salsa, Phragmites australis, and invasive Spartina alterniflora saltmarshes on the east coast of China.
Results
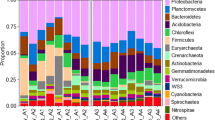
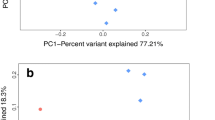
Embankments were found to significantly decrease the microbial diversity of S. alterniflora salt marsh, while increased the OTU richness of P. australis salt marsh. Embankments modified the compositions of soil bacterial and archaeal communities in both S. alterniflora and P. australis salt marshes. However, variations in the microbial diversity, richness, and community compositions between the native and embanked S. salsa salt marshes were insignificant.
Conclusions
These results were possibly because the embankment significantly altered soil nutrient substrate levels (e.g., soil organic C and N) by variations in plant residues and soil physiochemical properties in S. alterniflora and P. australis saltmarshes, whereas the embankment had no observable changes in the soil nutrient substrate and plant residue in S. salsa saltmarsh. This study also elucidated the effects of coastal embankments on biogeochemical cycles, and highlighted their potential hazards to ecosystems.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- ANOVA :
-
Analysis of variance
- ANOSIM :
-
Analysis of similarities
- C :
-
Carbon
- C/N :
-
Carbon: Nitrogen ratio
- DNA :
-
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- EPA :
-
Embanked Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin. ex Steud.
- ESA :
-
Embanked Spartina alterniflora Loisel.
- ESS :
-
Embanked Suaeda salsa (Linn.) Pall.
- LDA :
-
Linear discriminant analysis
- LEfSe :
-
Linear discriminant analysis effect size
- N :
-
Nitrogen
- NMDS :
-
Nonmetric multidimensional scaling
- OTUs :
-
Operational taxonomic units
- PCoA :
-
Principal coordinates analysis
- PSB :
-
Photosynthetic bacteria
- QIIME :
-
Quantitative insights into microbial ecology
- qPCR :
-
Quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- RDA:
-
Redundancy analysis
- RMSEA:
-
Root-mean-square error of approximation
- RNA :
-
Ribonucleic acid
- SEM :
-
Structural equation modelling
- SLOC:
-
Soil labile organic carbon
- SLON :
-
Soil labile organic nitrogen
- SOC :
-
Soil organic carbon
- SON :
-
Soil organic nitrogen
- SROC :
-
Soil recalcitrant organic carbon
- SRON :
-
Soil recalcitrant organic nitrogen
- UPA :
-
Unembanked Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin. ex Steud.
- USA :
-
Unembanked Spartina alterniflora Loisel.
- USS :
-
Unembanked Suaeda salsa (Linn.) Pall.
- WSOC :
-
Water-soluble organic carbon
- WSON :
-
Water-soluble organic nitrogen
References
Acosta-González A, Rossellό-Mόra R, Marqués S (2013) Characterization of the anaerobic microbial community in oil-polluted subtidal sediments: aromatic biodegradation potential after the Prestige oil spill. Environ Microbiol 15:77–92
An SQ, Gu BH, Zhou CF, Wang ZS, Deng ZF, Zhi YB, Li HL, Chen L, Yu DH, Liu YH (2007) Spartina invasion in China: implications for invasive species management and future research. Weed Res 47:183–191
Angel R, Soars MI, Ungar ED, Gillor O (2010) Biogeography of soil archaea and bacteria along a steep precipitation gradient. ISME J 4:553–563
Bai J, Xiao R, Zhang K, Gao H, Cui B, Liu X (2013) Soil organic carbon as affected by land use in young and old reclaimed regions of a coastal estuary wetland, China. Soil Use Manage 29:57–64
Bainard LD, Hamel C, Gan YT (2016) Edaphic properties override the influence of crops on the composition of the soil bacterial community in a semiarid agroecosystem. Appl Soil Ecol 105:160–168
Baña Z, Abad N, Uranga A, Azúa I, Artolozaga I, Unanue M, Iriberri J, Arrieta JM, Ayo B (2020) Recurrent seasonal changes in bacterial growth efficiency, metabolism and community composition in coastal waters. Environ Microbiol 22:369–380
Bates ST, Berg-Lyons DB, Caporaso JG, Walters WA, Knight R, Fierer N (2011) Examining the global distribution of dominant archaeal populations in soil. ISME J 5:908–917
Bayer-Santos E, Ceseti LD, Farah CS, Alvarez-Martinez CE (2019) Distribution, function and regulation of type 6 secretion systems of Xanthomonadales. Frontiers Microbiol 10:1635
Belay-Tedla A, Zhou XH, Su B, Wan SQ, Luo YQ (2009) Labile, recalcitrant, and microbial carbon and nitrogen pools of a tallgrass prairie soil in the US Great Plains subjected to experimental warming and clipping. Soil Biol Biochem 41:110–116
Bokulich NA, Subramanian S, Faith JJ, Gevers D, Gordon JI, Knight R, Mills DA, Caporaso JG (2013) Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat Methods 10:57–59
Boldea O, Magnus JR (2009) Maximum likelihood estimation of the multivariate normal mixture model. J Am Stat Assoc 104:1539–1549
Brotosudarmo THP, Limantara L, Heriyanto PMNU (2015) Adaptation of the photosynthetic unit of purple bacteria to changes of light illumination intensities. Procedia Chem 14:414–421
Bu NS, Qu JF, Li G, Zhao B, Zhang RJ, Fang CM (2015) Reclamation of coastal salt marshes promoted carbon loss form previously-sequestered soil carbon pool. Ecol Eng 81:335–339
Buckley D, Schmidt T (2002) Exploring the biodiversity of soil - a microbial rain forest. In: Staley J, Reysenbach A (eds) Biodiversity of microbial life. Wiley, New York, pp 183–208
Buttner D, Bonas U (2003) Common infection strategies of plant and animal pathogenic bacteria. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:312–319
Cabrera ML, Beare MH (1993) Alkaline persulfate oxidation for determining total nitrogen in microbial biomass extracts. Soil Sci Soc Am J 57:1007–1012
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Tumbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Chantigny MH (2003) Dissolved and water-extractable organic matter in soils: a review on the influence of land use and management practices. Geoderma 113:357–380
Chen L, Deng Z, An SQ, Zhao CJ, Zhou CF, Zhi YB (2007) Alternate irrigation of fresh and salt water restrains clonal growth and reproduction of Spartina alterniflora. J Plant Ecol 31:645–651
Chung CH, Zhuo RZ, Xu GW (2004) Creation of Spartina plantations for reclaiming Dongtai, China, tidal flats and offshore sands. Ecol Eng 23:135–150
Cleveland CC, Nemergut DR, Schmidt SK, Townsend AR (2007) Increases in soil respiration following labile carbon additions linked to rapid shifts in soil microbial community composition. Biogeochemistry 82:229–240
Cotrufo MF, Ranalli MG, Haddix ML (2019) Soil carbon storage informed by particulate and mineral-associated organic matter. Nat Geosci 12:989–994
Cui J, Liu C, Li ZL, Wang L, Chen XF, Ye ZZ, Fang CM (2012) Long-term changes in topsoil chemical properties under centuries of cultivation after reclamation of coastal wetlands in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Soil till Res 123:50–60
Cui L, Pan X, Li W, Zhang X, Liu G, Song YB, Yu FH, Prinzing A, Cornelissen JHC (2019) Phragmites australis meets Suaeda salsa on the “red beach”: effects of an ecosystem engineer on salt-marsh litter decomposition. Sci Total Environ 693:133477
Dai L, Liu C, Peng L, Song C, Li X, Tao L, Li G (2021) Different distribution patterns of microorganisms between aquaculture pond sediment and water. J Microbiol 59:376–388
Dangl JL, Jones JDG (2001) Plant pathogens and integrated defence responses to infection. Nature 411:826–833
DeCrappeo NM, DeLorenze EJ, Giguere AT, Pyke DA, Bottomley PJ (2017) Fungal and bacterial contributions to nitrogen cycling in cheatgrass-invaded and uninvaded native sagebrush soils of the western USA. Plant Soil 416:271–281
Dick TM, Osunkoya OO (2000) Influence of tidal restriction floodgates on decomposition of mangrove litter. Aquat Bot 68:273–280
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792–1797
Edgar RC (2013) UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods 10:996–998
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R (2011) UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27:2194–2200
Feng HY, Zhao H, Xia L, Yang W, Zhao YQ, Jeelani N, An SQ (2022) Nitrogen cycling in plant and soil subsystems is driven by changes in soil salinity following coastal embankment in typical coastal saltmarsh ecosystems of Eastern China. Ecol Eng 174:106467
Fierer N, Jackson RB (2006) The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities. P Natl Acad Sci USA 103:626–631
Fierer N, Jackson JA, Vilgalys R, Jackson RB (2005) Assessment of soil microbial community structure by use of taxon specific quantitative PCR assays. Appl Environ Microb 71:4117–4120
Fierer N, Bradford MA, Jackson RB (2007a) Toward an ecological classification of soil bacteria. Ecology 88:1354–1364
Fierer N, Breitbart M, Nulton J, Salamon P, Lozupone C, Jones R, Robeson M, Edwards RA, Felts B, Rayhawk S, Knight R, Rohwer F, Jackson RB (2007b) Metagenomic and small-subunit rRNA analyses reveal the genetic diversity of bacteria, archaea, fungi and viruses in soil. Appl Environ Microb 73:7059–7066
Figueroa D, Capo E, Lindh MV, Rowe OF, Paczkowska J, Pinhassi J, Andersson A (2021) Terrestrial dissolved organic matter inflow drives temporal dynamics of the bacterial community of a subarctic estuary (northern Baltic Sea). Environ Microbiol 23:4200–4213
Gao GF, Peng D, Zhang YH, Li YT, Fan KK, Tripathi BM, Adams JM, Chu HY (2020) Dramatic change of bacterial assembly process and co-occurrence pattern in Spartina alterniflora salt marsh along an inundation frequency gradient. Sci Total Environ 755:142546
Garrity GM, Bell JA, Lilburn T (2005) The revised road map to the manual. In: Brenner DJ, Krieg NR, Staley JT, Garrity GM (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 2, 2ndedn, The proteobacteria, Part A. Introductory essays. Springer, New York, p 169
Glazebrook J (2005) Contrasting mechanisms of defense against biotrophic and necrotrophic pathogens. Annu Rev Phytopathol 43:205–227
Gryta A, Frac M (2020) Methodological aspects of multiplex terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism-technique to describe the genetic diversity of soil bacteria, archaea and fungi. Sensors 20:3292
Guo HP, Jiao JJ (2007) Impact of coastal land reclamation on ground water level and the sea water interface. Ground Water 45:362–367
Guo XL, Zhou YB (2020) Effects of land use patterns on the bacterial community structure and diversity of wetland soil in the Sanjiang Plain. J Soil Sci Plant Nut 21:1–12
Haas BJ, Gevers D, Earl AM, Feldgarden M, Ward DV, Giannoukos G, Ciulla D, Tabbaa D, Highlander SK, Sodergren E, Methe B, DeSantis TZ, Petrosino JF, Knight R, Birren BW (2011) Chimeric 16S rRNA sequence formation and detection in Sanger and 454-pyrosequenced PCR amplicons. Genome Res 21:494–504
Han J, Dong Y, Zhang M (2021) Chemical fertilizer reduction with organic fertilizer effectively improve soil fertility and microbial community from newly cultivated land in the Loess Plateau of China. Appl Soil Ecol 165:103966
Hanada S (2014) The phylum Chloroflexi, the family Chloroflexaceae, and the related phototrophic families Oscillochloridaceae and Roseiflexaceae. In: Rosenberg E, DeLong EF, Lory S, Stackebrandt E, Thompson F (eds) The Prokaryotes, Other major lineages of bacteria and the archaea. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 515–529
He Q, Cui B, An Y (2012) Physical stress, not biotic interactions, preclude an invasive grass from establishing in forb-dominated salt marshes. PLoS ONE 7:e33164
Högberg MN, Högberg P, Myrold DD (2007) Is microbial community composition in boreal forest soils determined by pH, C-to-N ratio, the trees, or all three? Oecologia 150:590–601
Idi A, Nor MHM, Wahab MFA, Ibrahim Z (2014) Photosynthetic bacteria: an eco-friendly and cheap tool for bioremediation. Rev Environ Sci Bio 14:271–285
Imhoff JF (2005) Family I. Bavendamm. In: Brenner DJ, Krieg NR, Staley JT, Garrity GM (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 2, 2ndedn, The proteobacteria, Part B. The gammaproteobacteria. Springer, New York, p 3
Ji YF, Wu BL, Ding YH, Qin P (2011) Nutritional components of Phragmites australis and Spartina alterniflora in Dafeng free-range David’s Deer habitat of Jiangsu Province, East China: a comparative analysis. Chin J Ecol 30:2240–2244
Kim SJ, Kwon KK (2010) Bacteroidetes. In: Timmis KN (ed) Handbook of hydrocarbon and lipid microbiology, The Actinobacteria. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, p 1813
Kirchman DL (2002) The ecology of Cytophaga – Flavobacteria in aquatic environments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 39:91–100
Kuang SP, Dong ZW, Wang BC, Wang HH, Li JL, Shao HB (2021) Changes of sensitive microbial community in oil polluted soil in the coastal area in Shandong, China for ecorestoration. Ecotox Environ Safe 207:111551
Kuske CR, Ticknor LO, Miller ME, Dunbar JM, Davis JA, Barns SM, Belnap J (2002) Comparison of soil bacterial communities in rhizospheres of three plant species and the interspaces in an arid grassland. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1854–1863
Laudicina VA, Hurtado MD, Badalucco L, Delgado A, Palazzolo E, Panno M (2009) Soil chemical and biochemical properties of a salt-marsh alluvial Spanish area after long-term reclamation. Biol Fert Soil 45:691–700
Lee H, Heo YM, Kwon SL, Yoo Y, Lee AH, Kwon BO, Kim GH, Khim JS, Kim JJ (2020) Recovery of the benthic bacterial community in coastal abandoned saltern required over 35 years: a comparative case study in the Yellow Sea. Environ Int 135:105412
Li DL, Ding YQ, Yuan Y, Lloyd H, Zhang ZW (2014a) Female tidal mudflat crabs represent a critical food resource for migratory red-crowned cranes in the Yellow River Delta, China. Bird Conserv Int 24:416–428
Li ZJ, Wang WQ, Zhang YH (2014b) Recruitment and herbivory affect spread of invasive Spartina alterniflora in China. Ecology 95:1972–1980
Li XB, Kang YH, Wang XM (2019) Response of soil properties and vegetation to reclamation period using drip irrigation in coastal saline soils of the Bohai Gulf. Paddy Water Environ 17:803–812
Liao CZ, Luo YQ, Jiang LF, Zhou XH, Wu XW, Fang CM, Chen JQ, Li B (2007) Invasion of Spartina alterniflora enhanced ecosystem carbon and nitrogen stocks in the Yangtze estuary, China. Ecosystems 10:1351–1361
Liu MY (2018) Remote sensing analysis of Spartina alterniflora in the coastal areas of China during 1990 to 2015. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Northeast Institute of Geography and Agroecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Changchun
Liu CY, Jiang HX, Hou YQ, Zhang SQ, Su LY, Li XF, Pan X, Wen ZF (2010) Habitat changes for breeding waterbirds in Yancheng national reserve, China: a remote sensing study. Wetlands 30:879–888
Liu Q, Wu YH, Liao L, Zhang DS, Yuan YP, Wang Z, Wang CS, Xu XW (2018) Shift of bacterial community structures in sediments from the Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary to the East China Sea linked to environmental gradients. Geomicrobiol J 35:898–907
Lormieres F, Oger PM (2017) Epsilonproteobacteria dominate bacterial diversity at a natural tar seep. Curr Biol 340:238–243
Ma ZJ, Wang ZJ, Tang HX (1999) Habitat use and selection by Red-crowned Crane Grus japonensis in winter in Yancheng Biosphere Reserve, China. IBIS 141:135–139
Ma ZJ, Melville DS, Liu JG, Chen Y, Yang HY, Ren WW, Zhang ZW, Piersma T, Li B (2014) Ecosystems management rethinking China’s new great wall. Science 346:912–914
Ma TT, Li XW, Bai JH, Cui BS (2019) Impacts of coastal reclamation on natural wetlands in large river deltas in China. Chinese Geogr Sci 29:640–651
Magoč T, Salzberg SL (2011) Flash: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 27:2957–2963
Nannipieri P, Ascher J, Ceccherini MT, Landi L, Pietramellara G, Renella G (2003) Microbial diversity and soil functions. Eur J Soil Sci 54:655–670
Newton RJ, McMahon KD (2011) Seasonal differences in bacterial community composition following nutrient additions in a eutrophic lake. Environ Microbiol 13:887–899
Nguyen LTT, Osanai Y, Lai K, Anderson IC, Bange MP, Tissue DT, Singh BK (2018) Responses of the soil microbial community to nitrogen fertilizer regimes and historical exposure to extreme weather events: flooding or prolonged-drought. Soil Biol Biochem 118:227–236
Novoa A, Keet JH, Lechuga-Lago Y, Pyšek P, Roux JJL (2020) Urbanization and Carpobrotus edulis invasion alter the diversity and composition of soil bacterial communities in coastal areas. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 96:1–12
Okubo Y, Futamata H, Hiraishi A (2006) Characterization of phototrophic purple nonsulfur bacteria forming colored microbial mats in a swine wastewater ditch. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:6225–6233
Orwin KH, Dickie IA, Wood JR, Bonner KI, Holdaway RJ (2016) Soil microbial community structure explains the resistance of respiration to a dry-rewet cycle, but not soil functioning under static conditions. Funct Ecol 30:1430–1439
Palleroni NJ (2005) Genus I. Pseudomonas Migula1894, 237AL (Nom. Cons., Opin. 5 of the Jud. Comm. 1952, 121). In: Brenner DJ, Krieg NR, Staley JT, Garrity GM (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 2, 2ndedn, The proteobacteria, Part B. The gammaproteobacteria. Springer, New York, p 323
Pascault N, Ranjard L, Kaisermann A, Bachar D, Christen R, Terrat S, Mathieu O, Leveque J, Mougel C, Henault C, Lemanceau P, Pean M, Boiry S, Fontaine S, Maron PA (2013) Stimulation of different functional groups of bacteria by various plant residues as a driver of soil priming effect. Ecosystem 16:810–822
Peix A, Ramirez-Bahena MH, Velázquez E (2009) Historical evolution and current status of the taxonomy of genus Pseudomonas. Infect Genet Evol 9:1132–1147
Peralta RM, Ahn C, Gillevet PM (2013) Characterization of soil bacterial community structure and physiochemical properties in created and natural wetlands. Sci Total Environ 443:725–732
Pereira MC, O’Riordan R, Stevens C (2021) Urban soil microbial community and microbial-related carbon storage are severely limited by sealing. J Soil Sediment 21:1455–1465
Philippot L, Raaijmakers JM, Lemanceau P, van der Putten WH (2013) Going back to the roots: the microbial ecology of the rhizosphere. Nat Rev Microbiol 11:789–799
Podosokorskaya OA, Bonch-Osmolovskaya EA, Novikov AA, Kolganova TV, Kublanov IV (2013) Ornatilineaapprima gen. Nov, sp. Nov., a cellulolytic representative of the class Anaerolineae. Int J Syst Evol Micr 63:86–92
Qin P, Li SY (2012) Positive and negative effects of the non-native plant, Spartina alterniflora and its ecological control. J Biosafety 21:167–176
Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, Gerken J, Schweer T, Yarza P, Peplies J, Glockner FO (2013) The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D590–D596
Rasmussen AN, Damashek J, Eloe-Fadrosh EA, Francis CA (2021) In-depth spatiotemporal characterization of planktonic archaeal and bacterial communities in North and South San Francisco Bay. Microb Ecol 81:601–616
Rath KM, Rousk J (2015) Salt effects on the soil microbial decomposer community and their role in organic carbon cycling: a review. Soil Biol Biochem 81:108–123
Rovira P, Vallejo VR (2002) Labile and recalcitrant pools of carbon and nitrogen inorganic matter decomposing at different depths in soil: an acid hydrolysis approach. Geoderma 107:109–141
Ruiz‐González C, Salazar G, Logares R, Proia L, SergiSabater JMG, Sabater S (2015) Weak coherence in abundance patterns between bacterial classes and their constituent OTUs along a regulated river. Front Microbiol 6:1293
Santonja M, Fernandez C, Proffit M, Gers C, Gauquelin T, Reiter IM, Cramer W, Baldy V (2017) Plant litter mixture partly mitigates the negative effects of extended drought on soil biota and litter decomposition in a Mediterranean oak forest. J Ecol 105:801–815
Schermelleh-Engel K, Moosbrugger H, Müller H (2003) Evaluating the fit of structural equation models: tests of significance and descriptive goodness-of-fit measures. Method of Psychol Res Online 8:23–74
Segata N, Izard J, Waldron L, Gevers D, Miropolsky L, Garrett WS, Huttenhower C (2011) Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol 12:R60
Sun RB, Zhang XX, Guo XS, Wang DZ, Chu HY (2015) Bacterial diversity in soils subjected to long-term chemical fertilization can be more stably maintained with the addition of livestock manure than wheat straw. Soil Biol Biochem 88:9–18
Sun ML, Li T, Li DM, Zhao YL, Gao FM, Sun LF, Li X (2021) Conversion of land use from upland to paddy field changes soil bacterial community structure in Mollisols of Northeast China. Microb Ecol 81:1018–1028
Tian Q, Jiang Y, Tang Y, Wu Y, Tang Z, Liu F (2021) Soil pH and organic carbon properties drive soil bacterial communities in surface and deep layers along an elevational gradient. Front Microbiol 12:646124
Trevathan-Tackett SM, Jeffries TC, Macreadie PI, Manojlovic B, Ralph P (2020) Long-term decomposition captures key steps in microbial breakdown of seagrass litter. Sci Total Environ 705:135806
Trivedi P, Anderson IC, Singh BK (2013) Microbial modulators of soil carbon storage: integrating genomic and metabolic knowledge for global prediction. Trends Microbiol 21:641–651
Urbanová M, Snajdr J, Baldrian P (2015) Composition of fungal and bacterial communities in forest litter and soil is largely determined by dominant trees. Soil Biol Biochem 84:53–64
Vasquez EA, Glenn EP, Guntenspergen GR, Brown JJ, Nelson SG (2006) Salt tolerance and osmotic adjustment of Spartina alterniflora (Poaceae) and the invasive M haplotype of Phragmites australis (Poaceae) along a salinity gradient. Am J Bot 93:1784–1790
Ventosa A, Haba RRDL (2011) Archea. In: Gargaud M, Amils R, Cernicharo Quintanilla J, Cleaves HJ, Irvine WM, Pinti D, Viso M (eds) Encyclopedia of astrobiology. Springer, New York, p 57
Verzeaux J, Alahmad A, Habbib H, Nivelle E, Roger D, Lacoux J, Decocq G, Hirel B, Catterou M, Spicher F, Dubois F, Duclercq J, Tetu T (2016) Cover crops prevent the deleterious effect of nitrogen fertilization on bacterial diversity by maintaining the carbon content of ploughed soil. Geoderma 281:49–57
Wang JL, Liu ZQ (2005) Protection and sustainable utilization for the biodiversity of Yancheng seashore. Chin J Ecol 24:1090–1094
Wang F, Wall G (2010) Mudflat development in Jiangsu Province, China: Practices and experiences. Ocean Coast Manage 53:691–699
Wang DD, Gao S, Du YF, Gao WH (2012) Distribution patterns of sediment chlorophyll-a in Spartina alterniflora salt marshes at Rudong coast of Jiangsu, East China. Chin J Ecol 31:2247–2254
Wang YD, Wang ZL, Feng XP, Guo CC, Chen Q (2014) Long-term effect of agricultural reclamation on soil chemical properties of a coastal saline marsh in Bohai Rim, Northern China. PLoS One 9:e93727
Wang J, Liu HY, Li YF, Liu L, Xie FF, Lou CR, Zhang HB (2019a) Effects of Spartina alterniflora invasion on quality of the red-crowned crane (Grus japonensis) wintering habitat. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:21546–21555
Wang ZY, Zhang HY, He CQ, Liu C, Liang X, Chen XP (2019b) Spatiotemporal variability in soil sulfur storage is changed by exotic Spartina alterniflora in the Jiuduansha wetland, China. Ecol Eng 133:160–166
Wang W, Tao J, Liu H, Li P, Chen S, Wang P, Zhang C (2020) Contrasting bacterial and archaeal distributions reflecting different geochemical processes in a sediment core from the Pearl River estuary. AMB Express 10:16
Xie ZF, Wang ZW, Wang QY, Zhu CW, Wu ZC (2014) An anaerobic dynamic membrane bioreactor (AnDMBR) for landfill leachate treatment: performance and microbial community identification. Bioresource Technol 161:29–39
Xu SQ, Wang YD, Guo CC, Zhang ZG, Shang YT, Chen Q, Wang ZL (2017) Comparison of microbial community composition and diversity in native coastal wetlands and wetlands that have undergone long-term agricultural reclamation. Wetlands 37:99–108
Yan DD, Li JT, Yao XY, Luan ZQ (2022) Integrating UAV data for assessing the ecological response of Spartina alterniflora towards inundation and salinity gradients in coastal wetland. Sci Total Environ 814:152631
Yang W, Li N, Leng X, Qiao YJ, Cheng XL, An SQ (2016) The impact of sea embankment on soil organic carbon and nitrogen pools in invasive Spartina alterniflora and native Suaeda salsa saltmarshes in eastern China. Ecol Eng 97:582–592
Yang W, Xia L, Zhu ZH, Jiang LF, Cheng XL, An SQ (2019) Shift in soil organic carbon and nitrogen pools in different reclaimed lands following intensive coastal reclamation on the coasts of eastern China. Sci Rep 9:5921
Yang W, Cai AD, Wang JS, Luo YQ, Cheng XL, An SQ (2020) Exotic Spartina alterniflora Loisel. invasion significantly shifts soil bacterial communities with the successional gradient of saltmarsh in eastern China. Plant Soil 449:97–115
Yu ZS, Northup RR, Dahlgren RA (1994) Determination of dissolved organic nitrogen using persulfate oxidation and conductimetric quantification of nitrate-nitrogen. Commun Soil Sci Plan 25:3161–3169
Yu JB, Wang XH, Ning K, Li YZ, Wu HF, Fu YQ, Zhou D, Guan B, Lin QX (2012) Effects of salinity and water depth on germination of Phragmites australis in coastal wetland of the Yellow River Delta. Clean Soil Air Water 40:1154–1158
Yu HL, Ling N, Wang TT, Zhu C, Wang Y, Wang SJ, Gao Q (2019) Responses of soil biological trains and bacterial communities to nitrogen fertilization mediate maize yields across three soil types. Soil till Res 185:61–69
Zechmeister-Boltenstern S, Keiblinger KM, Mooshammer M, Penuelas J, Richter A, Sardans J, Wanek W (2015) The application of ecological stoichiometry to plant-microbial-soil organic matter transformations. Ecol Monogr 85:133–155
Zhang GL, Bai JH, Tebbe CC, Zhao QQ, Jia J, Wang W, Wang X, Yu L (2021) Salinity controls soil microbial community structure and function in coastal estuarine wetlands. Environ Microbiol 23:1020–1037
Zhang ZR, Jing MD, Qin P, Xie M (1985) Preliminary report on salt tolerance response of Spartina alterniflora grown in sand culture. J Nanjing Univ 40:268–279 (Special edition for research advances in Spartina–achievements of past 22 years)
Zhao QQ, Zhao HX, Gao YC, Zheng LW, Wang JN, Bai JH (2020) Alterations of bacterial and archaeal communities by freshwater input in coastal wetlands of the Yellow River Delta, China. Appl Soil Ecol 153:103581
Zhong CQ, Wang JX, Qin P (2011) Relationship of salt marsh plant distribution and soil physical and chemical characteristic in coastal saltmarsh plant of north Jiangsu Province. Trans Oceanol Limnol 4:151–157
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National 973 Key Project of Basic Science Research (grant No. 2013CB430405), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No. 31600427; 32071632). We would like to thank Hui Zhao for assistance with the fieldwork, and all of the members of the Dafeng Milu National Nature Reserve and Yancheng National Nature Reserve for supporting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hongyu Feng: Conceptualization, Software, Formal analysis, Data Curation, Writing – Original Draft. Yajun Qiao: Methodology, Investigation. Lu Xia: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Formal analysis, Data Curation, Writing – Original Draft, Writing – Review & Editing, Visualization. Wen Yang: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – Review & Editing, Project administration, Funding acquisition. Yongqiang Zhao: Resources, Investigation. Nasreen Jeelani: Writing – Review & Editing. Shuqing An: Conceptualization, Resources, Writing – Review & Editing, Project administration, Funding acquisition.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
All authors participated in this manuscript.
Consent for publication
All authors revised the manuscript critically and approved the final manuscript for publication.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Felipe E. Albornoz.
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, H., Qiao, Y., Xia, L. et al. The responses of soil bacterial and archaeal communities to coastal embankments in three typical salt marshes of Eastern China. Plant Soil 477, 439–459 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-022-05423-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-022-05423-3