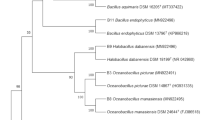
Abstract
Background and aims
The plant growth promoting rhizobacteria have been extensively implicated in plant responses to changing environments. However, the action mechanisms still need to be elucidated. This study addressed the effect of Paraburkholderia sp. GD17 on rice seedlings in responses to salt stress.
Methods
The experiment consisted of GD17-inoculated and non-inoculated plants, with or without NaCl treatment. Physiological and biochemical parameters, and gene expression were analyzed.
Results
GD17 efficiently colonized inside roots, and provided a protection against salt stress. Following exposure to 68 mM of NaCl for 48 h, although the accumulation of Na+ was not affected in GD17-inoculated (+ GD17) roots relative to non-inoculated ones, its concentration was substantially reduced in + GD17 shoots. The contents of K and other mineral elements were higher in + GD17 plants. The expression of Na+ and K+ transporter-encoding genes generally presented a higher level in + GD17 plants. The antioxidative defense especially related to the removal of H2O2 was more strongly activated in + GD17 plants. Correspondingly, salt-induced oxidative damage was significantly ameliorated. A substantial increase in proline content and gene expression was observed in + GD17 plants. Additionally, the cell wall invertase-encoding gene displayed a dramatically higher expression level in + GD17 plants.
Conclusions
GD17 efficiently improved rice seedling tolerance to salt stress. The possible mechanisms might be associated with the absorption and redistribution of mineral elements, the vacuolar sequestration of Na+ as well as exclusion of Na+, antioxidative defense, the production of proline, and the sucrose catabolism in apoplast.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abogadallah GM (2010) Antioxidative defense under salt stress. Plant Signal Behav 5:369–374
Aebi HE (1983) Catalase. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methods of enzymatic analyses. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 273–282
Ahanger MA, Tomar NS, Tittal M, Argal S, Agarwal RM (2017) Plant growth under water/salt stress: ROS production; antioxidants and significance of added potassium under such conditions. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 23:731–744
Aharon G, Apse M, Duan S, Hua X, Blumwald E (2003) Characterization of a family of vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporters in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Soil 253:245–256
Albacete A, Cantero-Navarro E, Großkinsky DK, Arias CL, Balibrea ME, Bru R, Fragner L, Ghanem ME, González Mde L, Hernández JA et al (2015) Ectopic overexpression of the cell wall invertase gene CIN1 leads to dehydration avoidance in tomato. J Exp Bot 66:863–878
Almeida DM, Gregorio GB, Oliveira MM, Saibo NJ (2017) Five novel transcription factors as potential regulators of OsNHX1 gene expression in a salt tolerant rice genotype. Plant Mol Biol 93:61–77
Apse MP, Sottosanto JB, Blumwald E (2003) Vacuolar cation/H+ exchange, ion homeostasis, and leaf development are altered in a T-DNA insertional mutant of AtNHX1, the Arabidopsis vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter. Plant J 36:229–239
Artigas MR, España M, Aguirre C, Kojima K, Ohkama-Ohtsu N, Sekimoto H, Yokoyama T (2019) Burkholderia and Paraburkholderia are predominant soybean rhizobial genera in Venezuelan soils in different climatic and topographical regions. Microbes Environ 34:43–58
Barragan V, Leidi EO, Andrés Z, Rubio L, De Luca A, Fernández JA, Cubero B, Pardoa JM (2012) Ion exchangers NHX1 and NHX2 mediate active potassium uptake into vacuoles to regulate cell turgor and stomatal function in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24:1127–1142
Bassil E, Coku A, Blumwald E (2012) Cellular ion homeostasis: emerging roles of intracellular NHX Na+/H+ antiporters in plant growth and development. J Exp Bot 63:5727–5740
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Berendsen RL, Pieterse CMJ, Bakker PAHM (2012) The rhizosphere microbiome and plant health. Trends Plant Sci 17:478–486
Bertani G (1951) Studies on lysogenesis I.: the mode of phage liberation by lysogenic Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 62:293–300
Beyer WF, Fridovich I (1987) Assaying for superoxide dismutase activity: some large consequences of minor changes in conditions. Anal Biochem 161:559–566
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chatterjee P, Kanagendran A, Samaddar S, Pazouki L, Sa TM, Niinemets Ü (2018a) Inoculation of Brevibacterium linens RS16 in Oryza sativa genotypes enhanced salinity resistance: impacts on photosynthetic traits and foliar volatile emissions. Sci Total Environ 645:721–732
Chatterjee P, Samaddar S, Niinemets Ü, Sa TM (2018b) Brevibacterium linens RS16 confers salt tolerance to Oryza sativa genotypes by regulating antioxidant defense and H+ ATPase activity. Microbiol Res 215:89–101
Chen JB, Wang SM, Jing RL, Mao XG (2009) Cloning the PvP5CS gene from common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) and its expression patterns under abiotic stresses. J Plant Physiol 166:12–19
Chen G, Hu Q, Luo L, Yang T, Zhang S, Hu Y, Yu L, Xu G (2015) Rice potassium transporter OsHAK1 is essential for maintaining potassium-mediated growth and functions in salt tolerance over low and high potassium concentration ranges. Plant Cell Environ 38:2747–2765
Coenye T, Vandamme P (2003) Diversity and significance of Burkholderia species occupying diverse ecological niches. Environ Microbiol 5:719–729
Estrada GA, Baldani VLD, de Oliveira DM, Urquiaga S, Baldani JI (2013) Selection of phosphate-solubilizing diazotrophic Herbaspirillum and Burkholderia strains and their effect on rice crop yield and nutrient uptake. Plant Soil 369:115–129
Flowers TJ, Troke PF, Yeo AR (1977) The mechanism of salt tolerance in halophytes. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 28:89–121
Ganie SA, Molla KA, Henry RJ, Bhat KV, Mondal TK (2019) Advances in understanding salt tolerance in rice. Theor Appl Genet 132:851–870
Grattan S, Zeng L, Shannon M, Roberts S (2002) Rice is more sensitive to salinity than previously thought. Calif Agric 56:189–198
Griffith OW, Meister A (1979) Potent and specific inhibition of glutathione synthesis by buthionine sulfoximine (s-n-butylhomocysteine sulfoximine). J Biol Chem 254:7558–7560
Guo Y, Yang P, Zhang DY, Liu YY, Ma LJ, Bu N (2018) Screening, identification and growth-promoting effect of multifunction rhizosphere growth-promoting strain of wild soybean. Biotechnol Bull 34:108–115 (in Chinese)
Hao L, Zhao Y, Jin D, Zhang L, Bi XH, Chen HX, Xu Q, Ma CY, Li GZ (2012) Salicylic acid-altering Arabidopsis mutants response to salt stress. Plant Soil 354:81–95
Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA, Zhu JK, Bohnert HJ (2000) Plant cellular and molecular responses to high salt. Ann Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 51:463–499
Hemeda HM, Klein BP (1990) Effects of naturally occurring antioxidants on peroxidase activity of vegetable extracts. J Food Sci 55:184–185
Horie T, Sugawara M, Okada T, Taira K, Kaothien-Nakayama P, Katsuhara M, Shinmyo A, Nakayama H (2011) Rice sodium-insensitive potassium transporter, OsHAK5, confers increased salt tolerance in tobacco BY2 cells. J Biosci Bioeng 111:346–356
Hussain M, Ahmad S, Hussain S, Lal R, Ul-Allah S, Nawaz A (2018) Rice in saline soils: physiology, biochemistry, genetics, and management. Adv Agron 148:231–287
Igarashi Y, Yoshiba Y, Sanada Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Wada K, Shinozaki K (1997) Characterization of the gene for Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthatase and correlation between the expression of the gene and salt tolerance in Oryza sativa. Plant Mol Biol 33:857–865
Ji X, Van den Ende W, Van Laere A, Cheng S, Bennett JJ (2005) Structure, evolution, and expression of the two invertase gene families of rice. Mol Evol 60:615–634
Joseph EA, Mohanan KV (2013) A study on the effect of salinity stress on the growth and yield of some native rice cultivars of Kerala state of India. Agric for Fish 2:141–150
Kader MA, Seidel T, Golldack D, Lindberg S (2006) Expressions of OsHKT1, OsHKT2, and OsVHA are differentially regulated under NaCl stress in salt-sensitive and salt-tolerant rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars. J Exp Bot 57:4257–4268
Kasten D, Mithöfer A, Georgii E, Lang H, Durner J, Gaupels F (2016) Nitrite is the driver, phytohormones are modulators while NO and H2O2 act as promoters of NO2-induced cell death. J Exp Bot 67:6337–6349
Khan A, Numan M, Khan AL, Lee IJ, Imran M, Asaf S, Al-Harrasi A (2020a) Melatonin: awakening the defense mechanisms during plant oxidative stress. Plants 9:407
Khan MA, Asaf S, Khan AL, Adhikari A, Jan R, Ali S, Imran M, Kim KM, Lee IJ (2020b) Plant growth-promoting endophytic bacteria augment growth and salinity tolerance in rice plants. Plant Biol 22:850–862
Khanna K, Jamwal VL, Kohli SK, Gandhi SG, Ohri P, Bhardwaj R, Abd Allah EF, Hashem A, Ahmad P (2019) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria induced Cd tolerance in Lycopersicon esculentum through altered antioxidative defense expression. Chemosphere 217:463–474
King E, Wallner A, Rimbault I, Barrachina C, Klonowska A, Moulin L, Czernic P (2019) Monitoring of rice transcriptional responses to contrasted colonizing patterns of phytobeneficial Burkholderia s.l. reveals a temporal shift in JA systemic response. Front Plant Sci 10:1141
Kushwaha P, Kashyap PL, Bhardwaj AK, Kuppusamy P, Srivastava AK, Tiwari RK (2020) Bacterial endophyte mediated plant tolerance to salinity: growth responses and mechanisms of action. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 36:26
Lazof DB, Bernstein N (1999) The NaCl induced inhibition of shoot growth: the case for distributed nutrition with special consideration of calcium. Adv Bot Res 29:113–189
Leidi EO, Barragán V, Rubio L, El-Hamdaoui A, Ruiz MT, Cubero B, Fernández JA, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM, Quintero FJ, Pardo JM (2010) The AtNHX1 exchanger mediates potassium compartmentation in vacuoles of transgenic tomato. Plant J 61:495–506
Maathuis FJM, Amtmann A (1999) K+ nutrition and Na+ toxicity: the basis of cellular K+/Na+ ratios. Ann Bot 84:123–133
Mahi HE, Hormaeche JP, Luca AD, Villalta I, Espartero J, Arjona FG, Fernández JL et al (2019) A critical role of sodium flux via the plasma membrane Na+/H+ exchanger SOS1 in the salt tolerance of rice. Plant Physiol 180:1046–1065
Martínez-Atienza J, Jiang X, Garciadeblas B, Mendoza I, Zhu JK, Pardo JM, Quintero FJ (2007) Conservation of the salt overly sensitive pathway in rice. Plant Physiol 143:1001–1012
Mittler R (2002) Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 7:405–410
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681
Narsai R, Ivanova A, Ng S, Whelan J (2010) Defining reference genes in Oryza sativa using organ, development, biotic and abiotic transcriptome datasets. BMC Plant Biol 10:56
Pinedo I, Ledger T, Greve M, Poupin MJ (2015) Burkholderia phytofirmans PsJN induces long-term metabolic and transcriptional changes involved in Arabidopsis thaliana salt tolerance. Front Plant Sci 6:466
Pitman MG, Läuchli A (2002) Global impacts of salinity and agricultural ecosystem. In: Läuchli A, Lüttge U (eds) Salinity: environment-plants-molecules. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 3–20
Qin H, Li Y, Huang R (2020) Advances and challenges in the breeding of salt-tolerant rice. Int J Mol Sci 21:8385
Qiu QS, Guo Y, Dietrich MA, Schumaker KS, Zhu JK (2002) Regulation of SOS1, a plasma membrane Na+/H+ exchanger in Arabidopsis thaliana, by SOS2 and SOS3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:8436–8441
Qu Y, Wang YY, Yin QS, Huang LL, Jiang YG, Li GZ, Hao L (2018) Multiple biological processes involved in the regulation of salicylic acid in Arabidopsis response to NO2 exposure. Environ Exp Bot 149:9–16
Ruan YL, Jin Y, Yang YJ, Li GJ, Boyer JS (2010) Sugar input, metabolism, and signaling mediated by invertase: roles in development, yield potential, and response to drought and heat. Mol Plant 3:942–955
Sarkar A, Pramanik K, Mitra S, Soren T, Maiti TK (2018) Enhancement of growth and salt tolerance of rice seedlings by ACC deaminase-producing Burkholderia sp. MTCC 12259. J Plant Physiol 231:434–442
Sawana A, Adeolu M, Gupta RS (2014) Molecular signatures and phylogenomic analysis of the genus Burkholderia: proposal for division of this genus into the emended genus Burkholderia containing pathogenic organisms and a new genus Paraburkholderia gen. nov. harboring environmental species. Front Genet 5:429
Shi H, Quintero FJ, Pardo JM, Zhu JK (2002) The putative plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter SOS1 controls long-distance Na+ transport in plants. Plant Cell 14:465–477
Van Trân V, Berge O, Ngo Ke S, Balandreau J, Heulin T (2000) Repeated beneficial effects of rice inoculation with a strain of Burkholderia vietnamiensis on early and late yield components in low fertility sulphate acid soils of Vietnam. Plant Soil 218:273–284
Vaishnav A, Shukla AK, Sharma A, Kumar R, Choudhary DK (2019) Endophytic bacteria in plant salt stress tolerance: current and future prospects. J Plant Grow Regul 38:650–668
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3:0034
Verbruggen N, Hermans C (2008) Proline accumulation in plants: a review. Amino Acids 35:753–759
Wang Y, Wu WH (2013) Potassium transport and signaling in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 64:451–476
Wang S, Jiao HJ, Faust M (1991) Changes in ascorbate, glutathione and related enzyme activities during thidiazuron-induced bud break apple. Physiol Plant 82:231–236
Wang C, Huang Y, Yang X, Xue W, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Pang J, Liu Y, Liu Z (2020) Burkholderia sp. Y4 inhibits cadmium accumulation in rice by increasing essential nutrient uptake and preferentially absorbing cadmium. Chemosphere 252:126603
Yang Y, Guo Y (2018) Elucidating the molecular mechanisms mediating plant salt-stress responses. New Phytol 217:523–539
Yang Z, Gao Q, Sun C, Li W, Gu S, Xu C (2009) Molecular evolution and functional divergence of HAK potassium transporter gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Genet Genomics 36:161–172
Yang T, Zhang S, Hu Y, Wu F, Hu Q, Chen G et al (2014) The role of a potassium transporter OsHAK5 in potassium acquisition and transport from roots to shoots in rice at low potassium supply levels. Plant Physiol 166:945–959
Yang A, Akhtar SS, Fu Q, Naveed M, Iqbal S, Roitsch T, Jacobsen SE (2020a) Burkholderia Phytofirmans PsJN stimulate growth and yield of quinoa under salinity stress. Plants 9:672
Yang W, Chen S, Cheng Y, Zhang N, Ma Y, Wang W, Tian H, Li Y, Hussain S, Wang S (2020b) Cell wall/vacuolar inhibitor of fructosidase 1 regulates ABA response and salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Signal Behav 15:1744293
Yeo AR, Yeo ME, Flowers SA, Flowers TJ (1990) Screening of rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes for physiological characters contributing to salinity resistance, and their relationship to overall performance. Theor Appl Genet 79:377–384
Zhang ZL, Qu WJ (2003) The experimental guide for plant physiology, 3rd edn. Higher Education Press, Beijing, pp 60–160
Zhang H, Liu W, Wan L, Li F, Dai L, Li D, Zhang Z, Huang R (2010) Functional analyses of ethylene response factor JERF3 with the aim of improving tolerance to drought and osmotic stress in transgenic rice. Transgenic Res 19:809–818
Zhang Y, Fang J, Wu X, Dong L (2018) Na+/K+ balance and transport regulatory mechanisms in weedy and cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) under salt stress. BMC Plant Biol 18:375
Zhu JK (2000) Genetic analysis of plant salt tolerance using Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 124:941–948
Zhu B, Su J, Chang M, Verma DPS, Fan YL, Wu R (1998) Overexpression of a 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase gene and analysis of tolerance to water and salt-stress in transgenic rice. Plant Sci 139:41–48
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31572213 and 31270446 to HL).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HL and LGZ designed and carried out the research. ZYM, CYT, GY, MLJ and BN contributed to carry out the physiological, biochemical and the qRT-PCR analyses. HL and LGZ analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Birgit Mitter.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, R., Cao, Y., Li, G. et al. Paraburkholderia sp. GD17 improves rice seedling tolerance to salinity. Plant Soil 467, 373–389 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-021-05108-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-021-05108-3