Abstract
Background and aims
The deposition of atmospheric N is expected to increase in the future; however, our understanding of the responses of C:N stoichiometry to N deposition in plants, soil, and microorganisms remains elusive. We aim to explore the general patterns and mechanisms of terrestrial C:N stoichiometry to N addition.
Methods
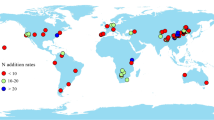
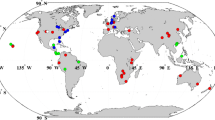
We present a global meta-analysis based on 827 paired observations from 183 studies to evaluate the responses of above- and belowground C and N concentrations ([C] and [N]) and C:N ratios across various ecosystems to N addition. Using linear mixed-effects models, we tested the effects of N input rates, experimental duration, ecosystem types and background climates on the responses.
Results
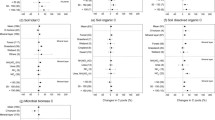
N addition increased [C] in plant shoots and soil, [N] in plant tissues and soil, but decreased microbial biomass [C], and C:N ratios in plant tissues, soil, and microbial biomass. These responses were more pronounced with higher N input rates and longer experimental durations. These N addition effects were similar among cropland, forest, and grassland ecosystems and were independent of background climates.
Conclusions
Our meta-analysis provided further evidence of the consistent responses of C:N stoichiometry in plants, soil, and microorganisms to N addition. Our results will be useful to modelling the responses of terrestrial C and N cycles to various N deposition scenarios.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bates D, Machler M, Bolker BM, Walker SC (2015) Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. Journal of statistical software 67:1–48. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v067.i01
Bobbink R, Hicks K, Galloway J, Spranger T, Alkemade R, Ashmore M, Bustamante M, Cinderby S, Davidson E, Dentener F, Emmett B, Erisman JW, Fenn M, Gilliam F, Nordin A, Pardo L, De Vries W (2010) Global assessment of nitrogen deposition effects on terrestrial plant diversity: a synthesis. Ecol Appl 20:30–59. https://doi.org/10.1890/08-1140.1
Brookes PC, Landman A, Pruden G, Jenkinson DS (1985) Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: a rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 17:837–842. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(85)90144-0
Burda BU, O'Connor EA, Webber EM, Redmond N, Perdue LA (2017) Estimating data from figures with a web-based program: considerations for a systematic review. Res Synth Methods 8:258–262. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.1232
Button KS, Ioannidis JPA, Mokrysz C, Nosek BA, Flint J, Robinson ESJ, Munafo MR (2013) Power failure: why small sample size undermines the reliability of neuroscience. Nat Rev Neurosci 14:365–376. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3475
Chapin FS, Matson PA, Mooney HA (2011) Principles of terrestrial ecosystem ecology. Springer-Verlag, New York
Chen C, Chen HYH, Chen XL (2020a) Functional diversity enhances, but exploitative traits reduce tree mixture effects on microbial biomass. Funct Ecol 34:276–286. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.13459
Chen X, Chen HYH (2018) Global effects of plant litter alterations on soil CO2 to the atmosphere. Glob Chang Biol 24:3462–3471. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.14147
Chen X, Chen HYH (2019) Plant diversity loss reduces soil respiration across terrestrial ecosystems. Glob Chang Biol 25:1482–1492. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.14567
Chen X, Chen HYH, Chen C, Ma Z, Searle EB, Yu Z, Huang Z (2020b) Effects of plant diversity on soil carbon in diverse ecosystems: a global meta-analysis. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc 95:167–183. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12554
DeForest JL, Zak DR, Pregitzer KS, Burton AJ (2004) Atmospheric nitrate deposition, microbial community composition, and enzyme activity in northern hardwood forests. Soil Sci Soc Am J 68:132–138. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2004.1320
Elser JJ, Fagan WF, Kerkhoff AJ, Swenson NG, Enquist BJ (2010) Biological stoichiometry of plant production: metabolism, scaling and ecological response to global change. New Phytol 186:593–608
Galloway JN, Townsend AR, Erisman JW, Bekunda M, Cai ZC, Freney JR, Martinelli LA, Seitzinger SP, Sutton MA (2008) Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 320:889–892. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1136674
Gruber N, Galloway JN (2008) An earth-system perspective of the global nitrogen cycle. Nature 451:293–296. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06592
Hedges LV, Gurevitch J, Curtis PS (1999) The meta-analysis of response ratios in experimental ecology. Ecology 80:1150–1156. https://doi.org/10.1890/0012-9658(1999)080[1150:TMAORR]2.0.CO:2
Hurlbert SH (1984) Pseudoreplication and the design of ecological Field experiments. Ecol Monogr 54:187–211. https://doi.org/10.2307/1942661
Iversen C, Bridgham S, Kellogg L (2010) Scaling plant nitrogen use and uptake efficiencies in response to nutrient addition in peatlands. Ecology 91:693–707. https://doi.org/10.1890/09-0064.1
Janssens IA, Dieleman W, Luyssaert S, Subke JA, Reichstein M, Ceulemans R, Ciais P, Dolman AJ, Grace J, Matteucci G, Papale D, Piao SL, Schulze ED, Tang J, Law BE (2010) Reduction of forest soil respiration in response to nitrogen deposition. Nat Geosci 3:315–322. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo844
Kramer C, Gleixner G (2008) Soil organic matter in soil depth profiles: distinct carbon preferences of microbial groups during carbon transformation. Soil Biol Biochem 40:425–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2007.09.016
Krause K, Cherubini P, Bugmann H, Schleppi P (2012) Growth enhancement of Picea abies trees under long-term, low-dose N addition is due to morphological more than to physiological changes. Tree Physiol 32:1471–1481. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tps109
Lange M, Eisenhauer N, Sierra CA, Bessler H, Engels C, Griffiths RI, Mellado-Vázquez PG, Malik AA, Roy J, Scheu S, Steinbeiss S, Thomson BC, Trumbore SE, Gleixner G (2015) Plant diversity increases soil microbial activity and soil carbon storage. Nat Commun 6:6707. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms7707
LeBauer DS, Treseder KK (2008) Nitrogen limitation of net primary productivity in terrestrial ecosystems is globally distributed. Ecology 89:371–379. https://doi.org/10.1890/06-2057.1
Liu L, Greaver TL (2010) A global perspective on belowground carbon dynamics under nitrogen enrichment. Ecol Lett 13:819–828. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2010.01482.x
Lloret F, Mattana S, Yuste JC (2015) Climate-induced die-off affects plant-soil-microbe ecological relationship and functioning FEMS microbiology ecology 91. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fiu014
Lu M, Yang YH, Luo YQ, Fang CM, Zhou XH, Chen JK, Yang X, Li B (2011) Responses of ecosystem nitrogen cycle to nitrogen addition: a meta-analysis. New Phytol 189:1040–1050. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03563.x
Luo Y, Su B, Currie WS, Dukes JS, Finzi AC, Hartwig U, Hungate B, McMurtrie RE, Oren R, Parton WJ, Pataki DE, Shaw MR, Zak DR, Field CB (2004) Progressive nitrogen limitation of ecosystem responses to rising atmospheric carbon dioxide. Bioscience 54:731–739. https://doi.org/10.1641/0006-3568(2004)054[0731:Pnloer]2.0.Co;2
Moe SJ, Stelzer RS, Forman MR, Harpole WS, Daufresne T, Yoshida T (2005) Recent advances in ecological stoichiometry: insights for population and community ecology. Oikos 109:29–39. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0030-1299.2005.14056.x
Pribyl DW (2010) A critical review of the conventional SOC to SOM conversion factor. Geoderma 156:75–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2010.02.003
R Development Core Team (2019) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. 3.6.0 edn. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria, http://www.Rproject.org/
Ren C, Zhao F, Shi Z, Chen J, Han X, Yang G, Feng Y, Ren G (2017) Differential responses of soil microbial biomass and carbon-degrading enzyme activities to altered precipitation. Soil Biol Biochem 115:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2017.08.002
Rennenberg H, Dannenmann M, Gessler A, Kreuzwieser J, Simon J, Papen H (2009) Nitrogen balance in forest soils: nutritional limitation of plants under climate change stresses. Plant Biol 11(Suppl 1):4–23. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1438-8677.2009.00241.x
Sardans J, Rivas-Ubach A, Peñuelas J (2012) The C:N:P stoichiometry of organisms and ecosystems in a changing world: a review and perspectives. Perspectives in Plant Ecology Evolution and Systematics 14:33–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ppees.2011.08.002
Strickland MS, Rousk J (2010) Considering fungal:bacterial dominance in soils - methods, controls, and ecosystem implications. Soil Biol Biochem 42:1385–1395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.05.007
Sullivan PF, Sommerkorn M, Rueth HM, Nadelhoffer KJ, Shaver GR, Welker JM (2007) Climate and species affect fine root production with long-term fertilization in acidic tussock tundra near Toolik Lake, Alaska. Oecologia 153:643–652. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-007-0753-8
Sun Y, Chen HYH, Jin L, Wang C, Zhang R, Ruan H, Yang J (2020a) Drought stress induced increase of fungi:bacteria ratio in a poplar plantation. Catena 193:104607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104607
Sun Y, Liao J, Zou X, Xu X, Yang J, Chen HYH, Ruan H (2020b) Coherent responses of terrestrial C:N stoichiometry to drought across plants, soil, and microorganisms in forests and grasslands. Agric For Meteorol 292-293:108104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2020.108104
Treseder KK (2008) Nitrogen additions and microbial biomass: a meta-analysis of ecosystem studies. Ecol Lett 11:1111–1120. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2008.01230.x
Wang M, Murphy MT, Moore TR (2014) Nutrient resorption of two evergreen shrubs in response to long-term fertilization in a bog. Oecologia 174:365–377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-013-2784-7
Xia J, Wan S (2008) Global response patterns of terrestrial plant species to nitrogen addition. New Phytol 179:428–439
Xu Y, Wang Z, Zhang L, Zhu W, Du A (2018) The stoichiometric characteristics of C, N and P in leaf-litter-soil of different aged Eucalyptus urophylla × E.grandis plantations. For Res 31:168–174
Yang YH, Luo YQ, Lu M, Schadel C, Han WX (2011) Terrestrial C:N stoichiometry in response to elevated CO2 and N addition: a synthesis of two meta-analyses. Plant Soil 343:393–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-011-0736-8
Yuan ZY, Chen HYH (2012) A global analysis of fine root production as affected by soil nitrogen and phosphorus. P Roy Soc B-Biol Sci 279:3796–3802. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2012.0955
Yuan ZY, Chen HYH (2015) Decoupling of nitrogen and phosphorus in terrestrial plants associated with global changes. Nat Clim Chang 5:465–469. https://doi.org/10.1038/Nclimate2549
Yuan ZY, Li LH, Han XG, Chen SP, Wang ZW, Chen QS, Bai WM (2006) Nitrogen response efficiency increased monotonically with decreasing soil resource availability: a case study from a semiarid grassland in northern China. Oecologia 148:564–572. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-006-0409-0
Yue K, Fornara DA, Yang W, Peng Y, Li Z, Wu F, Peng C (2017) Effects of three global change drivers on terrestrial C:N:P stoichiometry: a global synthesis. Glob Chang Biol 23:2450–2463. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13569
Zak DR, Freedman ZB, Upchurch RA, Steffens M, Kogel-Knabner I (2017) Anthropogenic N deposition increases soil organic matteraccumulation without altering its biochemical composition. Glob Chang Biol 23:933–944. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13480
Zechmeister-Boltenstern S, Keiblinger KM, Mooshammer M, Penuelas J, Richter A, Sardans J, Wanek W (2015) The application of ecological stoichiometry to plant-microbial-soil organic matter transformations. Ecol Monogr 85:133–155. https://doi.org/10.1890/14-0777.1
Zhang T, Chen HYH, Ruan H (2018) Global negative effects of nitrogen deposition on soil microbes. ISME J 12:1817–1825. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-018-0096-y
Zhang W, Chen Y, Shi L, Wang X, Liu Y, Mao R, Rao X, Lin Y, Shao Y, Li X, Zhao C, Liu S, Piao S, Zhu W, Zou X, Fu S (2019) An alternative approach to reduce algorithm-derived biases in monitoring soil organic carbon changes. Ecology and evolution 9:7586–7596. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.5308
Zhou ZH, Wang CK, Zheng MH, Jiang LF, Luo YQ (2017) Patterns and mechanisms of responses by soil microbial communities to nitrogen addition. Soil Biol Biochem 115:433–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2017.09.015
Zuur A, Ieno EN, Walker N, Saveliev AA, Smith GM (2009) Mixed effects models and extensions in ecology with R. Springer, New York
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to all the scientists whose work was included in this meta-analysis. This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2016YFD0600204) and Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Data accessibility
The data and R codes supporting the results of this study were archived in Figshare (data: https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.12640652 and R code: https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.12640688).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Katharina Maria Keiblinger.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 147 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y., Wang, C., Chen, H.Y.H. et al. Responses of C:N stoichiometry in plants, soil, and microorganisms to nitrogen addition. Plant Soil 456, 277–287 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-020-04717-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-020-04717-8