Abstract
Aims
The effects of iron plaque on the removal of antibiotic or antifungal drugs, such as macrolides (MLs) and sorption mechanism are important for the selection of plants in constructed wetlands. We aim to evaluate the sorption of water-borne MLs by iron plaque on root surfaces of plants with different rates of radial oxygen loss (ROL).
Methods
Aquatic sorption activity was determined in three wetland plant species, Canna indica, Juncus effusus and Iris pseudacorus) and four MLs, anhydroerythromycin A (ETM-H2O), roxithromycin (ROX), clarithromycin (CLA) and tilmicosin (TIL). The adsorption mechanism and iron plaque characteristics before/after adsorption were investigated.
Results
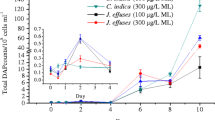
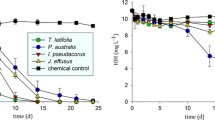
Roots of Juncus effusus removed more MLs than the other two plant species. This species with higher ROL also formed more iron plaques, which consequently adsorbed more MLs. MLs were largely immobilized by sorption onto the Fe (hydr)oxides formed. Multiple mechanisms included hydrophobic interaction, surface ionic exchange and surface complexation between the carbonyl group on the lactone ring of the ML and the ferric ions.
Conclusions
Iron plaque enhances MLs removal by wetland plants. Selecting the dominant plant with high ROL can improve the formation of iron plaque on root surfaces and promote the removal of antibiotics in constructed wetlands.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
A D, Yang Y, Dai YN, Chen CX, Wang SY, Tao R (2013) Removal and factors influencing removal of sulfonamides and trimethoprim from domestic sewage in constructed wetlands. Bioresour Technol 146:363–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.07.050
Akkanen J, Tuikka A, Kukkonen JVK (2005) Comparative sorption and desorption of benzo[a]pyrene and 3,4,3′,4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl in natural Lake water containing dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 39(19):7529–7534. https://doi.org/10.1021/es050835f
Akram R, Amin A, Hashmi MZ, Wahid A, Mubeen M, Hammad HM, Fahad S, Nasim W (2017) Fate of antibiotics in soil. In: Antibiotics and antibiotics resistance genes in soils. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66260-2_11
Armstrong W (1979) Aeration in higher plants. In: Woolhouse HW (ed) Advances in botanical research, vol 7. Academic Press, London, pp 225–332
Armstrong W, Cousins D, Armstrong J, Turner DW, Beckett PM (2000) Oxygen distribution in wetland plant roots and permeability barriers to gas-exchange with the rhizosphere: a microelectrode and modeling study with Phragmites australis. Ann Bot 86:687–703. https://doi.org/10.1006/anbo.2000.1236
Batty LC, Baker AJM, Wheeler BD (2002) Aluminium and phosphate uptake by Phragmites australis: the role of Fe, Mn and Al root plaques. Ann Bot 89:443–449. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcf067
Calamari D, Zuccato E, Castiglioni S, Bagnati R, Fanelli R (2003) Strategic survey of therapeutic drugs in the rivers Po and Lambro in Northern Italy. Environ Sci Technol 37:1241–1248. https://doi.org/10.1021/es020158e
Chen CC, Dixon JB, Turner FT (1980) Iron coating on rice roots: morphology and models of development. Soil Sci Soc Am J 44:1113–1119. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1980.03615995004400050046x
Cheng H, Wang M, Hung MW, Ye ZH (2014) Does radial oxygen loss and iron plaque formation on roots alter Cd and Pb uptake and distribution in rice plant tissues? Plant Soil 375:137–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1945-0
Ding ZC, Fu FL, Cheng ZH, Lu JW, Tang B (2017) Novel mesoporous Fe-Al bimetal oxides for As(III) removal: performance and mechanism. Chemosphere 169:297–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.11.057
Emerson D, Weiss JV, Megonigal JP (1999) Iron-oxidizing bacteria are associated with ferric hydroxide precipitates (Fe-plaque) on the roots of wetland plants. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(6):2758–2761
Feitosa-Felizzola J, Hanna K, Chiron S (2009) Adsorption and transformation of selected human-used macrolide antibacterial agents with iron (III) and manganese (IV) oxides. Environ Pollut 157(4):1317–1322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2008.11.048
Figueroa RA, MacKay AA (2005) Sorption of Oxytetracycline to Iron oxides and Iron oxide-rich soils. Environ Sci Technol 39(17):6664–6671. https://doi.org/10.1021/es048044l
Fu YQ, Yang XJ, Ye ZH, Shen H (2016) Identification, separation and component analysis of reddish brown and non-reddish brown iron plaque on rice (Oryza sativa) root surface. Plant Soil 402:277–290. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-016-2802-8
Giger W, Alder AC, Golet EM, Kohler HPE, McArdell CS, Molnar E, Siegrist H, Suter MJF (2003) Occurrence and fate of antibiotics as trace contaminants in wastewaters, sewage sludges, and surface waters. Chimia 57:485–491. https://doi.org/10.2533/000942903777679064
Green MS, Etherington JR (1977) Oxidation of ferrous iron by rice (Oryza -sativa- L.) roots: mechanism for waterlogging tolerance. J Exp Bot 28:678–690 http://www.jstor.org/stable/23689598
Gros M, Petrovic M, Barcelo D (2007) Wastewater treatment plants as a pathway for aquatic contamination by pharmaceuticals in the Ebro river basin (Northeast Spain). Environ Toxicol Chem 26:1553–1562. https://doi.org/10.1897/06-495R.1
Hamdan I (2003) Comparative in-vitro investigations of the interaction between some macrolides and Cu (II), Zn (II) and Fe (II). Pharmazie 58:223–224
Hernando MD, Mezcua M, Fernandez-Albá AR, Barceló D (2006) Environmental risk assessment of pharmaceutical residues in wastewater effluents, surface waters and sediments. Talanta 69:334–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2005.09.037
Hirsch R, Ternes T, Haberer K, Kratz KL (1999) Occurrence of antibiotics in the aquatic environment. Sci Total Environ 225:109–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(98)00337-4
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil, vol 39. University of California, Berkeley
Huang QQ, Wang Q, Luo Z, Yu Y, Jiang RF, Li HF (2015) Effects of root iron plaque on selenite and selenate dynamics in rhizosphere and uptake by rice (Oryza sativa). Plant Soil 388:255–266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2329-9
Keicho N, Kudoh S (2002) Diffuse panbronchiolitis: role of macrolides in therapy. Am J Resp Med 1(2):119–131. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03256601
King GM, Garey MA (1999) Ferric iron reduction by bacteria associated with the roots of freshwater and marine macrophytes. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:4393–4398
Kludze HK, DeLaune RD, Patrick WH (1994) A colorimetric method for assaying dissolved oxygen loss from container grown rice roots. Agron J 86(3):483–487. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj1994.00021962008600030005x
Kolpin DW, Furlong ET, Meyer MT, Thurman EM, Zaugg SD, Barber LB, Buxton HT (2002) Pharmaceuticals, hormones, and others organic wastewater contaminants in US streams, 1999–2000: a national reconnaissance. Environ Sci Technol 36:1202–1211. https://doi.org/10.1021/es011055j
Laan P, Smolders A, Blom CWPM, Armstrong W (1989) The relative roles of internal aeration, radial oxygen losses, iron exclusion and nutrient balances in flood-tolerance of Rumex species. Acta Bot Neerl 38:131–145. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1438-8677.1989.tb02036.x
Li B, Zhang T (2010) Biodegradation and adsorption of antibiotics in the activated sludge process. Environ Sci Technol 44:3468–3473. https://doi.org/10.1021/es903490h
Li B, Zhang T (2013) Removal mechanisms and kinetics of trace tetracycline by two types of activated sludge treating freshwater sewage and saline sewage. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 20(5):3024–3033. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1213-5
Lin JH, Yang Y, Li L, Mai XB (2015) Characteristics of growth and radial oxygen loss of eight wetland plants. J Lake Science (in chinese) 27(6):1042–1048. https://doi.org/10.18307/2015.0608
Liu WJ, Zhu YG, Hu Y, Smith FA (2006) Arsenic sequestration in iron plaque, its accumulation and speciation in mature rice plants (Oryza sativa L.). Environ Sci Technol 40(18):5730–5736. https://doi.org/10.1021/es060800v
Lopez-Boado YS, Rubin BK (2008) Macrolides as immunomodulatory medications for the therapy of chronic lung diseases. Curr Opin Pharmacol 8(3):286–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2008.01.010
Luo Y, Xu L, Rysz M, Wang YQ, Zhang H, Alvarez PJJ (2011) Occurrence and transport of tetracycline, sulfonamide, quinolone, and macrolide antibiotics in the Haihe River Basin, China. Environ Sci Technol 45:1827–1833. https://doi.org/10.1021/es104009s
Managaki S, Murata A, Takada H, Tuyen B, Chiem N (2007) Distribution of macrolides, sulfonamides and trimethoprim in tropical waters: ubiquitous occurrence of veterinary antibiotics in the Mekong delta. Environ Sci Technol 41:8004–8010. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0709021
Mei X, Yang Y, Tam NFY, Li L, Wang YW (2014) Roles of root porosity, radial oxygen loss, Fe plaque formation on nutrient removal and tolerance of wetland plants to domestic wastewater. Water Res 50:147–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.12.004
Møller CL, Sand-Jensen K (2008) Iron plaques improve the oxygen supply to root meristems of the freshwater plant, Lobelia dortmanna. New Phytol 179(3):848–856. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02506.x
Otte ML, Rozema J, Koster L, Haarsma MS, Broekman RA (1989) Iron plaque on roots of Aster tripolium L: interaction with zinc uptake. New Phythol 111(2):309–317. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.1989.tb00694.x
Pecher K, Haderlein SB, Schwarzenbach RP (2002) Reduction of polyhalogenated methanes by surface-bound Fe (II) in aqueous suspensions of iron oxides. Environ Sci Technol 36(8):1734–1741. https://doi.org/10.1021/es011191o
Pi N, Tam NFY, Wong MH (2010) Effects of wastewater discharge on formation of Fe plaque on root surface and radial oxygen loss of mangrove roots. Environ Pollut 158(2):381–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2009.09.004
Pi N, Tam N, Wong MH (2011) Formation of iron plaque on mangrove roots receiving wastewater and its role in immobilization of wastewater-borne pollutants. Mar Pollut Bull 63(5):402–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.05.036
Ryan JA, Bell RM, Davidson JM, O'Connor GA (1988) Plant uptake of non-ionic organic chemicals from soils. Chemosphere 17(12):2299–2323. https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-6535(88)90142-7
Saaltink RM, Dekker SC, Eppinga MB, Griffioen J, Wassen MJ (2017) Plant-specific effects of iron-toxicity in wetlands. Plant Soil 416:83–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-017-3190-4
Sand-Jensen K, Møller CL, Raun AL (2008) Outstanding Lobelia dortmanna in iron armor. Plant Signal Behav 3(10):882–884. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.3.10.6500
Silva-Costa C, Friães A, Ramirez M, Melo-Cristino J (2012) Differences between macrolide-resistant and -susceptible streptococcus pyogenes: importance of clonal properties in addition to antibiotic consumption. Antimicrob Agents Ch 56(11):5661–5666. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01133-12
Snowden RED, Wheeler BD (1993) Iron toxicity to fen plant species. J Ecol 81:35–46. https://doi.org/10.2307/2261222
Snowden RED, Wheeler BD (1995) Chemical changes in selected wetland plant species with increasing Fe supply, with specific reference to root precipitates and Fe tolerance. New Phytol 131:503–520. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.1995.tb03087.x
Sorrell BK (1999) Effect of external oxygen demand on radial oxygen loss by Juncus roots in titanium citrate solutions. Plant Cell Environ 22:1587–1593. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3040.1999.00517.x
Su YH, Zhu YG (2007) Transport mechanisms for the uptake of organic compounds by rice (Oryza sativa ) roots. Environ Pollut 148(1):94–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2006.11.004
Su HC, Ying GG, Tao R, Zhang RQ, Zhao JL, Liu YS (2012) Class 1 and 2 integrons, sul resistance genes and antibiotic resistance in Escherichia coliisolated from Dongjiang River, South China. Environ Pollut 169:42–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2012.05.007
Syu CH, Lee CH, Jiang PY, Chen MK, Lee DY (2014) Comparison of As sequestration in iron plaque and uptake by different genotypes of rice plants grown in As-contaminated paddy soils. Plant Soil 374(1–2):411–422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1893-8
Tai YP, Tam NFY, Dai YN, Yang Y, Lin JH, Tao R, Yang YF, Wang JX, Wang R, Huang WD, Xu XD (2017) Assessment of rhizosphere processes to remove water-borne macrolide antibiotics in constructed wetlands. Plant Soil 419(1–2):489–502. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-017-3359-x
Taylor GJ, Crowder AA (1983) Use of the DCB technique for extraction of hydrous iron oxides from roots of wetland plants. Am J Bot 70(8):1254–1257. https://doi.org/10.2307/2443295
Van der Welle MEW, Smolders AJP, Op den Camp HJP, Roelofs JGM, Lamers LPM (2007) Biogeochemical interactions between iron and sulphate in freshwater wetlands and their implications for interspecific competition between aquatic macrophytes. Freshw Biol 52:434–447. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2006.01683.x
Wang T, John P (1999) Iron oxidation states on root surfaces of a wetland plant (Phragmites australis). Soil Sci Soc Am J 63:247–252. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1999.03615995006300010036x
Wang S, Wang H (2015) Adsorption behavior of antibiotic in soil environment: a critical review. Front Environ Sci Eng 9(4):565–574. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-015-0801-2
Weiss JV, Emerson D, Backer SM, Megonigal JP (2003) Enumeration of Fe(II)-oxidizing and Fe(III)-reducing bacteria in the rootzone of wetland plants: implications for a rhizosphere iron cycle. Biogeochemistry 64:77–96
Weiss JV, Emerson D, Megonigal JP (2004) Geochemical control of microbial Fe(III) reduction potential in wetlands: comparison of the rhizosphere to non-rhizosphere soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 48(1):89–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsec.2003.12.014
Wheeler BD, Al-Farraj MM, Cook RED (1985) Iron toxicity to plants in base-rich wetlands: comparative effects on the distribution and growth of Epilobium hirsutum and Juncus subnodulosus Schrank. New Phytol 100:653–669. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.1995.tb03087.x
Wu SB, Chen ZB, Braeckevelt M, Seeger EM, Dong RJ, Kästner M, Paschke H, Hahn A, Kayser G, Kuschk P (2012a) Dynamics of Fe (II), sulphur and phosphate in pilot-scale constructed wetlands treating a sulphate-rich chlorinated hydrocarbon contaminated groundwater. Water Res 46(6):1923–1932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.01.011
Wu C, Ye ZH, Wu SC, Deng D, Zhu YG, Wang MH (2012b) Do radial oxygen loss and external aeration affect iron plaque formation and arsenic accumulation and speciation in rice? J Exp Bot 63(8):2961–2970. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ers017
Xu W, Zhang G, Li XD, Zou SC, Li P, Hu ZH, Li J (2007) Occurrence and elimination of antibiotics at four sewage treatment plants in the Pearl River Delta (PRD), South China. Water Res 41(19):4526–4534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.06.023
Yan DF, Ma W, Song XJ, Bao YY (2017) The effect of iron plaque on uptake and translocation of norfloxacin in rice seedlings grown in paddy soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:7544–7554. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8368-z
Yang JF, Ying GG, Zhao JL, Tao R, Su HC, Liu YS (2011) Spatial and seasonal distribution of selected antibiotics in surface waters of the pearl rivers. China. J Environ Sci Health B 46(3):272–280. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2011.540540
Zehnder AJ, Wuhrmann K (1976) Titanium (III) citrate as a nontoxic oxidation-reduction buffering system for the culture of obligate anaerobes. Science 194(4270):1165–1166. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.793008
Zhang G, Qu J, Liu H, Liu R, Wu R (2007) Preparation and evaluation of a novel Fe-Mn binary oxide adsorbent for effective arsenite removal. Water Res 41:1921–1928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.02.009
Zhang MK, Wang LP, Zheng SA (2008) Adsorption and transport characteristics of two exterior-source antibiotics in some agricultural soils. Acta Ecologica Sinica (In Chinese) 28(2):0761–0766. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.02.038
Zhao FJ, McGrath SP, Meharg AA (2010) Arsenic as a food chain contaminant: mechanism of plant uptake and metabolism and mitigation strategies. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:535–559. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-042809-112152
Zhou H, Zeng M, Zhou X, Liao BH, Peng PQ, Hu P, Hu M, Zhu W, Wu YJ, Wu Z, Zou ZJ (2015) Heavy metal translocation and accumulation in iron plaques and plant tissues for 32 hybrid rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars. Plant Soil 386:317–329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2268-5
Acknowledgements
The research is funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51509106,51579115), the National Science Foundation for Post-doctoral Scientists of China (2015 M572410), and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (2016A030310097), and Pearl River S&T Nova Program of Guangzhou, China (201710010052). We are also grateful to all reviewers for their kind suggestion and guidance in improving writing of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gustavo Gabriel Striker.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 3570 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tai, Y., Tam, N.FY., Wang, R. et al. Iron plaque formation on wetland-plant roots accelerates removal of water-borne antibiotics. Plant Soil 433, 323–338 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3843-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3843-y