Abstract
Background and aims
There is a wide variability in plant tolerance to boron (B) toxicity, which is often associated with the ability to limit B accumulation. This study was conducted on two cultivars of sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) with different B tolerance: ‘Tigullio’, less tolerant and with green leaves; ‘Red Rubin’, more tolerant and with purple leaves. The main goal was to verify whether the greater B tolerance of ‘Red Rubin’ is attributable to an exclusion mechanism.
Methods
In three greenhouse experiments, plants were grown hydroponically with solution B concentration ranging from 0.25 (control) to 25 mg L−1.
Results
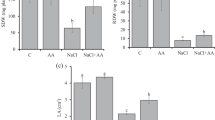
Tissue B concentration increased with increasing B supply. Boron concentrations in root and leaf tissues were comparable in ‘Tigullio’ and ‘Red Rubin’ or even higher in the purple cultivar. Boron supply did not affect the leaf concentration of total phenolic compounds and other nutrients. Leaf concentrations of total phenols and rosmarinic acid were remarkably higher in ‘Red Rubin’ than in ‘Tigullio’.
Conclusions
The greater B tolerance of ‘Red Rubin’ was associated with the ability to withstand higher concentrations of this element in plant tissues rather than to reduced B accumulation in the shoot. The high phenolic content was thought to contribute to the B tolerance of ‘Red Rubin’.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apostol KG, Zwiazek JJ (2004) Boron and water uptake in jack pine (Pinus banksiana) seedlings. Environ Exp Bot 51:145–153
Bell CF, Gallagher BC, Lott KAK, Short EL, Walton L (1991) Boric acid complexes of phenolics acids. Polyhedron 10:613–618
Bingham FT, Strong JE, Rhoades JD, Keren R (1985) An application of the Maas-Hoffman salinity response model for boron toxicity. Soil Sci Soc Am J 49:672–674
Brown PH, Hu H, Roberts WG (1999) Redefining boron toxicity symptoms in some ornamentals. Slosson Report 95–98. http://slosson.ucdavis.edu/newsletters/Brown_199829071.pdf Accessed 31 January 2015
Carmassi G, Romani M, Diara C, Massa D, Maggini R, Incrocci L, Pardossi A (2013) Response to sodium chloride salinity and excess boron in greenhouse tomato grown in semi-closed substrate culture in a Mediterranean climate. J Plant Nutr 36:1025–1042
Cervilla LM, Blasco B, Rìos JJ, Rosales MA, Rubio-Wilhelmi MM, Saàchez-Rodrìguez E, Romero L, Ruiz JM (2009) Response of nitrogen metabolism to boron toxicity in tomato plants. Plant Biol 11:671–677
del Carmen R-HM, Moreno DA, Carvajal M, del Carmen Martínez Ballesta M (2013) Interactive effects of boron and NaCl stress on water and nutrient transport in two broccoli cultivars. Funct Plant Biol 40:739–748
Dellantonio A, Schneider BU, Carter C, Fitz WJ, Grünewald H, Markovic M, Custovic H, Gruber V, Puschenreiter M, Repmann F, Zgorelec Z, Wenzel WW, Zerem N (2008) Environmental risks of farmed and barren alkaline coal ash landfills in Tuzla, Bosnia and Herzegovina. Environ Pollut 153:677–686
Edelstein M, Ben-Hur M, Cohen RL, Burger Y, Ravina I (2005) Boron and salinity effects on grafted and non-grafted melon plants. Plant Soil 269:273–284
El-Sheikh AM, Ulrich A, Awad SK, Mawardy AE (1971) Boron tolerance of squash, melon, cucumber, and corn. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 96:536–537
Eraslan F, Inal A, Gunes A, Alpaslan M (2007) Boron toxicity alters nitrate reductase activity, proline accumulation, membrane permeability, and mineral constituents of tomato and pepper plants. J Plant Nutr 30:981–994
Francois LE (1984) Effect of excess boron on tomato yield, fruit size and vegetative growth. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 109:322–324
Francois LE (1986) Effect of excess boron on broccoli, cauliflower, and radish. HortSci 111:494–498
Francois LE (1991) Yield and quality responses of garlic and onion to excess boron. HortSci 26:547–549
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:909–930
Grace SC, Logan BA (2000) Energy dissipation and radical scavenging by the plant phenylopropanoid pathway. Philos Trans R Soc Lond 35:1499–1510
Guidi L, Degl'Innocenti E, Carmassi G, Massa D, Pardossi A (2011) Effects of boron on leaf chlorophyll fluorescence of greenhouse tomato grown with saline water. Environ Exp Bot 73:57–63
Günes A, Alpaslan M (2008) Boron uptake and toxicity in maize genotypes in relation to boron and phosphorus supply. J Plant Nutr 23:541–550
Hale KL, McGrath S, Lombi E, Stack S, Terry N, Pickering IJ, George GN, Pilon-Smits EAH (2001) Molybdenum sequestration in Brassica: a role for anthocyanins? Plant Physiol 126:1391–1402
Hale KL, Tufan HA, Pickering IJ, George GN, Terry N, Pilon M, Pilon-Smits EAH (2002) Anthocyanins facilitate tungsten accumulation in Brassica. Physiol Plant 836(116):351–358
Hayes JE, Reid RJ (2004) Boron tolerance in barley is mediated by efflux of boron from the roots. Plant Physiol 136:3376–3382
Inal A, Tarakcioglu C (2001) Effects of nitrogen forms on growth, nitrate accumulation, membrane permeability, and nitrogen use efficiency of hydroponically grown bunch onion under boron deficiency and toxicity. J Plant Nutr 24:1521–1534
Javanmardi J, Khalighi A, Kashi A, Bais HP, Vivanco JM (2002) Chemical characterization of basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) found in local accessions and used in traditional medicines in Iran. J Agric Food Chem 50:5878–5883
Kang HM, Saltveit ME (2002) Antyoxidant capacity of lettuce leaf tissue increases after wounding. J Agric Food Chem 50:7536–7541
Kaya G, Tuna AL, Dikilitas M, Ashraf M, Koskeroglu S, Guneri M (2009) Supplementary phosphorus can alleviate boron toxicity in tomato. Sci Hortic 121:284–288
Keles Y, Öncel Y, Yenice N (2004) Relationship between boron content and antioxidant compounds in Citrus leaves taken from fields with different water source. Plant Soil 265:345–353
Kiferle C, Lucchesini M, Mensuali Sodi A, Maggini R, Raffaelli A, Pardossi A (2011) Rosmarinic acid content in basil plants grown in vitro and in hydroponics. Cent Eur J Biol 6:946–957
Kiferle C, Lucchesini M, Maggini R, Pardossi A, Mensuali Sodi A (2014) Gas exchanges, growth and rosmarinic acid production of in vitro sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum L.). Biol Plant 58:601–610
Landi M, Degl'innocenti E, Pardossi A, Guidi L (2012) Antioxidant and photosynthetic responses in plants under boron toxicity: a review. Am J Agric Biol Sci 7:255–270
Landi M, Pardossi A, Remorini D, Guidi L (2013a) Antioxidant and photosynthetic response of a purple-leafed and a green-leafed cultivar of sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum) to boron excess. Environ Exp Bot 85:64–75
Landi M, Remorini D, Pardossi A, Guidi L (2013b) Boron excess affects photosynthesis and antioxidant apparatus of greenhouse Cucurbita pepo and Cucumis sativus. J Plant Res 26:775–786
Landi M, Guidi L, Pardossi A, Tattini M, Gould KS (2014) Photoprotection by foliar anthocyanins mitigates effects of boron toxicity in sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum). Planta 240:941–953
Landi M, Tattini M, Gould KS (2015) Multiple functional roles of anthocyanins in plant-environment interactions. Environ Exp Bot. doi:10.1016/j.envexpbot.2015.05.012
Maas EV (1984) Salt tolerance of plants. In: Christie BR (ed) Handbook of plant science. CRC Press, Cleveland
Maas EV, Hoffman GJ (1977) Crop salt tolerance - current assessment. J Irrig Drain Eng 103:115–134
Magán JJ, Gallardo M, Thompson RB, Lorenzo P (2008) Effects of salinity on fruit yield and quality of tomato grown in soil-less culture in greenhouses in Mediterranean climatic conditions. Agric Water Manag 95:1041–1055
Mahboobi H, Yücel M, Öktem HA (2002) Nitrate reductase and glutamate dehydrogenase activities of resistant and sensitive cultivars of wheat and barley under boron toxicity. J Plant Nutr 25:1829–1837
Majkowska-Gadomska J, Arcichowska K, Wierzbicka B (2009) Nitrate content of the edible parts of vegetables and spice plants. Acta Sci Pol Hort Cultus 8:25–35
Makri O, Kintzios K (2007) Ocimum sp. (Basil): botany, cultivation, pharmaceutical properties, and biotechnology. J Herbs Spices Med Plants 13:123–150
Nable RO, Bañuelos GS, Paull JG (1997) Boron toxicity. Plant Soil 193:181–198
Nguyen P, Niemeyer E (2008) Effects of nitrogen fertilization on the phenolic composition and antioxidant properties of basil (Ocimum basilicum L.). J Agric Food Chem 56:8685–8691
Ochiai K, Uemura S, Shimizu A, Okumoto Y, Matoh T (2008) Boron toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). I. Quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis of tolerance to boron toxicity. Theor Appl Genet 117:125–133
Orsini F, De Pascale S (2007) Daily variation in leaf nitrate content of two cultivars of hydroponically grown basil. Acta Horticult 747:203–210
Pang Y, Li L, Ren F, Lu P, Pi W, Cai J, Xin L, Zhang J, Chen J, Wang X (2010) Overexpression of the tonoplast aquaporin AtTIP5;1 conferred tolerance to boron toxicity in Arabidopsis. J Genet Genomics 37:389–397
Petersen M, Simmonds MSJ (2003) Molecules of interest: rosmarinic acid. Phytochemistry 62:121–125
Rees R, Robinson BH, Menon M, Lehmann E, Gunthardt-Goerg MS, Schulin R (2011) Boron accumulation and toxicity in hybrid poplar (Popolus nigra x Euroamericana). Environ Sci Technol 45:10536–10543
Reid R (2007) Identification of boron transporter genes likely to be responsible for tolerance to boron toxicity in wheat and barley. Plant Cell Physiol 48:1673–1678
Reid R (2014) Understanding the boron transport network in plants. Plant Soil 385:1–13
Reid R, Fitzpatrick K (2009) Influence of leaf tolerance mechanisms and rain on boron toxicity in barley and wheat. Plant Physiol 151:413–420
Reid R, Hajes JE, Post A, Stangoulis JCR, Graham RD (2004) A critical analysis of the causes of boron toxicity in plants. Plant Cell Environ 25:1405–1414
Rojas-Lillo Y, Alberdi M, Acevedo P, Inostroza-Blancheteau C, Rengel Z, Mora MDLL, Reyes-Díaz M (2014) Manganese toxicity and UV-B radiation differentially influence the physiology and biochemistry of highbush blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum) cultivars. Funct Plant Biol 41:156–167
Santamaria P (2006) Nitrate in vegetables: toxicity, content, intake and EC regulation. J Sci Food Agric 86:10–17
Schurr U (1998) Xylem sap sampling: new approaches to an old topic. Trends Plant Sci 3:293–298
Schurr U, Schulze ED (1995) The concentration of xylem sap constituents in root exudate, and in sap from intact, transpiring castor bean plants (Ricinus communis L.). Plant Cell Environ 18:409–420
Sgherri C, Cecconami S, Pinzino C, Navari-Izzo F, Izzo R (2010) Levels of antioxidants and nutraceuticals in basil grown in hydroponics and soil. Food Chem 123:416–422
Simón I, Díaz-López L, Gimeno V, Nieves M, Pereira WE, Martínez V, Lidon V, García-Sánchez F (2013) Effects of boron excess in nutrient solution on growth, mineral nutrition, and physiological parameters of Jatropha curcas seedlings. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 176:165–174
Smith TE, Grattan SR, Grieve CM, Poss JA, Suarez DL (2010) Salinity’s influence on boron toxicity in broccoli: II. Impacts on boron uptake, uptake mechanisms and tissue ion relations. Agric Water Manag 97:783–791
Smith TE, Grattan SR, Grieve CM, Poss JA, Läuchli AE, Suarez DL (2013) pH dependent salinity-boron interactions impact yield, biomass, evapotranspiration and boron uptake in broccoli (Brassica oleracea L.). Plant Soil 370:541–554
Sonneveld C, Voogt W (2009) Plant nutrition of greenhouse crops. Springer, New York
Stiles A, Bautista D, Atalay E, Babaoglu M, Terry N (2010) Mechanisms of boron tolerance and accumulation in plants: a physiological comparison of the extremely boron-tolerant plant species, Puccinelliadistans, with the moderately boron-tolerant Gypsophila arrostil. Environ Sci Technol 44:7089–7095
Tattini M, Landi M, Brunetti C, Giordano C, Remorini GKS, Guidi L (2014) Epidermal coumaroyl anthocyanins protect sweet basil against excess light stress: multiple consequences of light attenuation. Physiol Plant 152:585–598
Tesi R, Ghiselli L, Tallarico R (1995) Accumulo di nitrati nel basilico (Ocimum basilicum L.) in rapporto a diversi fattori colturali. Italus Hortus 2:43–48
Umar AS, Iqbal M (2007) Nitrate accumulation in plants, factors affecting the process, and human health implications. a review. Agron Sustain Dev 27:45–57
Vlamis J, Ulrich A (1973) Boron tolerance of sugar beets in relation to the growth and boron content of tissues. J Am Soc Sugar Beet Technol 17:280–288
Wang R, Liu G, Liu L, Jiang C (2014) Relationship between leaf chlorosis and different boron forms in Trifoliate orange seedlings under excessive boron supply. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 60:325–332
Wimmer MA, Goldbach HE (2007) Boron in the apoplast of higher plants. In: Sattelmacher A, Horst A (eds) The apoplast of higher plants: compartment of storage, transport and reactions. Springer, New York, pp 19–32
Zheljazkov VD, Warman PR (2003) Application of high Cu compost to Swiss chard and basil. Sci Total Environ 302:13–26
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by MIUR-PRIN 2009 (Ministero dell’Istruzione, dell’Università e della Ricerca, Italy, Project “Physiological response of vegetables crops to excess boron”). We thank the reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Yong Chao Liang .
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pardossi, A., Romani, M., Carmassi, G. et al. Boron accumulation and tolerance in sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) with green or purple leaves. Plant Soil 395, 375–389 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2571-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2571-9