Abstract
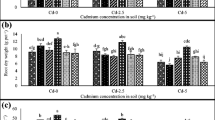
Cadmium concentration in durum (Triticum durum L.) grain may be influenced by fertilizer management. A three year field study was conducted at two locations in southwestern Manitoba, Canada, to determine the effect of source, timing and placement of N fertilizer on grain Cd concentration of durum wheat under reduced-tillage (RT) and conventional-tillage (CT) management. There was a significant year-to-year variation in grain yield and grain Cd concentration, indicating a strong effect of environment on phytoavailability of Cd. Soil type also had a dominating effect on Cd in durum grain. Grain Cd concentration and accumulation were always lower at the Newdale clay loam (CL) location than the Stockton fine sandy loam (FSL) location. Compared to CT, RT management decreased grain Cd concentration and accumulation. Application of N fertilizer significantly increased grain Cd concentration and decreased grain Zn concentration. The increase in grain Cd could be due to the increasing Cd concentration in soil solution, the improved crop growth, or a competitive interaction between Cd and Zn for binding sites in the soil system and for uptake sites in the roots, following the application of N fertilizer. Time, source and placement of N fertilization showed inconsistent effect on grain yield and grain Cd concentration. The effects when observed were minor compared to effects of year and soil type on grain Cd concentration. Application of anhydrous ammonia (NH3) generally resulted in higher Cd concentration in durum grain than application of same level of other N sources including urea ammonium nitrate (UAN), urea and ammonium nitrate (AN), probably due to greater N efficiency from the NH3 as compared to the other sources. Where differences due to placement occurred, banded application of fertilizers generally resulted in higher Cd concentration in durum grain than did dual-banded placement, indicating a higher fertilizer availability. Soil type, year and N fertilization greatly affected concentration of Cd in durum grain. Selection of a suitable source, timing and placement combination of N fertilization is important in optimizing crop yield and minimizing grain Cd concentration.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CT:
-
conventional-tillage
- RT:
-
reduced-tillage
- CL:
-
clay loam
- FSL:
-
fine sandy loam
- NH3 :
-
anhydrous ammonia
- UAN:
-
urea ammonium nitrate
- AN:
-
ammonium nitrate
References
Alloway BJ, Morgan H (1986) The behaviour and availability of Cd, Ni and Pb in polluted soils. In: Assink JW, Van den Brink WJ (eds) Contaminated Soil. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, pp 101–113
Andersson A, Siman G (1991) Levels of Cd and some other trace elements in soils and crops as influenced by lime and fertilizer level. Acta Agric Scand 41:3–11
Bandel VA, Dzienia S, Stanford G (1980) Comparisons of N fertilizers for no-till corn. Agron J 72:337–341
Brennan RF (1996) Availability of previous and current applications of zinc fertilizer using single superphosphate for the grain production of wheat on soils of South Western Australia. J Plant Nutr 19:1099–1115
Brown KR, Grant CA, Racz GJ (1994) The effect of nitrogen source, rate and placement on Cd bioavailability, Papers presented at the 37th Annual Manitoba Society of Soil Science Meeting Winnipeg, 4 and 5 January 1994, pp. 167–175
Carefoot JM, Nyborg M, Lindwall CW (1990) Tillageinduced soil changes and related grain yield in a semi-arid region. Can J Soil Sci 70:203–214
Carter MR (1993) Soil sampling and methods of analysis. Lewis, Lewis
Codex General Standard for Contaminants and Toxins in Foods (2009) CODEX STAN 193-1995, Rev. 5
Cox WJ, Zobel RW, van Es HM, Otis DJ (1990) Tillage effects on some soil physical and corn physiological characteristics. Agron J 82:806–812
Das P, Samantaray S, Rout GR (1997) Studies on cadmium toxicity in plants: a review. Environ Pollut 98:29–36
Eriksson J (1990) Factors influencing adsorption and plant uptake of cadmium from agricultural soils. Department of Soil Sciences Reports and Dissertations. Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, Uppsala, Sweden, p 29
Florijn PJ, Nelemans JA, van Beusichem ML (1992) The influence of the form of nitrogen nutrition on uptake and distribution of cadmium in lettuce varieties. J Plant Nutr 15:2405–2416
Gao X, Akhter F, Tenuta M, Flaten DN, Gawalko EJ, Grant CA (2010) Mycorrhizal colonization and grain Cd concentration of field-grown durum wheat in response to tillage, preceding crop and phosphorus fertilization. J Sci Food Agric 90:750–758
Grant CA, Bailey LD (1998) Nitrogen, phosphorus and zinc management effects on grain yield and cadmium concentration in two cultivars of durum wheat. Can J Plant Sci 78:63–70
Grant CA, Bailey LD, Therrien MC (1996) Effect of N, P, and KCl fertilizers on grain yield and Cd concentration of malting barley. Fertil Res 45:153–161
Grant CA, Bailey LD, McLaughlin MJ, Singh BR (1999) Management factors which influence cadmium concentration in crops. In: McLaughlin MJ, Singh BR (eds) Cadmium in soils and plants. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 151–198
Grant CA, Brown KR, Racz GJ, Bailey LD (2001) Influence of source, timing and placement of nitrogen on grain yield and nitrogen removal of durum wheat under reduced and conventional-tillage management. Can J Plant Sci 81:17–27
Grant CA, Clarke JM, Duguid S, Chaney RL (2008) Selection and breeding of plant cultivars to minimize cadmium accumulation. Sci Total Environ 390:301–310
Grant CA, Monreal MA, Irvine RB, Mohr RM, Mclaren DL, Khakbazan M (2010) Preceding crop and phosphorus fertilization affect cadmium and zinc concentration of flaxseed under conventional and reduced tillage. Plant Soil 333:337–350
He QB, Singh BR (1994) Crop uptake of Cd from phosphate fertilizers I.Yield and Cd content. Water Air Soil Pollut 74:251–65
Högbom L, Nohrstedt HÖ, Nordlund S (2001) Nitrogen fertilization effects on stream water cadmium concentration. J Environ Qual 30:189–193
International Grains Council (2003) Grain Market Report [Online]. Available: http://www.igc.org.uk/en/publications/default.aspx (4 January 2010)
Jansson G (2002) Cadmium in Arable Crops: The Influence of Soil Factors and Liming. Ph.D. thesis, Department of Soil Sciences, The Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, Uppsala, ISBN 91-576-6192-8
Kamewada K, Nakayama M (2009) Cadmium uptake by garland chrysanthemum can be predicted from the cadmium in the soil solution, independent of soil type. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 55:441–451
Karlen DL, Sharpley AN (1994) Management strategies for sustainable soil fertility. In: Hatfield JL, Karlen DL (eds) Sustainable agricultural systems. CRC, Boca Raton, pp 47–108
Krishnamurti GSR, Huang PM, Van Rees KCJ, Kozak LM, Rostad HPW (1994) Microwave digestion for detection of total cadmium in soils. Comm Soil Sci Plant Anal 25:615–625
Kutman UB, Yildiz B, Ozturk L, Cakmak I (2010) Biofortification of durum wheat with zinc through soil and foliar applications of nitrogen. Cereal Chem 87:1–9
Lindsay WL, Norvell WA (1978) Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese, and copper. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42:421–428
Lott JNA, Buttrose MS (1978) Globoids in protein bodies of legume seed cotyledons. Aust J Plant Physiol 5:89–111
Malhi SS, Nyborg M, Solberg ED (1996) Influence of source, method of placement and simulated rainfall on the recovery of 15N-labeled fertilizers under zero tillage. Can J Soil Sci 76:93–100
Mitchell L, Grant C, Racz G (2000) Effect of nitrogen application on concentration of cadmium and nutrient ions in soil solution and in durum wheat. Can J Soil Sci 80:107–115
Oliver DP, Schultz JE, Tiller KG, Merry RH (1993) The effect of crop rotations and tillage practices on cadmium concentrations in wheat grain. Aust J Agric Res 44:1221–1234
Olsson IM, Eriksson J, Öborn I, Skerfving S, Oskarsson A (2005) Cadmium in food production systems - a health risk for sensitive population groups. Ambio 34:344–351
Perilli P, Mitchell LG, Grant CA, Pisante M (2010) Cadmium concentration in durum wheat grain (Triticum turgidum) as influenced by nitrogen rate, seeding date and soil type. J Sci Food Agric 90:813–822
Reuter DJ, Robinson JB, Dutkiewicz C (1997) Plant analysis: an interpretation manual, 2nd edn. Springer, Netherlands
Sauvé S, Hendershot W, Allen HE (2000) Solid-sohitiun partitioning of metals in contaminated soils: dependence on pH, total metal burden, and organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 34:1125–113l
Selles F, Zentner RP, Lafond GP, Janzen HH (1996) Effect of fertilizer management on grain cadmium. In: Proceeding of the 33rd Annual Alberta Soil Science Workshop. Convention Inn, Edmonton, AB, 20–22 Feb 1996, pp 130–135
Shi RL, Zhang YQ, Chen XP, Sun QP, Zhang FS, Römheld ZCQ (2010) Influence of long-term introgen fertilization on micronutrient density in grain of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Cereal Sci 51:165–170
Singh B, Kumar V, Antil RS, Ahlawat VS (1992) Cadmium intake by wheat as influenced by nitrogen and FYM application in sandy soil. Crop Res 5:243–248
Smettem KRJ, Rovira AD, Wace SA, Wilson BR, Simon A (1992) Effect of tillage and crop rotation on the surface stability and chemical properties of a red-brown earth (Alfisol) under wheat. Soil Tillage Res 22:27–40
Tiessen H, Moir JO (1993) Total organic carbon. In: Carter MR (ed) Soil sampling and methods of analysis. Lewis, Lewis, pp 187–200
Wångstrand H, Eriksson J, Öborn I (2007) Cadmium concentration in winter wheat as affected by nitrogen fertilization. Euro J Agron 26:209–214
Welch RM (1986) Effects of nutrient deficiencies on seed production and quality. Adv Plant Nutr 2:205–247
Westman RL (1990) Soil testing and plant analysis. Soil Science Society of America, Madison
Willaert G, Verloo M (1992) Effect of various nitrogen fertilizers on the chemical and biological activity of major and trace elements in a cadmium contaminated soil. Pédologie 43:83–91
Wolnick KA, Fricke FL, Capar SG, Braude GL, Meyer MW, Satzger RD, Bonnin E (1983) Elements in major raw agricultural crops in the United States. 1. Cadmium and lead in lettuce, peanuts, potatoes, soybeans, sweet corn and wheat. J Agr Food Chem 31:1240–1244
Xie HL, Jiang RF, Zhang FS, McGrath SP, Zhao FJ (2009) Effect of nitrogen form on the rhizosphere dynamics and uptake of cadmium and zinc by the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. Plant Soil 318:205–215
Zebarth BJ, Warren CJ, Sheard RW (1992) Influence of the rate of nitrogen fertilization on the mineral content of winter wheat in Ontario. J Agr Food Chem 40:1528–1530
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) of Canada, Metals in the Human Environment (MITHE) Research Network, the Fluid Fertilizer Foundation, International Plant Nutrition Institute, and the Program for Energy Research and Development. The technical assistance of Josh Price, Brian Hadley and Mike Svistovski is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Fangjie Zhao.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, X., Brown, K.R., Racz, G.J. et al. Concentration of cadmium in durum wheat as affected by time, source and placement of nitrogen fertilization under reduced and conventional-tillage management. Plant Soil 337, 341–354 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-010-0531-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-010-0531-y