Abstract
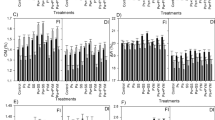
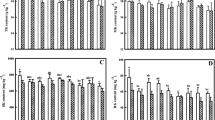
A three-year field study, conducted on two Orthic Black Chernozemic soils, investigated the effects of application of N, P and KCl fertilizers on grain yield and Cd concentration of two cultivars of malting barley (Hordeum vulgare). Soil levels of N and P were good predictors of the likelihood of a yield response to fertilizer applications, while increases in yield with potassium chloride (KCl) application occurred in spite of high levels of soil K. Additions of ammonium nitrate increased Cd concentration in malting barley when soil nitrate levels were low, with increased Cd concentrations in the grain generally being associated with increasing crop yields. Applications of monoammonium phosphate or KCl tended to increase concentrations of Cd in malting barley, with the significance of the effect varying from year to year. Response of Cd concentration in the grain to P and KCl application was not related to levels of these nutrients in the soil. As the N and K fertilizer used in the study did not contain significant quantities of Cd, the increase in Cd concentration in the grain with fertilizer application was not solely a result of Cd addition as a fertilizer contaminant. The fertilizer salts may increase Cd concentration in the soil solution, increasing availability for crop uptake. Increased crop yield associated with N application may also increase Cd accumulation through increased root interception and enhanced mass flow.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson A (1976) On the influence of manure and fertilizers on the distribution and amounts of plant-available Cd in soils. Swed J Agric 6:27–36
Andersson A & Siman G (1991) Levels of Cd and some other trace elements in soils and crops as influenced by lime and fertilizer level. Acta Agric Scand 41: 3–11
Anonymous (1992) Guide to chemical Control of Weeds and Plant Diseases. Manitoba Agriculture, Winnipeg USA. 150 p
Bailey VL, Grant CA Racz GJ & Bailey LD (1995) A practical method for assessing cadmium levels in soil using the DTPA extraction technique with graphite furnace analysis. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 26:961–968
Carter MR (1993) Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, USA. 823
Doner HE (1978) Chloride as a factor in mobilities of N1 (II), Cu (II), and Cd (II) in soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42:882–885
Eriksson JE (1990) Factors influencing adsorption and plant uptake of cadmium from agricultural soils. Reports and Dissertations 4. Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, Dept of Soil Sciences Uppsala, Sweden.
Fixen PE, Gelderman RH, Gerwing JR & Cholick FA (1986a) Response of spring wheat, barley and oats to chloride in potassium chloride fertilizers. Agron J 78:664–668
Fixen PE, Buchenau GW, Gelderman RH Schumacher TE, Gerwing JR, Cholick FA & Farber BG (1986b) Influence of soil and applied chloride on several wheat parameters. Agron J 78:736–740
Hahne HCH & Kroontje W (1973) Significance of pH and chloride concentration on behavior of heavy metal pollutants: mercury (II), cadmium (II), Zinc (II) and lead (II). J Environ Qual 2:444–450
He QB & Singh BR (1994) Crop uptake of cadmium from phosphorus fertilizer: 1. Yield and cadmium content. Water Air Soil Pollut 74:251–265
Jackson AP & Alloway BJ (1992) The transfer of cadmium from agricultural soils to the human food chain. In: Adriano DC (ed) Biogeochemistry of Trace Metals. Advances in Trace Substance Research, pp 109–150. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, USA
John MK (1976) Interrelations between plant cadmium and uptake of other elements from culture solution. Environ Pollut 11:85–95
Kuboi T, Noguchi A & Yazaki J (1986) Family-dependent cadmium accumulation characteristics in higher plants. Plant Soil 92:405–41
Lorenz SE, Hamon RE, McGrath SP, Holm PE & Christensen TH (1994) Application of fertilizer cations affect cadmium and zinc concentrations in soil solutions and uptake by plants. Eur J Soil Sci 45:159–165
Mortvedt JJ (1987) Cadmium levels in soils and plants from some long-term soil fertility experiments in the United States of America. J Environ Qual 16:137–142
Naidu R, Bolan NS, Kookana RS & Tiller KG (1994) Ionic-strength and pH effects on the sorption of cadmium and the surface charge of soils. Eur J Soil Sci 45:419–429
Sparrow LA, Salardini AA & Johnstone J (1994) Field studies of cadmium in potatoes (Solanum tuberosum L.) III. Response of cv. Russet Burbank to sources of banded potassium. Aust J Agric Res 45:243–249
Statistical Analysis Systems, Inc. (1985) SAS User's Guide: Statistics. Version 5. SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC, USA 957p
Therrien MC, Carmichael CA, Noll JS & Grant CA (1994) Effect of fertilizer management, genotype, and environmental factors on some malting quality characteristics in barley. Can J Plant Sci 74:545–547
Tu S & Racz GJ (1994) Effect on KCl on bioavailability of manganese. Can J Soil Sci 74:93–98
Williams CH & David DJ (1976) The accumulation in soil of cadmium residues from phosphate fertilizers and their effect on the cadmium content of plants. Soil Sci 121:86–93
World Health Organization (1972) Evaluation of certain food additions and of the contaminants mercury, lead and cadmium. FAO Nutrition Meetings Report Series No. 51. WHO Technical Report Series 505. Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations, Rome, Italy. 33p
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grant, C.A., Bailey, L.D. & Therrien, M.C. The effect of N, P and KCl fertilizers on grain yield and Cd concentration of malting barley. Fertilizer Research 45, 153–161 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00790665
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00790665