Abstract
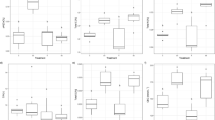
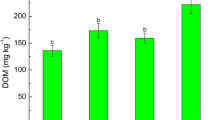
Contamination of agricultural topsoils with Cd above guideline values is of concern in many countries throughout the world. Extraction of metals from contaminated soils using high-biomass, metal-accumulating Salix sp. has been proposed as a low-cost, gentle remediation strategy, but reasonable phytoextraction rates remain to be demonstrated. In an outdoor pot experiment we assessed the phytoextraction potential for Cd and Zn of four willow species (Salix caprea, S. fragilis, S. × smithiana, S. × dasyclados) and intercropping of S. caprea with the hyperaccumulator Arabidopsis halleri on three moderately contaminated, agricultural soils. Large concentrations of Cd (250 mg kg−1) and Zn (3,300 mg kg−1) were determined in leaves of Salix × smithiana grown on a soil containing 13.4 mg kg−1 Cd and 955 mg kg−1 Zn, resulting in bioaccumulation factors of 27 (Cd) and 3 (Zn). Total removal of up to 20% Cd and 5% Zn after three vegetation periods were shown for Salix × smithiana closely followed by S. caprea, S. fragilis and S. × dasyclados. While total Cd concentrations in soils were reduced by up to 20%, 1 M NH4NO3-extractable metal concentrations did not significantly decrease within 3 years. Intercropping of S. caprea and A. halleri partly increased total removal of Zn, but did not enhance total Cd extraction compared to single plantings of S. caprea after two vegetation periods.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker AJM, McGrath SP, Reeves RD, Smith JAC (2000) Metal hyperaccumulator plants: a review of the ecology and physiology of a biochemical resource for phytoremediation of metal-polluted soils. In: Terry N, Bañuelos G, Vangronsveld J (eds) Phytoremediation of contaminated soil and water. Lewis, Boca Raton, pp 85–107
Brooks RR (1998) Plants that hyperaccumulate heavy metals. CAB international Wallingford
Cherian S, Oliveira MM (2005) Transgenic plants in phytoremediation: recent advances and new possibilities. Environ Sci Technol 39:9377–9390
Dos Santos Utmazian MN, Wenzel WW (2007) Cadmium and zinc accumulation in willow and poplar species grown on polluted soils. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 170:265–272
Dos Santos Utmazian MN, Wieshammer G, Vega R, Wenzel WW (2007) Hydroponic screening for metal resistance and accumulation of cadmium and zinc in twenty clones of willows and poplars. Environ Pollut 148:155–165
Felix H (1997) Field trials for in situ decontamination of heavy metal polluted soils using crops of metal-accumulating plants. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 160:525–529
Fischerová Z, Tlustoš P, Száková J, Šicherorová K (2006) A comparison of phytoremediation capability of selected plant species for given trace elements. Environ Pollut 144:93–100
Fitz WJ, Wenzel WW, Zhang H, Nurmi J, Stipek K, Fischerova Z, Schweiger P, Köllersperger G, Ma LQ, Stingeder G (2003) Rhizosphere characteristics of the arsenic hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata L. and monitoring of phytoremoval efficiency. Environ Sci Technol 37:5008–5014
Gove B, Hutchinson JJ, Young SD, Craigon J, McGrath SP (2002) Uptake of metals by plants sharing a rhizosphere with the hyperaccumualator Thlaspi caerulescens. Int J Phytoremediat 4:267–281
Granel T, Robinson B, Mills T, Clothier B, Green S, Fung L (2002) Cadmium accumulation by willow clones used for soil conservation, stock fodder and phytoremediation. Aust J Soil Res 40:1331–1337
Hammer D, Kayser A, Keller C (2003) Phytoextraction of Cd and Zn with S. viminalis in field trials. Soil Use Manage 19:187–192
Kayser A, Wenger K, Keller W, Attinger W, Felix HR, Gupta SK, Schulin R (2000) Enhancement of phytoextraction of Zn, Cd and Cu from calcareous soil: the use of NTA and sulfur amendments. Environ Sci Technol 34:1778–1783
Keller C, Hammer D, Kayser A, Richner W, Brodbeck M, Sennhauser M (2003) Root development and heavy metal phytoextraction efficiency: comparison of different plant species in the field. Plant Soil 249:67–81
Klang-Westin E, Perttu K (2002) Effect of nutrient supply and soil cadmium concentration on cadmium removal by willow. Biomass Bioenergy 23:415–426
Klang-Westin E, Eriksson J (2003) Potential of Salix as phytoextractor for Cd on moderately contaminated soils. Plant Soil 249:127–137
Küpper H, Lombi E, Zhao F, McGrath SP (2000) Cellular compartmentation of cadmium and zinc in relation to other elements in the hyperaccumulator Arabidopsis halleri. Planta 212:75–84
Landberg T, Greger M (1996) Differences in uptake and tolerance to heavy metals in Salix from unpolluted and polluted areas. Appl Geochem 11:175–180
McGrath SP, Zhao FJ, Lombi E (2001) Plant and rhizosphere processes involved in phytoremediation of metal-contaminated soils. Plant Soil 232:207–214
McGrath SP, Lombi E, Gray CW, Caille N, Dunham SJ, Zhao FJ (2006) Field evaluation of Cd and Zn phytoextraction potential by the hyperaccumulators Thlaspi caerulescens and Arabidopsis halleri. Environ Pollut 141:115–125
Menzies NW, Donn MJ, Kopittke PM (2007) Evaluation of extractants for estimation of the phytoavailable trace metals in soils. Environ Pollut 145:121–130
ÖNORM L 1075 (2003) Österreichisches Normungsinstitut, Grundlagen für die Bewertung der Gehalte ausgewählter Elemente in Böden
ÖNORM L 1085 (1999) Österreichisches Normungsinstitut, Chemische Bodenuntersuchungen. Säureextrakt zur Bestimmung von Nähr- und Schadelementen
ÖNORM L 1094 (1999) Österreichisches Normungsinstitut. Chemische Bodenuntersuchungen. Extraktion von Spurenelementen mit Ammoniumnitratlösung
Pulford ID, Watson C (2002) Phytoremediation of heavy metal-contaminated land by trees – a review. Environ Int 29:529–540
Pulford ID, Dickinson NM (2005) Phytoremediation technologies using trees. In: Prasad MNV, Sajwan KS, Naidu R (eds) Trace elements in the environment. Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, pp 375–395
Riddell-Black D, Pulford ID, Stewart C (1997) Clonal variation of heavy metal uptake by willow. Asp Appl Biol 49:327–334
Rosselli W, Keller C, Boschi K (2003) Phytoextraction capacity of trees growing on a metal contaminated soil. Plant Soil 256:265–272
Vandecasteele B, Meers E, Vervaeke P, De Vos B, Quataert P, Tack FMG (2005) Growth and trace metal accumulation of two Salix clones on sediment-derived soils with increasing contamination levels. Chemosphere 58:995–1002
Vervaeke P, Luyssaert S, Mertens J, Meers E, Tack FMG, Lust N (2003) Phytoremediation prospects of willow stands on contaminated sediment: a field trial. Environ Pollut 126:275–282
Vollenweider P, Günthardt-Goerg MS (2005) Diagnosis of abiotic and biotic stress factors using the visible symptoms in foliage. Environ Pollut 137:455–465
Vyslouzilová M, Tlustoš P, Száková J, Pavlíková D (2003) As, Cd, Pb and Zn uptake by Salix ssp. clones grown in soils enriched by high loads of these elements. Plant Soil Environ 49:191–196
Vyslouzilová M, Puschenreiter M, Wieshammer G, Wenzel WW (2006) Rhizosphere chracteristics, heavy metal accumulation and growth performance of two willow (Salix × rubens) clones. Plant Soil Environ 52:353–361
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge financial support for this study by the Austrian Federal Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, Environment and Water Management (INTERLAND-Project Package 3). We thank two anonymous reviewers for valuable comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Fangjie J. Zhao.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wieshammer, G., Unterbrunner, R., García, T.B. et al. Phytoextraction of Cd and Zn from agricultural soils by Salix ssp. and intercropping of Salix caprea and Arabidopsis halleri . Plant Soil 298, 255–264 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-007-9363-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-007-9363-9