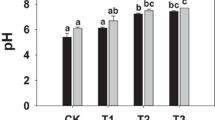
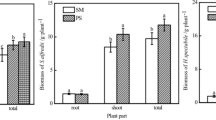
Abstract
Intercropping of specific accumulators with industrial crops is used in moderately metal contaminated agricultural land. The distribution characteristics and environmental risks of non-accumulated ions in intercropping fields have rarely been reported. This study analyzed dissolved organic matter (DOM) fractionation and metal chemical forms to investigate the bioavailability, transformation, and uptake of non-hyperaccumulated metals in different cultivation patterns of a Cd hyperaccumulator (Sedum alfredii Hance) and a commercial crop (Cicer arietinum L.). The study focused on the distribution and transformation of heavy metals, with a particular emphasis on the role of DOM in intercropping. The contents of DOM in the rhizosphere soils of the Cd hyperaccumulator monoculture and the intercropping field were obviously greater than the DOM concentration in the commercial crop monoculture. The content of soluble Cd was significantly lower in the former two planting patterns than in the latter. In contrast, soluble Pb and Cu exhibited opposite content characteristics. In addition, the metal extraction ability of DOM extracted from the C. arietinum monoculture was lower than those from the Cd hyperaccumulator monoculture and the intercropping field. The concentrations of Cd in both below-ground and aerial parts of C. arietinum intercropping were significantly lower than those in its monoculture, since S. alfredii depleted soil Cd. Contrastingly, the contents of Cu and Pb in C. arietinum harvested from intercropping were significantly greater than those in its monoculture because the intercropped Cd hyperaccumulator activated Cu and Pb by changing soil DOM content and fractionations without absorbing them. The findings provide valuable insights into the use of intercropping to remediate moderately metal-contaminated agricultural land and highlight the potential risks associated with intercropping in multi-metal-contaminated fields.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Anando SN, Sakhen S, Sonika Y, Jeti K (2021) Enhancing pulse productivity under rice based production system through chickpea and lentil based intercropping systems in North East India. Legum Res 44:215–220. https://doi.org/10.18805/LR-4203
Baldantoni D, Cicatelli A, Bellino A, Castiglione S (2014) Different behaviours in phytoremediation capacity of two heavy metal tolerant poplar clones in relation to iron and other trace elements. J Environ Manage 146:94–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.07.045
Banik P, Midya A, Sarkar BK, Ghose SS (2006) Wheat and chickpea intercropping systems in an additive series experiment: advantages and weed smothering. Eur J Agron 24:325–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2005.10.010
Burges A, Epelde L, Blanco F, Becerril JM, Garbisu C (2017) Ecosystem services and plant physiological status during endophyte-assisted phytoremediation of metal contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 584–585:329–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.12.146
Cao B, Jiang Z, Li J, Zhang X, Hu Y, Chen J, Zhang Y (2018) Different dissolved organic matter (DOM) characteristics lead to diverse atrazine adsorption traits on the non-rhizosphere and rhizosphere soil of Pennisetum americanum (L.) K. Schum. Chemosphere 209:608–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.06.069
Chen Y, Shi J, Tian X, Jia Z, Wang S, Chen J, Zhu W (2018) Impact of dissolved organic matter on Zn extractability and transfer in calcareous soil with maize straw amendment. J Soil Sediment 19:774–784. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-2060-x
Christensen JB, Christensen TH (2000) The effect of pH on the complexation of Cd, Ni and Zn by dissolved organic carbon from leachate-polluted groundwater. Water Res 34:3743–3754. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00127-5
Conesa HM, Moradi AB, Robinson BH, Kühne G, Lehmann E, Schulin R (2009) Response of native grasses and Cicer arietinum to soil polluted with mining wastes: Implications for the management of land adjacent to mine sites. Environ Exp Bot 65:198–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2008.09.004
De Conti L, Ceretta CA, Melo GWB, Tiecher TL, Silva LOS, Garlet LP, Mimmo T, Cesco S, Brunetto G (2019) Intercropping of young grapevines with native grasses for phytoremediation of Cu-contaminated soils. Chemosphere 216:147–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.134
Farahat EA, Galal TM (2018) Trace metal accumulation by Ranunculus sceleratus: implications for phytostabilization. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:4214–4222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0808-2
Farooq A, Nadeem M, Abbas G, Shabbir A, Khalid MS, Javeed HMR, Saeed MF, Akram A, Younis A, Akhtar G (2020) Cadmium partitioning, physiological and oxidative stress responses in marigold (Calendula calypso) grown on contaminated soil: implications for phytoremediation. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 105:270–276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-02934-6
Gonzaga MIS, Ma LQ, Santos JAG, Matias MIS (2009) Rhizosphere characteristics of two arsenic hyperaccumulating Pteris ferns. Sci Total Environ 407:4711–4716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.04.037
Gove B, Hutchinson JJ, Young SD, Craigon J, McGrath SP (2002) Uptake of metals by plants sharing a rhizosphere with the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. Int J Phytoremediation 4:267–281
Hong Y, Heerink N, Jin S, Berentsen P, Zhang L, van der Werf W (2017) Intercropping and agroforestry in China – current state and trends. Agric Ecosyst Environ 244:52–61. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226510208500087
Hu Y, Cheng H, Tao S (2016) The challenges and solutions for cadmium-contaminated rice in China: a critical review. Environ Int 92–93:515–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.04.042
Hu Y, Huang Y, Su J, Gao Z, Li S, Nan Z (2018) Temporal changes of metal bioavailability and extracellular enzyme activities in relation to afforestation of highly contaminated calcareous soil. Sci Total Environ 622–623:1056–1066. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.027
Hu Y, Tian S, Foyer CH, Hou D, Wang H, Zhou W, Liu T, Ge J, Lu L, Lin X (2019) Efficient phloem transport significantly remobilizes cadmium from old to young organs in a hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii. J Hazard Mater 365:421–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.11.034
Jones DL, Willett VB (2006) Experimental evaluation of methods to quantify dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 38:991–999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.08.012
Kim KR, Owens G, Naidu R, Kwon SL (2010) Influence of plant roots on rhizosphere soil solution composition of long-term contaminated soils. Geoderma 155:86–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2009.11.028
Kim S, Xu X, Zhang Y, Zheng X, Liu R, Dietrich K, Reponen T, Ho SM, Xie C, Sucharew H, Huo X (2019) Metal concentrations in pregnant women and neonates from informal electronic waste recycling. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 29:406–415. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41370-018-0054-9
Li JT, Gurajala HK, Wu LH, Van Der Ent A, Qiu RL, Baker AJM, Tang YT, Yang XE, Shu WS (2018a) Hyperaccumulator plants from China: a synthesis of the current state of knowledge. Environ Sci Tech 52:11980–11994. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b01060
Li T, Liang C, Han X, Yang X (2013a) Mobilization of cadmium by dissolved organic matter in the rhizosphere of hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii. Chemosphere 91:970–976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.100
Li T, Tao Q, Han X, Yang X (2013b) Effects of elevated CO2 on rhizosphere characteristics of Cd/Zn hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii. Sci Total Environ 454–455:510–516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.03.054
Li T, Xu Z, Han X, Yang X, Sparks DL (2012) Characterization of dissolved organic matter in the rhizosphere of hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii and its effect on the mobility of zinc. Chemosphere 88:570–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.03.031
Li X, Thornton I (2001) Chemical partitioning of trace and major elements in soils contaminated bymining and smelting activities. Appl Geochem 16:1693–1706. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(01)00065-8
Li Z, Wu L, Luo Y, Christie P (2018b) Changes in metal mobility assessed by EDTA kinetic extraction in three polluted soils after repeated phytoremediation using a cadmium/zinc hyperaccumulator. Chemosphere 194:432–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.005
Lin LY, Yan XL, Liao XY, Zhang YX, Ma X (2015) Arsenic accumulation in Panax notoginseng monoculture and intercropping with Pteris vittata. Water Air Soil Pollut 226:113–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2375-9
Liu L, Zhang Q, Hu L, Tang J, Xu L, Yang X, Yong JWH, Chen X (2012) Legumes can increase cadmium contamination in neighboring crops. PloS One 7:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0042944
Liu Q, Loganathan P, Hedley MJ, Skinner MF (2004) The mobilisation and fate of soil and rock phosphate in the rhizosphere of ectomycorrhizal Pinus radiata seedlings in an Allophanic soil. Plant and Soil 264:219–229. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PLSO.0000047758.77661.57
Luo J, He W, Rinklebe J, Igalavithana AD, Tack FMG, Ok YS (2019a) Distribution characteristics of Cd in different types of leaves of Festuca arundinacea intercropped with Cicer arietinum L.: a new strategy to remove pollutants by harvesting senescent and dead leaves. Environ Res 179:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.108801
Luo J, He W, Yang D, Wu J, Gu XWS (2019b) Magnetic field enhance decontamination efficiency of Noccaea caerulescens and reduce leaching of non-hyperaccumulated metals. J Hazard Mater 368:141–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.01.046
Luo J, Qi S, Gu XWS, Wang J, Xie X (2016) Evaluation of the phytoremediation effect and environmental risk in remediation processes under different cultivation systems. J Clean Prod 119:25–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.01.043
Luo J, Qi S, Peng L, Xie X (2017) Enhanced phytoremediation capacity of a mixed-species plantation of Eucalyptus globulus and Chickpeas. J Geochem Explor 182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2017.01.006
MARA (Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, P.R. China) (2004) Limits of eight elements in cereals, legumes, tubers, and their products ((NY861-2004)). MARA, Beijing
Martínez-Alcalá I, Bernal MP, de la Fuente C, Gondar D, Clemente R (2016) Changes in the heavy metal solubility of two contaminated soils after heavy metals phytoextraction with Noccaea caerulescens. Ecol Eng 89:56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.11.055
MEP (Ministry of Environmental Protection, P.R. China) (2008) Environmental Quality Standard for Soils (GB15618-2008). MEP, Beijing
MEP (Ministry of Environmental Protection, P.R. China) (2017) National Food Safety Standard for Maximum Levels of Contaminants in Foods (GB2762-2017). MEP, Beijing
Mridha N, Chattaraj S, Chakraborty D, Anand A, Aggarwal P, Nagarajan S (2016) Pre-sowing static magnetic field treatment for improving water and radiation use efficiency in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) under soil moisture stress. Bioelectromagnetics 37:400–408. https://doi.org/10.1002/bem.21994
Niu H, Wu H, Chen K, Sun J, Cao M, Luo J (2021) Effects of decapitated and root-pruned Sedum alfredii on the characterization of dissolved organic matter and enzymatic activity in rhizosphere soil during Cd phytoremediation. J Hazard Mater 417:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125977
Ok YS, Kim SC, Kim DK, Skousen JG, Lee JS, Cheong YW, Kim SJ, Yang JE (2011) Ameliorants to immobilize Cd in rice paddy soils contaminated by abandoned metal mines in Korea. Environ Geochem Health 33:23–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-010-9364-0
Rafiq MT, Aziz R, Yang X, Xiao W, Rafiq MK, Ali B, Li T (2014) Cadmium phytoavailability to rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown in representative Chinese soils. A model to improve soil environmental quality guidelines for food safety. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 103:101–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.10.016
Singh B, Aulakh CS, Walia SS (2019) Productivity and water use of organic wheat-chickpea intercropping system under limited moisture conditions in Northwest India. Renewable Agric Food Syst 34:134–143. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742170517000370
Strobel BW, Borggaard OK, Hansen HCB, Andersen MK, Raulund-Rasmussen K (2005) Dissolved organic carbon and decreasing pH mobilize cadmium and copper in soil. Eur J Soil Sci 56:189–196. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.2004.00661.x
Tang Y, He J, Yu X, Xie Y, Lin L, Sun G, Li H, Liao M, Liang D, Xia H, Wang X, Zhang J, Liu Z, Tu L, Liu L (2017) Intercropping with solanum nigrum and solanum photeinocarpum from two ecoclimatic regions promotes growth and reduces cadmium uptake of eggplant seedlings. Pedosphere 27:638–644. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(17)60358-8
Tume P, González E, King RW, Cuitiño L, Roca N, Bech J (2018) Distinguishing between natural and anthropogenic sources for potentially toxic elements in urban soils of Talcahuano, Chile. J Soil Sediment 18:2335–2349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-017-1750-0
Vashisth A, Nagarajan S (2008) Exposure of seeds to static magnetic field enhances germination and early growth characteristics in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Bioelectromagnetics 29:571–578. https://doi.org/10.1002/bem.20426
Wan X, Lei M, Chen T, Yang J (2017) Intercropped Pteris vittata L. and Morus alba L. presents a safe utilization mode for arsenic-contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 579:1467–1475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.11.148
Wang XH, Fan LY, Wang S, Wang Y, Yan LC, Zheng SS, Martyniuk CJ, Zhao YH (2017) Relationship between acute and chronic toxicity for prevalent organic pollutants in Vibrio fischeri based upon chemical mode of action. J Hazard Mater 338:458–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.05.058
Wu QT, Wei ZB, Ouyang Y (2007) Phytoextraction of metal-contaminated soil by Sedum alfredii H: effects of chelator and co-planting. Water Air Soil Pollut 180:131–139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-006-9256-1
Xiao W, Li D, Ye X, Xu H, Yao G, Wang J, Zhang Q, Hu J, Gao N (2017) Enhancement of Cd phytoextraction by hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii using electrical field and organic amendments. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:5060–5067. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8277-6
Yang J, Yang J, Huang J (2017) Role of co-planting and chitosan in phytoextraction of As and heavy metals by Pteris vittata and castor bean – a field case. Ecol Eng 109:35–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.09.001
Zeng P, Guo Z, Xiao X, Peng C (2019a) Effects of tree-herb co-planting on the bacterial community composition and the relationship between specific microorganisms and enzymatic activities in metal(loid)-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 220:237–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.12.073
Zeng P, Guo Z, Xiao X, Peng C, Feng W, Xin L, Xu Z (2019b) Phytoextraction potential of Pteris vittata L. co-planted with woody species for As, Cd, Pb and Zn in contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 650:594–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.055
Zhan J, Huang H, Yu H, Zhang X, Wang Y, Li T (2020) Characterization of dissolved organic matter in the rhizosphere of phytostabilizer Athyrium wardii (Hook.) involved in enhanced metal accumulation when exposed to Cd and Pb co-contamination. Environ Pollut 266:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115196
Zhan J, Li T, Zhang X, Yu H, Zhao L (2018) Rhizosphere characteristics of phytostabilizer Athyrium wardii (Hook.) involved in Cd and Pb accumulation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:892–900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.11.070
Zhang J, Cao X, Yao Z, Lin Q, Yan B, Cui X, He Z, Yang X, Wang C-H, Chen G (2021) Phytoremediation of Cd-contaminated farmland soil via various Sedum alfredii-oilseed rape cropping systems: efficiency comparison and cost-benefit analysis. J Hazard Mater 419:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126489
Zhao W, Ding L, Gu X, Luo J, Liu Y, Guo L, Shi Y, Huang T, Cheng S (2015) Levels and ecological risk assessment of metals in soils from a typical e-waste recycling region in southeast China. Ecotoxicology 24:1947–1960. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-015-1532-7
Zu Y, Qin L, Zhan F, Wu J, Li Y, Chen J, Wang J, Hu W (2020) Intercropping of Sonchus asper and Vicia faba affects plant cadmium accumulation and root responses. Pedosphere 30:457–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(17)60484-3
Funding
The authors thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 21876014) for financial support to carry out this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hongwei He: formal analysis, investigation, and writing—original draft; Yifan Jia: formal analysis and writing—original draft; Ruyi Li: investigation and writing—original draft; Pan Yang: formal analysis; Min Cao: writing—review and editing; Jie Luo: conceptualization, methodology, validation, writing—review and editing, supervision, and funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable. This work did not describe experiments with animals, human subjects, or human tissue samples.
Consent to participate
Not applicable. This work did not describe experiments with animals, human subjects, or human tissue samples.
Consent for publication
The manuscript entitled “Intercropping Sedum alfredii and Cicer arietinum L. does not present a suitable land use pattern for multi-metal-polluted soil” is prepared in accordance with the guide for authors available on the journal’s website and it has not been published elsewhere in part or in its entirety. All authors attest to the validity of its contents and agree to its submission in Environmental Science and Pollution Research.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Elena Maestri
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
He, ., Jia, Y., Li, R. et al. Intercropping Sedum alfredii Hance and Cicer arietinum L. does not present a suitable land use pattern for multi-metal-polluted soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 89616–89626 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28756-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28756-7