Abstract
Key message
We identified a dosage-dependent dominant negative form of Sar1c, which confirms the essential role of COPII system in mediating ER export of storage proteins in rice endosperm.
Abstract
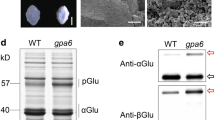
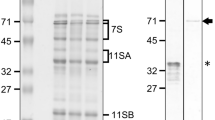
Higher plants accumlate large amounts of seed storage proteins (SSPs). However, mechanisms underlying SSP trafficking are largely unknown, especially the ER-Golgi anterograde process. Here, we showed that a rice glutelin precursor accumulation13 (gpa13) mutant exhibited floury endosperm and overaccumulated glutelin precursors, which phenocopied the reported RNAi-Sar1abc line. Molecular cloning revealed that the gpa13 allele encodes a mutated Sar1c (mSar1c) with a deletion of two conserved amino acids Pro134 and Try135. Knockdown or knockout of Sar1c alone caused no obvious phenotype, while overexpression of mSar1c resulted in seedling lethality similar to the gpa13 mutant. Transient expression experiment in tobacco combined with subcellular fractionation experiment in gpa13 demonstrated that the expression of mSar1c affects the subcellular distribution of all Sar1 isoforms and Sec23c. In addition, mSar1c failed to interact with COPII component Sec23. Conversely, mSar1c competed with Sar1a/b/d to interact with guanine nucleotide exchange factor Sec12. Together, we identified a dosage-dependent dominant negative form of Sar1c, which confirms the essential role of COPII system in mediating ER export of storage proteins in rice endosperm.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data openly available in a public repository.
References
Aridor M, Weissman J, Bannykh S, Nuoffer C, Balch WE (1998) Cargo selection by the COPII budding machinery during export from the ER. J Cell Biol 141:61–70
Barlowe C, Schekman R (1993) SEC12 encodes a guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor essential for transport vesicle budding from the ER. Nature 365:347–349
Barlowe C, Orci L, Yeung T, Hosobuchi M, Hamamoto S, Salama N, Rexach MF, Ravazzola M, Amherdt M, Schekman R (1994) COPII: a membrane coat formed by Sec proteins that drive vesicle budding from the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell 77:895–907
Bar-Peled M, Raikhel NV (1997) Characterization of AtSEC12 and AtSAR1 (Proteins likely involved in endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi transport). Plant Physiol 114:315–324
Bi X, Mancias JD, Goldberg J (2007) Insights into COPII coat nucleation from the structure of Sec23.Sar1 complexed with the active fragment of Sec31. Dev Cell 13:635–645
Chang M, Wu SZ, Ryken SE, O’Sullivan JE, Bezanilla M (2022) COPII Sec23 proteins form isoform-specific endoplasmic reticulum exit sites with differential effects on polarized growth. Plant Cell 34:333–350
Chen SB, Tao LZ, Zeng LR, Vega-Sanchez ME, Umemura K, Wang GL (2006) A highly efficient transient protoplast system for analyzing defence gene expression and protein-protein interactions in rice. Mol Plant Pathol 7:417–427
Chen H, Zou Y, Shang Y, Lin H, Wang Y, Cai R, Tang X, Zhou JM (2008) Firefly luciferase complementation imaging assay for protein-protein interactions in plants. Plant Physiol 146:368–376
Colicelli J (2004) Human RAS superfamily proteins and related GTPases. Sci SKTE RE13. https://doi.org/10.1126/stke.2502004re13
Dever TE, Glynias MJ, Merrick WC (1987) GTP-binding domain: three consensus sequence elements with distinct spacing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:1814–1818
Hanton SL, Chatre L, Matheson LA, Rossi M, Held MA, Brandizzi F (2008) Plant Sar1 isoforms with near-identical protein sequences exhibit different localisations and effects on secretion. Plant Mol Biol 67:283–294
Huang M, Weissman JT, Beraud-Dufour S, Luan P, Wang C, Chen W, Aridor M, Wilson IA, Balch WE (2001) Crystal structure of Sar1-GDP at 1.7 A resolution and the role of the NH2 terminus in ER export. J Cell Biol 155:937–948
Lee MC, Miller EA (2007) Molecular mechanisms of COPII vesicle formation. Semin Cell Dev Biol 18:424–434
Li LX, Shimada T, Takahashi H, Ueda H, Fukao Y, Kondo M, Nishimura M, Hara-Nishimura I (2006) MAIGO2 is involved in exit of seed storage proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 18:3535–3547
Li L, Shimada T, Takahashi H, Koumoto Y, Shirakawa M, Takagi J, Zhao X, Tu B, Jin H, Shen Z, Han B, Jia M, Kondo M, Nishimura M, Hara-Nishimura I (2013) MAG2 and three MAG2-INTERACTING PROTEINs form an ER-localized complex to facilitate storage protein transport in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 76:781–791
Li B, Zeng Y, Cao W, Zhang W, Cheng L, Yin H, Wu Q, Wang X, Huang Y, Lau WCY, Yao ZP, Guo Y, Jiang L (2021) A distinct giant coat protein complex II vesicle population in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Plants 10:1335–1346
Liu F, Ren Y, Wang Y, Peng C, Zhou K, Lv J, Guo X, Zhang X, Zhong M, Zhao S, Jiang L, Wang H, Bao Y, Wan J (2013) OsVPS9A functions cooperatively with OsRAB5A to regulate post-Golgi dense vesicle-mediated storage protein trafficking to the protein storage vacuole in rice endosperm cells. Mol Plant 6:1918–1932
Lord C, Ferro-Novick S, Miller EA (2013) The highly conserved COPII coat complex sorts cargo from the endoplasmic reticulum and targets it to the Golgi. CSH Perspect Biol 5:306–307
Melville DB, Studer S, Schekman R (2020) Small sequence variations between two mammalian paralogs of the small GTPase SAR1 underlie functional differences in coat protein complex II assembly. J Biol Chem 295:8401–8412
Miller EA, Schekman R (2013) COPII - a flexible vesicle formation system. Curr Opin Cell Biol 25:420–427
Miller EA, Beilharz TH, Malkus PN, Lee MC, Hamamoto S, Orci L, Schekman R (2003) Multiple cargo binding sites on the COPII subunit Sec24p ensure capture of diverse membrane proteins into transport vesicles. Cell 114:497–509
Miyagishima SY, Froehlich JE, Osteryoung KW (2006) PDV1 and PDV2 mediate recruitment of the dynamin-related protein ARC5 to the plastid division site. Plant Cell 18:2517–2530
Osterrieder A, Hummel E, Carvalho CM, Hawes C (2010) Golgi membrane dynamics after induction of a dominant-negative mutant Sar1 GTPase in tobacco. J Exp Bot 61:405–422
Pan T, Wang Y, Jing R, Wang Y, Wei Z, Zhang B, Lei C, Qi Y, Wang F, Bao X, Yan M, Zhang Y, Zhang P, Yu M, Wan G, Chen Y, Yang W, Zhu J, Zhu Y, Zhu S, Cheng Z, Zhang X, Jiang L, Ren Y, Wan J (2021) Post-Golgi trafficking of rice storage proteins requires the small GTPase Rab7 activation complex MON1–CCZ1. Plant Physiol 187:2174–2191
Ren Y, Wang Y, Liu F, Zhou K, Ding Y, Zhou F, Wang Y, Liu K, Gan L, Ma W, Han X, Zhang X, Guo X, Wu F, Cheng Z, Wang J, Lei C, Lin Q, Jiang L, Wu C, Bao Y, Wang H, Wan J (2014) GLUTELIN PRECURSOR ACCUMULATION3 encodes a regulator of post-Golgi vesicular traffic essential for vacuolar protein sorting in rice endosperm. Plant Cell 26:410–425
Ren Y, Wang Y, Pan T, Wang Y, Wang Y, Gan L, Wei Z, Wang F, Wu M, Jing R, Wang J, Wan G, Bao X, Zhang B, Zhang P, Zhang Y, Ji Y, Lei C, Zhang X, Cheng Z, Lin Q, Zhu S, Zhao Z, Wang J, Wu C, Qiu L, Wang H, Wan J (2020) GPA5 encodes a Rab5a effector required for post-Golgi trafficking of rice storage proteins. Plant Cell 32:758–777
Takagi J, Renna L, Takahashi H, Koumoto Y, Tamura K, Stefano G, Fukao Y, Kondo M, Nishimura M, Shimada T, Brandizzi F, Hara-Nishimura I (2013) MAIGO5 functions in protein export from Golgi-associated endoplasmic reticulum exit sites in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25:4658–4675
Takahashi H, Tamura K, Takagi J, Koumoto Y, Hara-Nishimura I, Shimada T (2010) MAG4/Atp115 is a Golgi-localized tethering factor that mediates efficient anterograde transport in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 51:1777–1787
Takemoto Y, Coughlan SJ, Okita TW, Satoh H, Ogawa M, Kumamaru T (2002) The rice mutant esp2 greatly accumulates the glutelin precursor and deletes the protein disulfide isomerase. Plant Physiol 128:1212–1222
Takeuchi M, Ueda T, Sato K, Abe H, Nagata T, Nakano A (2000) A dominant negative mutant of sar1 GTPase inhibits protein transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus in tobacco and Arabidopsis cultured cells. Plant J 23:517–525
Tian L, Dai LL, Yin ZJ, Fukuda M, Kumamaru T, Dong XB, Xu XP, Qu LQ (2013) Small GTPase Sar1 is crucial for proglutelin and alpha-globulin export from the endoplasmic reticulum in rice endosperm. J Exp Bot 64:2831–2845
Ueda, Y., Satoh-Cruz, M., Matsusaka, H., Takemoto-Kuno, Y., Fukuda, M., Okita, T.W., Ogawa, M., Satoh, H., and Kumamaru, T. (2010). Gene-gene interactions between mutants that accumulate abnormally high amounts of proglutelin in rice seed. Breed. Sci. 60: 568–574.
Venditti R, Wilson C, De Matteis MA (2014) Exiting the ER: what we know and what we don’t. Trends Cell Biol 24:9–18
Vitale A, Denecke J (1999) The endoplasmic reticulum-gateway of the secretory pathway. Plant Cell 11:615–628
Waadt R, Kudla J. (2008) In planta visualization of protein interactions using bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC). CSH Protoc 2008: pdb prot4995.
Wang Y, Ren Y, Liu X, Jiang L, Chen L, Han X, Jin M, Liu S, Liu F, Lv J, Zhou K, Su N, Bao Y, Wan J (2010) OsRab5a regulates endomembrane organization and storage protein trafficking in rice endosperm cells. Plant J 64:812–824
Wang Y, Liu F, Ren Y, Wang Y, Liu X, Long W, Wang D, Zhu J, Zhu X, Jing R, Wu M, Hao Y, Jiang L, Wang C, Wang H, Bao Y, Wan J (2016) GOLGI TRANSPORT 1B regulates protein export from the endoplasmic reticulum in rice endosperm cells. Plant Cell 28:2850–2865
Wang Z, Yu G, Liu Y, Liu S, Aridor M, Huang Y, Hu Y, Wang L, Li S, Xiong H, Tang B, Li X, Cheng C, Chakrabarti S, Wang F, Wu Q, Karnik SS, Xu C, Chen Q, Wang QK (2018) Small GTPases SAR1A and SAR1B regulate the trafficking of the cardiac sodium channel Nav1.5. BBA-MOL BASIS DIS 1864:3672–3684
Ward TH, Polishchuk RS, Caplan S, Hirschberg K, Lippincott-Schwartz J (2001) Maintenance of Golgi structure and function depends on the integrity of ER export. J Cell Biol 155:557–570
Weissman JT, Plutner H, Balch WE (2001) The mammalian guanine nucleotide exchange factor mSec12 is essential for activation of the Sar1 GTPase directing endoplasmic reticulum export. Traffic 2:465–475
White MA, Nicolette C, Minden A, Polverino A, Van Aelst L, Karin M, Wigler MH (1995) Multiple Ras functions can contribute to mammalian cell transformation. Cell 80:533–541
Yang YD, Elamawi R, Bubeck J, Pepperkok R, Ritzenthaler C, Robinson DG (2005) Dynamics of COPII vesicles and the Golgi apparatus in cultured Nicotiana tabacum BY-2 cells provides evidence for transient association of Golgi stacks with endoplasmic reticulum exit sites. Plant Cell 17:1513–1531
Zeng Y, Chung KP, Li B, Lai CM, Lam SK, Wang X, Cui Y, Gao C, Luo M, Wong KB, Schekman R, Jiang L (2015) Unique COPII component AtSar1a/AtSec23a pair is required for the distinct function of protein ER export in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:14360–14365
Zeng Y, Li B, Ji C, Feng L, Niu F, Deng C, Chen S, Lin Y, Cheung KCP, Shen J, Wong KB, Jiang L (2021) A unique AtSar1D-AtRabD2a nexus modulates autophagosome biogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 118:e2021293118
Zhu J, Ren Y, Wang Y, Liu F, Teng X, Zhang Y, Duan E, Wu M, Zhong M, Hao Y, Zhu X, Lei J, Wang Y, Yu Y, Pan T, Bao Y, Wang Y, Wan J (2019) OsNHX5-mediated pH homeostasis is required for post-Golgi trafficking of seed storage proteins in rice endosperm cells. BMC Plant Biol 19:295
Zhu J, Ren Y, Zhang Y, Yang J, Duan E, Wang Y, Liu F, Wu M, Pan T, Wang Y, Hu T, Hao Y, Teng X, Zhu X, Lei J, Jing R, Yu Y, Sun Y, Bao X, Bao Y, Wang Y, Wan J (2021) Subunit E isoform 1 of vacuolar H+-ATPase OsVHA enables post-Golgi trafficking of rice seed storage proteins. Plant Physiol 187:2192–2208
Acknowledgements
We thank the Core Facility Platform, Institute of Crop Sciences, CAAS, for assistance with confocal imaging and TEM.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2021YFF1000200), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31830064), Jiangsu Natural Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars (BK20180024), and the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program of CAAS (grants CAAS-ZDXT202001, CAAS-ZDXT2019003 and Leading Talent to Y.R.). This work was also supported by International Science & Technology Innovation Program of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAASTIP), the Central Public-Interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, China (Y2021YJ18), and Jiangsu Nanjing National Field Scientific Observation and Research Station for rice germplasm.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JW supervised the project; JW, YW, and YR designed the research; XB, YW, YQ, TP, MY, YZ, HW, PZ, YJ, HY, XJ, RJ, MY, BZ, CG, JL, JZ, YH, XC, RC, SZ, and YS performed research; YR, YW, YQ, GV, CL, XZ, YZ, and LJ provided technical assistance; XB and YW wrote, YR and JW revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, X., Wang, Y., Qi, Y. et al. A deleterious Sar1c variant in rice inhibits export of seed storage proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum. Plant Mol Biol 111, 291–307 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-022-01327-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-022-01327-z