Abstract
Key message
CYSTM3, a small mitochondrial protein, acts as a negative regulator in salt stress response by preventing Na+ efflux and disturbing reactive oxygen species (ROS) homeostasis in Arabidopsis.
Abstract
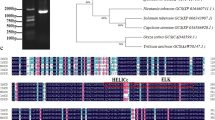
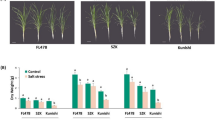
Cysteine-rich transmembrane module (CYSTM) is a not well characterized small peptide family in plants. In this study, we identified a novel mitochondrion-localized CYSTM member CYSTM3 from Arabidopsis, which was ubiquitously expressed in different tissues and dramatically induced by salt stress. Transgenic plants overexpressing CYSTM3 (OE) displayed hypersensitivity to salt stress compared with wild type (WT) plants, whereas a knockout mutant cystm3 was more tolerant to high salinity than WT. Moreover, OE lines accumulated higher contents of Na+ and ROS than WT and cystm3 upon exposure to high salinity. Further analysis revealed that CYSTM3 could deter root Na+ efflux and inhibit the activities of a range of ROS scavenging enzymes in Arabidopsis. In addition, the transcripts of nuclear salt stress-responsive genes were over-activated in cystm3 than those in WT and OE lines. Taken together, Arabidopsis CYSTM3 acts as a negative regulator in salt stress tolerance.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Anjum NA et al (2016) Catalase and ascorbate peroxidase-representative H2O2-detoxifying heme enzymes in plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23:19002–19029. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7309-6
Apse MP, Aharon GS, Snedden WA, Blumwald E (1999) Salt tolerance conferred by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H + antiport in Arabidopsis. Science 285:1256–1258
Arnon DI (1949) Copper ENZYMES in isolated chloroplasts. polyphenoloxidase in Beta Vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24:1–15
Barrero JM, Rodriguez PL, Quesada V, Piqueras P, Ponce MR, Micol JL (2006) Both abscisic acid (ABA)-dependent and ABA-independent pathways govern the induction of NCED3, AAO3 and ABA1 in response to salt stress. Plant Cell Environ 29:2000–2008. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2006.01576.x
Beers RF Jr, Sizer IW (1952) A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J Biol Chem 195:133–140
Boudsocq M, Lauriere C (2005) Osmotic signaling in plants: multiple pathways mediated by emerging kinase families. Plant Physiol 138:1185–1194. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.105.061275
Butow RA, Avadhani NG (2004) Mitochondrial signaling: the retrograde response. Mol Cell 14:1–15
Choudhury FK, Rivero RM, Blumwald E, Mittler R (2016) Reactive oxygen species, abiotic stress and stress combination. Plant J. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13299
Choudhury FK, Rivero RM, Blumwald E, Mittler R (2017) Reactive oxygen species, abiotic stress and stress combination. Plant J 90:856–867. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13299
Darley CP, van Wuytswinkel OC, van der Woude K, Mager WH, de Boer AH (2000) Arabidopsis thaliana and Saccharomyces cerevisiae NHX1 genes encode amiloride sensitive electroneutral Na+/H + exchangers. Biochem J 351:241–249
Davletova S, Schlauch K, Coutu J, Mittler R (2005) The zinc-finger protein Zat12 plays a central role in reactive oxygen and abiotic stress signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 139:847–856. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.105.068254
De Clercq I et al (2013) The membrane-bound NAC transcription factor ANAC013 functions in mitochondrial retrograde regulation of the oxidative stress response in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25:3472–3490. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.117168
Gaxiola RA, Li J, Undurraga S, Dang LM, Allen GJ, Alper SL, Fink GR (2001) Drought- and salt-tolerant plants result from overexpression of the AVP1 H+-pump. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:11444–11449. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.191389398
Goyal K, Walton LJ, Tunnacliffe A (2005) LEA proteins prevent protein aggregation due to water stress. Biochem J 388:151–157. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20041931
Huseynova IM, Aliyeva DR, Aliyev JA (2014) Subcellular localization and responses of superoxide dismutase isoforms in local wheat varieties subjected to continuous soil drought. Plant Physiol Biochem PPB 81:54–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.01.018
Inze A, Vanderauwera S, Hoeberichts FA, Vandorpe M, Van Gaever T, Van Breusegem F (2012) A subcellular localization compendium of hydrogen peroxide-induced proteins. Plant Cell Environ 35:308–320. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2011.02323.x
Ji H, Pardo JM, Batelli G, Van Oosten MJ, Bressan RA, Li X (2013) The salt overly sensitive (SOS) pathway: established and emerging roles. Mol Plant 6:275–286 https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/sst017
Jia F, Wang C, Huang J, Yang G, Wu C, Zheng C (2015) SCF E3 ligase PP2-B11 plays a positive role in response to salt stress in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 66:4683–4697. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv245
Kuzniak E, Sklodowska M (2004) The effect of Botrytis cinerea infection on the antioxidant profile of mitochondria from tomato leaves. J Exp Bot 55:605–612. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erh076
Li D et al (2011) Transcriptional profiling of Medicago truncatula under salt stress identified a novel CBF transcription factor MtCBF4 that plays an important role in abiotic stress responses. BMC Plant Biol 11:109. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-11-109
Marklund S, Marklund G (1974) Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur J Biochem 47:469–474
Mir R, Leon J (2014) Pathogen and circadian controlled 1 (PCC1) protein is anchored to the plasma membrane and interacts with subunit 5 of COP9 signalosome in Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 9:e87216. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0087216
Mir R, Hernandez ML, Abou-Mansour E, Martinez-Rivas JM, Mauch F, Metraux JP, Leon J (2013) Pathogen and circadian controlled 1 (PCC1) regulates polar lipid content, ABA-related responses, and pathogen defence in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 64:3385–3395. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert177
Mittler R, Vanderauwera S, Gollery M, Van Breusegem F (2004) Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trends Plant Sci 9:490–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2004.08.009
Moller IM (2001) Plant mitochondria and oxidative stress: electron transport, NADPH turnover, and metabolism of reactive oxygen species. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 52:561–591. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.52.1.561
Moller IM, Kristensen BK (2004) Protein oxidation in plant mitochondria as a stress indicator. Photochem Photobiol Sci 3:730–735. https://doi.org/10.1039/b315561g
Moller IM, Jensen PE, Hansson A (2007) Oxidative modifications to cellular components in plants. Ann Rev Plant Biol 58:459–481. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.58.032806.103946
Moller IS et al (2009) Shoot Na + exclusion and increased salinity tolerance engineered by cell type-specific alteration of Na + transport. in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21:2163–2178. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.064568
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092911
Ng S et al (2014) Anterograde and retrograde regulation of nuclear genes encoding mitochondrial proteins during growth, development, and stress. Mol Plant 7:1075–1093. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssu037
Noctor G, Reichheld JP, Foyer CH (2018) ROS-related redox regulation and signaling in plants semin. Cell Dev Biol 80:3–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.07.013
Osakabe Y, Osakabe K, Shinozaki K, Tran LS (2014) Response of plants to water stress. Front Plant Sci 5:86. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00086
Rubio F, Gassmann W, Schroeder JI (1995) Sodium-driven potassium uptake by the plant potassium transporter HKT1 and mutations conferring salt tolerance. Science 270:1660–1663
Sauerbrunn N, Schlaich NL (2004) PCC1: a merging point for pathogen defence and circadian signalling in Arabidopsis. Planta 218:552–561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-003-1143-z
Seligman AM, Karnovsky MJ, Wasserkrug HL, Hanker JS (1968) Nondroplet ultrastructural demonstration of cytochrome oxidase activity with a polymerizing osmiophilic reagent, diaminobenzidine (DAB). J Cell Biol 38:1–14
Shen Y, Li J, Gu R, Yue L, Wang H, Zhan X, Xing B (2018) Carotenoid and superoxide dismutase are the most effective antioxidants participating in ROS scavenging in phenanthrene accumulated wheat leaf. Chemosphere 197:513–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.01.036
Sun W, Van Montagu M, Verbruggen N (2002) Small heat shock proteins and stress tolerance in plants. Biochim et Biophys Acta 1577:1–9
Sun J et al (2009) NaCl-induced alternations of cellular and tissue ion fluxes in roots of salt-resistant and salt-sensitive poplar species. Plant Physiol 149:1141–1153. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.129494
Suzuki N, Koussevitzky S, Mittler R, Miller G (2012) ROS and redox signalling in the response of plants to abiotic stress. Plant Cell Environ 35:259–270. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2011.02336.x
Tuteja N (2007) Mechanisms of high salinity tolerance in plants. Methods Enzymol 428:419–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(07)28024-3
Venancio TM, Aravind L (2010) CYSTM, a novel cysteine-rich transmembrane module with a role in stress tolerance across eukaryotes. Bioinformatics 26:149–152. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp647
Xu Y et al (2018a) CYSTM, a novel non-secreted cysteine-rich peptide family, involved in environmental stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol 59:423–438. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcx202
Xu Y et al (2018b) NtLTP4, a lipid transfer protein that enhances salt and drought stresses tolerance in Nicotiana tabacum. Sci Rep 8:8873. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-27274-8
Yao X, Li J, Liu J, Liu K (2015) An Arabidopsis mitochondria-localized RRL protein mediates abscisic acid signal transduction through mitochondrial retrograde regulation involving ABI4. J Exp Bot 66:6431–6445. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv356
Yoshiba Y, Kiyosue T, Nakashima K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (1997) Regulation of levels of proline as an osmolyte in plants under water stress. Plant Cell Physiol 38:1095–1102
Zhang JL, Shi H (2013) Physiological and molecular mechanisms of plant salt tolerance. Photosynth Res 115:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-013-9813-6
Zhao Y et al (2013) The actin-related Protein2/3 complex regulates mitochondrial-associated calcium signaling during salt stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25:4544–4559. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.117887
Zhou H et al (2014) Inhibition of the Arabidopsis salt overly sensitive pathway by 14-3-3 proteins. Plant Cell 26:1166–1182. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.117069
Zhu JK (2001) Plant salt tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 6:66–71
Zhu JK (2002) Salt and drought stress signal transduction. in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:247–273. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.53.091401.143329
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 31570271 and 31771878), and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (Grant No. ZR2016CM22).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.H. and C.Z. conceived the original screening and research plans; Z.Y., and Y.X. performed experiments; Z.Y., and Y.X. conceived the project and wrote the article; S.Z., C.W., G.Y. and K.Y. provided suggestions and proofed the article; J.H. and C.Z. supervised and complemented the writing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Yu, Z., Zhang, S. et al. CYSTM3 negatively regulates salt stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 99, 395–406 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-019-00825-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-019-00825-x