Abstract
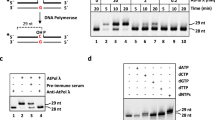
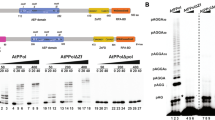
Besides the KU-dependent classical non-homologous end-joining (C-NHEJ) pathway, an alternative NHEJ pathway first identified in mammalian systems, which is often called the back-up NHEJ (B-NHEJ) pathway, was also found in plants. In mammalian systems PARP was found to be one of the essential components in B-NHEJ. Here we investigated whether PARP1 and PARP2 were also involved in B-NHEJ in Arabidopsis. To this end Arabidopsis parp1, parp2 and parp1parp2 (p1p2) mutants were isolated and functionally characterized. The p1p2 double mutant was crossed with the C-NHEJ ku80 mutant resulting in the parp1parp2ku80 (p1p2k80) triple mutant. As expected, because of their role in single strand break repair (SSBR) and base excision repair (BER), the p1p2 and p1p2k80 mutants were shown to be sensitive to treatment with the DNA damaging agent MMS. End-joining assays in cell-free leaf protein extracts of the different mutants using linear DNA substrates with different ends reflecting a variety of double strand breaks were performed. The results showed that compatible 5′-overhangs were accurately joined in all mutants, that KU80 protected the ends preventing the formation of large deletions and that PARP proteins were involved in microhomology mediated end joining (MMEJ), one of the characteristics of B-NHEJ.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad A, Robinson AR, Duensing A, van Drunen E, Beverloo HB, Weisberg DB, Hasty P, Hoeijmakers JHJ, Niedernhofer LJ (2008) ERCC1-XPF endonuclease facilitates DNA double-strand break repair. Mol Cell Biol 28:5082–5092
Alonso J, Stepanova A, Leisse T, Kim C (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301:653–657
Amé J-C, Rolli V, Schreiber V, Niedergang C, Apiou F, Decker P, Muller S, Höger T, Ménissier-de Murcia J, de Murcia G (1999) PARP-2, a novel mammalian DNA damage-dependent poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. J Biol Chem 274:17860–17868
Amé J-C, Spenlehauer C, de Murcia G (2004) The PARP superfamily. BioEssays 26:882–893
Amor Y, Babiychuk E, Inze D, Levine A (1998) The involvement of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in the oxidative stress responses in plants. FEBS Lett 440:1–7
Audebert M, Salles B, Calsou P (2004) Involvement of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 and XRCC1/DNA ligase III in an alternative route for DNA double-strand breaks rejoining. J Biol Chem 279:55117–55126
Babiychuk E, Cottrill PB, Storozhenko S, Fuangthong M, Chen Y, O’Farrell MK, Van Montagu M, Inzé D, Kushnir S (1998) Higher plants possess two structurally different poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases. Plant J 15:635–645
Boehler C, Gauthier LR, Mortusewicz O, Biard DS, Saliou J-M, Bresson A, Sanglier-Cianferani S, Smith S, Schreiber V, Boussin F, Dantzer F (2011) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 3 (PARP3), a newcomer in cellular response to DNA damage and mitotic progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:2783–2788
Bryant HE, Petermann E, Schultz N, Jemth A-S, Loseva O, Issaeva N, Johansson F, Fernandez S, McGlynn P, Helleday T (2009) PARP is activated at stalled forks to mediate Mre11-dependent replication restart and recombination. EMBO J 28:2601–2615
Bundock P, van Attikum H, Hooykaas P (2002) Increased telomere length and hypersensitivity to DNA damaging agents in an Arabidopsis KU70 mutant. Nucleic Acids Res 30:3395–3400
Caldecott KW (2003) XRCC1 and DNA strand break repair. DNA Repair 2:955–969
Charbonnel C, Gallego ME, White CI (2010) Xrcc1-dependent and Ku-dependent DNA double-strand break repair kinetics in Arabidopsis plants. Plant J 64:280–290
Charbonnel C, Allain E, Gallego ME, White CI (2011) Kinetic analysis of DNA double-strand break repair pathways in Arabidopsis. DNA Repair 10:611–619
Chen Y-M, Shall S, O’Farrell M (1994) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in plant nuclei. Eur J Biochem 224:135–142
Chen S, Inamdar KV, Pfeiffer P, Feldmann E, Hannah MF, Yu Y, Lee JW, Zhou T, Lees-Miller SP, Povirk LF (2001) Accurate in vitro end joining of a DNA double strand break with partially cohesive 3′-overhangs and 3′-phosphoglycolate termini: effect of Ku on repair fidelity. J Biol Chem 276:24323–24330
Cheng Q, Barboule N, Frit P, Gomez D, Bombarde O, Couderc B, Ren G-S, Salles B, Calsou P (2011) Ku counteracts mobilization of PARP1 and MRN in chromatin damaged with DNA double-strand breaks. Nucleic Acids Res 39:9605–9619
De Block M, Verduyn C, De Brouwer D, Cornelissen M (2005) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in plants affects energy homeostasis, cell death and stress tolerance. Plant J 41:95–106
de Pater S, Caspers M, Kottenhagen M, Meima H, ter Stege R, de Vetten N (2006) Manipulation of starch granule size distribution in potato tubers by modulation of plastid division. Plant Biotech J 4:123–134
Dibiase SJ, Zeng Z-C, Chen R, Hyslop T, Curran WJ, Iliakis G (2000) DNA-dependent protein kinase stimulates an independently active, nonhomologous, end-joining apparatus. Cancer Res 60:1245–1253
Fattah F, Lee EH, Weisensel N, Wang Y, Lichter N, Hendrickson EA (2010) Ku regulates the non-homologous end joining pathway choice of DNA double-strand break repair in human somatic cells. PLoS Genet 6:e1000855
Feldmann E, Schmiemann V, Goedecke W, Reichenberger S, Pfeiffer P (2000) DNA double-strand break repair in cell-free extracts from Ku80-deficient cells: implications for Ku serving as an alignment factor in non-homologous DNA end joining. Nucleic Acids Res 28:2585–2596
Fidantsef AL, Mitchell DL, Britt AB (2000) The Arabidopsis UVH1 gene is a homolog of the yeast repair endonuclease RAD1. Plant Physiol 124:579–586
Friesner J, Britt AB (2003) Ku80- and DNA ligase IV-deficient plants are sensitive to ionizing radiation and defective in T-DNA integration. Plant J 34:427–440
Gallego ME, Bleuyard J-Y, Daoudal-Cotterell S, Jallut N, White CI (2003) Ku80 plays a role in non-homologous recombination but is not required for T-DNA integration in Arabidopsis. Plant J 35:557–565
Gorbunova V, Levy AA (1997) Non-homologous DNA end joining in plant cells is associated with deletions and filler DNA insertions. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4650–4657
Haber JE (2008) Alternative endings. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:405–406
Heacock M, Spangler E, Riha K, Puizina J, Shippen DE (2004) Molecular analysis of telomere fusions in Arabidopsis: multiple pathways for chromosome end-joining. EMBO J 23:2304–2313
Hiom K (2010) Coping with DNA double strand breaks. DNA Repair 9:1256–1263
Huefner ND, Mizuno Y, Weil CF, Korf I, Britt AB (2011) Breadth by depth: expanding our understanding of the repair of transposon-induced DNA double strand breaks via deep-sequencing. DNA Repair 10:1023–1033
Iliakis G (2009) Backup pathways of NHEJ in cells of higher eukaryotes: cell cycle dependence. Radiother Onc 92:310–315
Jia Q, Bundock P, Hooykaas PJJ, de Pater S (2012) Agrobacterium tumefaciens T-DNA integration and gene-targeting in Arabidopsis thaliana non-homologous end-joining mutants. J Bot. doi:10.1155/2012/989272
Katsura Y, Sasaki S, Sato M, Yamaoka K, Suzukawa K, Nagasawa T, Yokota J, Kohno T (2007) Involvement of Ku80 in microhomology-mediated end joining for DNA double-strand breaks in vivo. DNA Repair 6:639–648
Kuhfittig-Kulle S, Feldmann E, Odersky A, Kuliczkowska A, Goedecke W, Eggert A, Pfeiffer P (2007) The mutagenic potential of non-homologous end joining in the absence of the NHEJ core factors Ku70/80, DNA-PKcs and XRCC4-LigIV. Mutagenesis 22:217–233
Lepiniec L, Babiychuk E, Kushnir S, Van Montagu M, Inze M (1995) Characterization of an Arabidopsis thaliana cDNA homologue to animal poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. FEBS Lett 364:103–108
Li J, Vaidya M, White C, Vainstein A, Citovsky V, Tzfira T (2005) Involvement of KU80 in T-DNA integration in plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:19231–19236
Li Y, Rosso MG, Viehoever P, Weisshaar B (2007) GABI-Kat SimpleSearch: an Arabidopsis thaliana T-DNA mutant database with detailed information for confirmed insertions. Nucleic Acids Res 35:874–878
Liang L, Deng L, Nguyen SC, Zhao X, Maulion CD, Shao C, Tischfield JA (2008) Human DNA ligases I and III, but not ligase IV, are required for microhomology-mediated end joining of DNA double-strand breaks. Nucleic Acids Res 36:3297–3310
Lieber MR (2010) The mechanism of double-strand DNA break repair by the nonhomologous DNA end joining pathway. Ann Rev Biochem 3:181–211
Lloyd AH, Wang D, Timmis JN (2012) Single molecule PCR reveals similar patterns of non-homologous DSB repair in tobacco and arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 7:e32255
Mansour WY, Rhein T, Dahm-Daphi J (2010) The alternative end-joining pathway for repair of DNA double-strand breaks requires PARP1 but is not dependent upon microhomologies. Nucleic Acids Res 38:6065–6077
Masaoka A, Horton JK, Beard WA, Wilson SH (2009) DNA polymerase β and PARP activities in base excision repair in living cells. DNA Repair 8:1290–1299
McVey M, Lee SE (2008) MMEJ repair of double-strand breaks (director’s cut): deleted sequences and alternative endings. Trends Genet 24:529–538
Menke M, Chen I-P, Angelis K, Schubert I (2001) DNA damage and repair in Arabidopsis thaliana as measured by the comet assay after treatment with different classes of genotoxins. Mut Res 493:87–93
Mladenov E, Iliakis G (2011) Induction and repair of DNA double strand breaks: the increasing spectrum of non-homologous end joining pathways. Mut Res 711:61–72
Nussenzweig A, Nussenzweig MC (2007) A backup DNA repair pathway moves to the forefront. Cell 131:223–225
O’Connor PJ (1981) Interaction of chemical carcinogens with macromolecules. J Cancer Res Clinical Onc 99:167–186
Osakabe K, Osakabe Y, Toki S (2010) Site-directed mutagenesis in Arabidopsis using custom-designed zinc finger nucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:12034–12039
Pacher M, Schmidt-Puchta W, Puchta H (2007) Two unlinked double-strand breaks can induce reciprocal exchanges in plant genomes via homologous recombination and nonhomologous end joining. Genetics 175:21–29
Puizina J, Siroky J, Mokros P, Schweizer D, Riha K (2004) Mre11 deficiency in arabidopsis is associated with chromosomal instability in somatic cells and Spo11-dependent genome fragmentation during meiosis. Plant Cell 16:1968–1978
Riha K, Watson JM, Parkey J, Shippen DE (2002) Telomere length deregulation and enhanced sensitivity to genotoxic stress in Arabidopsis mutants deficient in Ku70. EMBO J 21:2819–2826
Robert I, Dantzer F, Reina-San-Martin B (2009) Parp1 facilitates alternative NHEJ, whereas Parp2 suppresses IgH/c-myc translocations during immunoglobulin class switch recombination. J Exp Med 206:1047–1056
Rosidi B, Wang M, Wu W, Sharma A, Wang H, Iliakis G (2008) Histone H1 functions as a stimulatory factor in backup pathways of NHEJ. Nucleic Acids Res 36:1610–1623
San Filippo J, Sung P, Klein H (2008) Mechanism of eukaryotic homologous recombination. Ann Rev Biochem 77:229–257
Schreiber V, Amé J-C, Dollé P, Schultz I, Rinaldi B, Fraulob V, Ménissier-de Murcia J, de Murcia G (2002) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-2 (PARP-2) is required for efficient base excision DNA repair in association with PARP-1 and XRCC1. J Biol Chem 277:23028–23036
Schreiber V, Dantzer F, Ame J-C, de Murcia G (2006) Poly(ADP-ribose): novel functions for an old molecule. Nature Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:517–528
Shrivastav M, De Haro LP, Nickoloff JA (2008) Regulation of DNA double-strand break repair pathway choice. Cell Res 18:134–147
Tamura K, Adachi Y, Chiba K, Oguchi K, Takahashi H (2002) Identification of Ku70 and Ku80 homologues in Arabidopsis thaliana: evidence for a role in the repair of DNA double- strand breaks. Plant J 29:771–781
Uchiyama Y, Suzuki Y, Sakaguchi K (2008) Characterization of plant XRCC1 and its interaction with proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Planta 227:1233–1241
van Attikum H, Bundock P, Overmeer RM, Lee L-Y, Gelvin SB, Hooykaas PJJ (2003) The Arabidopsis AtLIG4 gene is required for the repair of DNA damage, but not for the integration of Agrobacterium T-DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 31:4247–4255
Vanderauwera S, De Block M, Van de Steene N, van de Cotte B, Metzlaff M, Van Breusegem F (2007) Silencing of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in plants alters abiotic stress signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:15150–15155
Wang H, Perrault AR, Takeda Y, Qin W, Wang H, Iliakis G (2003) Biochemical evidence for Ku-independent backup pathways of NHEJ. Nucleic Acids Res 31:5377–5388
Wang M, Wu W, Wu W, Rosidi B, Zhang L, Wang H, Iliakis G (2006) PARP-1 and Ku compete for repair of DNA double strand breaks by distinct NHEJ pathways. Nucleic Acids Res 34:6170–6182
West CE, Waterworth WM, Jiang Q, Bray CM (2000) Arabidopsis DNA ligase IV is induced by γ-irradiation and interacts with an Arabidopsis homologue of the double strand break repair protein XRCC4. Plant J 24:67–78
West CE, Waterworth WM, Story GW, Sunderland PA, Jiang Q, Bray CM (2002) Disruption of the Arabidopsis AtKu80 gene demonstrates an essential role for AtKu80 protein in efficient repair of DNA double-strand breaks in vivo. Plant J 31:517–528
Woodhouse BC, Dianov GL (2008) Poly ADP-ribose polymerase-1: an international molecule of mystery. DNA Repair 7:1077–1086
Woodhouse BC, Dianova II, Parsons JL, Dianov G (2008) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 modulates DNA repair capacity and prevents formation of DNA double strand breaks. DNA Repair 7:932–940
Wu W, Wang M, Wu W, Singh SK, Mussfeldt T, Iliakis G (2008) Repair of radiation induced DNA double strand breaks by backup NHEJ is enhanced in G2. DNA Repair 7:329–338
Xie A, Kwok A, Scully R (2009) Role of mammalian Mre11 in classical and alternative nonhomologous end joining. Nature Struct Mol Biol 16:814–818
Yélamos J, Schreiber V, Dantzer F (2008) Toward specific functions of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-2. Trends Mol Med 14:169–178
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Li Liang for providing the plasmid PUC19PD1/4. This work was financially supported by the Chinese Scholarship Council (CSC) (QJ, HS) and the European Union Program EU Recbreed (KBBE-2008-227190) (SdP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, Q., Dulk-Ras, A.d., Shen, H. et al. Poly(ADP-ribose)polymerases are involved in microhomology mediated back-up non-homologous end joining in Arabidopsis thaliana . Plant Mol Biol 82, 339–351 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-013-0065-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-013-0065-9