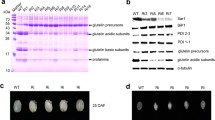
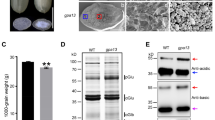
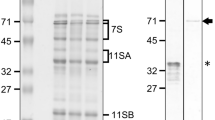
Abstract
The high accumulation of a recombinant protein in rice endosperm causes endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and in turn dramatically affects endogenous storage protein expression, protein body morphology and seed phenotype. To elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying these changes in transgenic rice seeds, we analyzed the expression profiles of endogenous storage proteins, ER stress-related and programmed cell death (PCD)-related genes in transgenic lines with different levels of Oryza sativa recombinant alpha antitrypsin (OsrAAT) expression. The results indicated that OsrAAT expression induced the ER stress and that the strength of the ER stress was dependent on OsrAAT expression levels. It in turn induced upregulation of the expression of the ER stress response genes and downregulation of the expression of the endogenous storage protein genes in rice endosperm. Further experiments showed that the ER stress response upregulated the expression of PCD-related genes to disturb the rice endosperm development and induced pre-mature PCD. As consequence, it resulted in decrease of grain weight and size. The mechanisms for the detriment seed phenotype in transgenic lines with high accumulation of the recombinant protein were elucidated.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berger F (1999) Endosperm development. Curr Opin Plant Biol 2(1):28–32
Brown RC, Lemmon BE, Olsen OA (1996) Development of the endosperm in rice (Oryza sativa L.): cellularization. J Plant Res 109(3):301–313
Cacas JL (2010) Devil inside: does plant programmed cell death involve the endomembrane system. Plant Cell Environ 33(9):1453–1473
Calfon M, Zeng H, Urano F, Till JH, Hubbard SR, Harding HP, Clark SG, Ron D (2002) IRE1 couples endoplasmic reticulum load to secretory capacity by processing the XBP-1 mRNA. Nature 415(6867):92–96
Guiboileau A, Sormani R, Meyer C, Masclaux-Daubresse C (2010) Senescence and death of plant organs: nutrient recycling and developmental regulation. Comptes Rendus Biol 333(4):382–391
Harding HP, Novoa I, Zhang Y, Zeng H, Wek R, Schapira M, Ron D (2000) Regulated translation initiation controls stress-induced gene expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell 6(5):1099–1108
Hayashi S, Wakasa Y, Takahashi H, Kawakatsu T, Takaiwa F (2011) Signal transduction by IRE1-mediated splicing of bZIP50 and other stress sensors in the endoplasmic reticulum stress response of rice. Plant J 96:946–956
Hayashi S, Wakasa Y, Takaiwa F (2012) Functional integration between defence and IRE1-mediated ER stress response in rice. Sci Rep 2(670):1–5
He Y, Ning T, Xie T, Qiu Q, Zhang L, Sun Y, Jiang D, Fu K, Yin F, Zhang W, Shen L, Wang H, Li J, Lin Q, Sun Y, Li H, Zhu Y, Yang D (2011) Large-scale production of functional human serum albumin from transgenic rice seeds. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(47):19078–19083
Hetz C, Martinon F, Rodriguez D, Glimcher LH (2011) The unfolded protein response: integrating stress signals through the stress sensor IRE1α. Physiol Rev 91(4):1219–1243
Hetz C (2012) The unfolded protein response: controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13(2):89–102
Howell SH (2013) Endoplasmic reticulum stress responses in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol. doi:10.1146/annurev-arplant-050312-120053
Iwata Y, Koizumi N (2012) Plant transducers of the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Trends Plant Sci 17(12):720–727
Jin Y, Zhuang M, Hendershot LM (2008) ERdj3, a luminal ER DnaJ homologue, binds directly to unfolded proteins in the mammalian ER: identification of critical residues†. Biochemistry 48(1):41–49
Kawakatsu T, Takaiwa F (2010) Differences in transcriptional regulatory mechanisms functioning for free lysine content and seed storage protein accumulation in rice grain. Plant Cell Physiol 51(12):1964–1974
Kawakatsu T, Hirose S, Yasuda H, Takaiwa F (2010) Reducing rice seed storage protein accumulation leads to changes in nutrient quality and storage organelle formation. Plant Physiol 154(4):1842–1854
Kobayashi H, Ikeda TM, Nagata K (2013) Spatial and temporal progress of programmed cell death in the developing starchy endosperm of rice. Planta. doi:10.1007/s00425-013-1854-8
Lee K, Tirasophon W, Shen X, Michalak M, Prywes R, Okada T, Yoshida H, Mori K, Kaufman RJ (2002) IRE1-mediated unconventional mRNA splicing and S2P-mediated ATF6 cleavage merge to regulate XBP1 in signaling the unfolded protein response. Genes Dev 16(4):452–466
Lim DH, Kim TS, Joo SP, Kim SH (2007) Intracerebral hematoma caused by ruptured traumatic pseudoaneurysm of the middle meningeal artery: a case report. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 42(5):416–418
Logue SE, Cleary P, Saveljeva S, Samali A (2013) New directions in ER stress-induced cell death. Apoptosis. doi:10.1007/s10495-10013-10818-10496
Luo J, Ning T, Sun Y, Zhu J, Zhu Y, Lin Q, Yang D (2008) Proteomic analysis of rice endosperm cells in response to expression of hGM–CSF. J Proteome Res 8(2):829–837
Meunier L, Usherwood YK, Chung KT, Hendershot LM (2002) A subset of chaperones and folding enzymes form multiprotein complexes in endoplasmic reticulum to bind nascent proteins. Mol Biol Cell 13(12):4456–4469
Olsen OA, Potter R, Kalla R (1992) Histo-differentiation and molecular biology of developing cereal endosperm. Seed Sci Res 2(03):117–131
Olsen OA, Brown R, Lemmon B (1995) Pattern and process of wall formation in developing endosperm. BioEssays 17(9):803–812
Olvera-Carrillo Y, Salanenka Y, Nowack MK (2012) Control of programmed cell death during plant reproductive development. Biocommun Plants 14(2012):171–196
Ron D, Walter P (2007) Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8(7):519–529
Schroder M, Clark R, Kaufman RJ (2003) IRE1- and HAC1-independent transcriptional regulation in the unfolded protein response of yeast. Mol Microbiol 49(3):591–606
Steedman HF (1957) Polyester wax: a new ribboning embedding medium for histology. Nature 179(4574):1345
van Doorn WG, Woltering EJ (2008) Physiology and molecular biology of petal senescence. J Exp Bot 59(3):453–480
Vitha S, Baluska F, Mews M, Volkmann D (1997) Immunofluorescence detection of F-actin on low melting point wax sections from plant tissues. J Histochem Cytochem 45(1):89–95
Wakasa Y, Yasuda H, Oono Y, Kawakatsu T, Hirose S, Takahashi H, Hayashi S, Yang L, Takaiwa F (2010) Expression of ER quality control-related genes in response to changes in BiP1 levels in developing rice endosperm. Plant J 65(5):675–689
Wakasa Y, Yasuda H, Oono Y, Kawakatsu T, Hirose S, Takahashi H, Hayashi S, Yang L, Takaiwa F (2011) Expression of ER quality control-related genes in response to changes in BiP1 levels in developing rice endosperm. Plant J 65(5):675–689
Wakasa Y, Yasuda H, Takaiwa F (2012) Secretory type of recombinant thioredoxin h induces ER stress in endosperm cells of transgenic rice. J Plant Physiol 170(2013):202–210
Wang W, Liu Z, Guo Z, Song G, Cheng Q, Jiang D, Zhu Y, Yang D (2011) Comparative transcriptomes profiling of photoperiod-sensitive male sterile rice Nongken 58S during the male sterility transition between short-day and long-day. BMC Genomics 12(1):462
Wei CX, Lan SY, Xu ZX (2002) Ultrastructural features of nucleus degradation during programmed cell death of starchy endosperm cells in rice. Acta Bot Sin Chin Ed 44(12):1396–1402
Woehlbier U, Hetz C (2011) Modulating stress responses by the UPRosome: a matter of life and death. Trends Biochem Sci 36(6):329–337
Xie T, Qiu Q, Zhang W, Ning T, Yang W, Zheng C, Wang C, Zhu Y, Yang D (2008) A biologically active rhIGF-1 fusion accumulated in transgenic rice seeds can reduce blood glucose in diabetic mice via oral delivery. Peptides 29(11):1862–1870. doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2008.07.014
Yang D, Guo F, Liu B, Huang N, Watkins SC (2003) Expression and localization of human lysozyme in the endosperm of transgenic rice. Planta 216(4):597–603
Yang J, Zhao X, Cheng K, Du H, Ouyang Y, Chen J, Qiu S, Huang J, Jiang Y, Jiang L (2012) A killer–protector system regulates both hybrid sterility and segregation distortion in rice. Science 337(6100):1336–1340
Yoshida H, Matsui T, Yamamoto A, Okada T, Mori K (2001) XBP1 mRNA is induced by ATF6 and spliced by IRE1 in response to ER stress to produce a highly active transcription factor. Cell 107(7):881–892
Young TE, Gallie DR (1999) Analysis of programmed cell death in wheat endosperm reveals differences in endosperm development between cereals. Plant Mol Biol 39(5):915–926
Young TE, Gallie DR, DeMason DA (1997) Ethylene-mediated programmed cell death during maize endosperm development of wild-type and shrunken2 genotypes. Plant Physiol 115(2):737–751
Zhang L, Shi J, Jiang D, Stupak J, Ou J, Qiu Q, An N, Li J, Yang D (2013) Expression and characterization of recombinant human alpha-antitrypsin in transgenic rice seed. J Biotechnol. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2013.01.008
Zuppini A, Navazio L, Mariani P (2004) Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced programmed cell death in soybean cells. J Cell Sci 117(12):2591–2598
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Masahiro Ogawa for kindly providing the prolamin antibody. This work was supported by the National Scientific Foundation (No. 30671286), the National High-tech R&D Program (863 Program) of China (No. 2011AA100604) and the Major Projects of Genetically Modified Crop of China (No. 2011ZX08001-006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Figure 1 The expression profiles of the different storage protein genes at 3, 6, 9 DAP
11103_2013_56_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Supplementary Figure 2 PCD signals were monitored by TUNEL assay in rice seed development cells at 2, 4, and 6 DAP. The red signal indicates DNA, and the green signal indicates DNA fragmentation
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Jiang, D., Pang, J. et al. The endoplasmic reticulum stress induced by highly expressed OsrAAT reduces seed size via pre-mature programmed cell death. Plant Mol Biol 83, 153–161 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-013-0056-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-013-0056-x