Abstract
Purpose
Microbiota has crucial biological importance for human well-being. Bidirectional interaction exists between microbiota and the host, and there have been no studies investigating this interaction in patients with acromegaly. We aimed to analyze the composition of microbiota in patients with newly diagnosed acromegaly.
Method
Stool samples were obtained from the patients with newly diagnosed acromegaly in the Endocrinology Clinic of Erciyes University Medical School. The composition of microbiota was analyzed, and the results were compared to healthy volunteers matched to the patients in terms of age, gender and body mass index.
Results
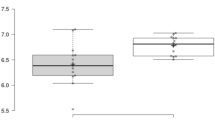
Seven patients (three male, four female) with a mean age of 48 ± 17.6 years were included in the study. The stool analysis revealed a significantly lower bacterial diversity in the patients with acromegaly. Bacteroidetes phylum was predominating in the patient group, and Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio was altered significantly. Bifidobacterium, Collinsella, Bacteroides, Butyricimonas, Clostridium, Oscillospira, and Dialister were predominating in the control group.
Conclusion
The gut microbiota is significantly altered in patients with newly diagnosed acromegaly. Further prospective studies are needed to elucidate the causative relationship between acromegaly, colorectal pathologies, and microbial alterations.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Sender R, Fuchs S, Milo R (2016) Revised estimates for the number of human and bacteria cells in the body. PLoS Biol 14(8):e1002533. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1002533
Bolnick DI, Snowberg LK, Hirsch PE, Lauber CL, Org E, Parks B, Lusis AJ, Knight R, Caporaso JG, Svanback R (2014) Individual diet has sex-dependent effects on vertebrate gut microbiota. Nat Commun 5:4500. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5500
Takagi T, Naito Y, Inoue R, Kashiwagi S, Uchiyama K, Mizushima K, Tsuchiya S, Dohi O, Yoshida N, Kamada K, Ishikawa T, Handa O, Konishi H, Okuda K, Tsujimoto Y, Ohnogi H, Itoh Y (2019) Differences in gut microbiota associated with age, sex, and stool consistency in healthy Japanese subjects. J Gastroenterol 54(1):53–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-018-1488-5
Rastelli M, Cani PD, Knauf C (2019) The gut microbiome ınfluences host endocrine functions. Endocr Rev 40(5):1271–1284. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2018-00280
Valdes AM, Walter J, Segal E, Spector TD (2018) Role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health. BMJ 361:k2179. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.k2179
Yan J, Herzog JW, Tsang K, Brennan CA, Bower MA, Garrett WS, Sartor BR, Aliprantis AO, Charles JF (2016) Gut microbiota induce IGF-1 and promote bone formation and growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113(47):E7554–E7563. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1607235113
Yan J, Charles JF (2018) Gut microbiota and IGF-1. Calcif Tissue Int 102(4):406–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-018-0395-3
Jensen EA, Young JA, Jackson Z, Busken J, List EO, Carroll RK, Kopchick JJ, Murphy ER, Berryman DE (2020) Growth hormone deficiency and excess alter the gut microbiome in adult male mice. Endocrinology. https://doi.org/10.1210/endocr/bqaa02
Yuen KCJ, Masel BE, Reifschneider KL, Sheffield-Moore M, Urban RJ, Pyles RB (2020) Alterations of the GH/IGF-I axis and gut microbiome after traumatic brain ınjury: a new clinical syndrome? J Clin Endocrinol Metab. https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgaa398
Melmed S (2006) Medical progress: acromegaly. N Engl J Med 355(24):2558–2573. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra062453
Ferrau F, Albani A, Ciresi A, Giordano C, Cannavo S (2018) Diabetes secondary to acromegaly: physiopathology, clinical features and effects of treatment. Front Endocrinol (Lansanne) 9:358. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2018.00358
Gadelha MR, Kasuki L, Lim DST, Fleseriu M (2019) Systemic complications of acromegaly and the ımpact of the current treatment landscape: an update. Endocr Rev 40(1):268–332. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2018-00115
Petrossians P, Daly AF, Natchev E, Maione L, Blijdorp K, Sahnoun-Fathallah M, Auriemma R, Diallo AM, Hulting AL, Ferone D, Hana V Jr, Filipponi S, Sievers C, Nogueira C, Fajardo-Montanana C, Carvalho D, Hana V, Stalla GK, Jaffrain-Rea ML, Delemer B, Colao A, Brue T, Neggers S, Zacharieva S, Chanson P, Beckers A (2017) Acromegaly at diagnosis in 3173 patients from the Liege Acromegaly Survey (LAS) Database. Endocr Relat Cancer 24(10):505–518. https://doi.org/10.1530/ERC-17-0253
Larsen N, Vogensen FK, van den Berg FW, Nielsen DS, Andreasen AS, Pedersen BK, Al-Soud WA, Sorensen SJ, Hansen LH, Jakobsen M (2010) Gut microbiota in human adults with type 2 diabetes differs from non-diabetic adults. PLoS ONE 5(2):e9085. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0009085
Li J, Zhao F, Wang Y, Chen J, Tao J, Tian G, Wu S, Liu W, Cui Q, Geng B, Zhang W, Weldon R, Auguste K, Yang L, Liu X, Chen L, Yang X, Zhu B, Cai J (2017) Gut microbiota dysbiosis contributes to the development of hypertension. Microbiome 5(1):14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-016-0222-x
Tilg H, Adolph TE, Gerner RR, Moschen AR (2018) The ıntestinal microbiota in colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell 33(6):954–964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2018.03.004
Melmed S (2009) Acromegaly pathogenesis and treatment. J Clin Invest 119(11):3189–3202. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI39375
Klindworth A, Pruesse E, Schweer T, Peplies J, Quast C, Horn M, Glockner FO (2013) Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Res 41(1):e1. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks808
Bolyen E, Rideout JR, Dillon MR, Bokulich NA, Abnet CC, Al-Ghalith GA, Alexander H, Alm EJ, Arumugam M, Asnicar F, Bai Y, Bisanz JE, Bittinger K, Brejnrod A, Brislawn CJ, Brown CT, Callahan BJ, Caraballo-Rodriguez AM, Chase J, Cope EK, Da Silva R, Diener C, Dorrestein PC, Douglas GM, Durall DM, Duvallet C, Edwardson CF, Ernst M, Estaki M, Fouquier J, Gauglitz JM, Gibbons SM, Gibson DL, Gonzalez A, Gorlick K, Guo J, Hillmann B, Holmes S, Holste H, Huttenhower C, Huttley GA, Janssen S, Jarmusch AK, Jiang L, Kaehler BD, Kang KB, Keefe CR, Keim P, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koester I, Kosciolek T, Kreps J, Langille MGI, Lee J, Ley R, Liu YX, Loftfield E, Lozupone C, Maher M, Marotz C, Martin BD, McDonald D, McIver LJ, Melnik AV, Metcalf JL, Morgan SC, Morton JT, Naimey AT, Navas-Molina JA, Nothias LF, Orchanian SB, Pearson T, Peoples SL, Petras D, Preuss ML, Pruesse E, Rasmussen LB, Rivers A, Robeson MS 2nd, Rosenthal P, Segata N, Shaffer M, Shiffer A, Sinha R, Song SJ, Spear JR, Swafford AD, Thompson LR, Torres PJ, Trinh P, Tripathi A, Turnbaugh PJ, Ul-Hasan S, van der Hooft JJJ, Vargas F, Vazquez-Baeza Y, Vogtmann E, von Hippel M, Walters W, Wan Y, Wang M, Warren J, Weber KC, Williamson CHD, Willis AD, Xu ZZ, Zaneveld JR, Zhang Y, Zhu Q, Knight R, Caporaso JG (2019) Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat Biotechnol 37(8):852–857. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0209-9
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30(15):2114–2120. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170
Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, Gerken J, Schweer T, Yarza P, Peplies J, Glockner FO (2013) The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D590–D596. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1219
Tianqi Chen CG (2016) XGBoost: a scalable tree boosting system. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2016. KDD '16, pp 785–794. Association for Computing Machinery
Mosca A, Leclerc M, Hugot JP (2016) Gut microbiota diversity and human diseases: should we reintroduce key predators in our ecosystem? Front Microbiol 7:455. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00455
Fedor IFSPJ (2003) A tribute to Claude Shannon (1916–2001) and a plea for more rigorous use of species richness, species diversity and the ‘Shannon–Wiener’ Index. Global Ecol Biogeogr 12:177–179
Lozupone C, Knight R (2005) UniFrac: a new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(12):8228–8235. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.12.8228-8235.2005
Llew Mason JB, Bartlett P, Frean M (2000) boosting algorithms as gradient descent. In Advances in neural ınformation processing systems, vol 12, pp 512–518. MIT Press
Shin SC, Kim SH, You H, Kim B, Kim AC, Lee KA, Yoon JH, Ryu JH, Lee WJ (2011) Drosophila microbiome modulates host developmental and metabolic homeostasis via insulin signaling. Science 334(6056):670–674. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1212782
Schwarzer M, Makki K, Storelli G, Machuca-Gayet I, Srutkova D, Hermanova P, Martino ME, Balmand S, Hudcovic T, Heddi A, Rieusset J, Kozakova H, Vidal H, Leulier F (2016) Lactobacillus plantarum strain maintains growth of infant mice during chronic undernutrition. Science 351(6275):854–857. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad8588
Kareem KY, Loh TC, Foo HL, Akit H, Samsudin AA (2016) Effects of dietary postbiotic and inulin on growth performance, IGF1 and GHR mRNA expression, faecal microbiota and volatile fatty acids in broilers. BMC Vet Res 12(1):163. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-016-0790-9
Tilg H, Kaser A (2011) Gut microbiome, obesity, and metabolic dysfunction. J Clin Invest 121(6):2126–2132. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI58109
Le Chatelier E, Nielsen T, Qin J, Prifti E, Hildebrand F, Falony G, Almeida M, Arumugam M, Batto JM, Kennedy S, Leonard P, Li J, Burgdorf K, Grarup N, Jorgensen T, Brandslund I, Nielsen HB, Juncker AS, Bertalan M, Levenez F, Pons N, Rasmussen S, Sunagawa S, Tap J, Tims S, Zoetendal EG, Brunak S, Clement K, Dore J, Kleerebezem M, Kristiansen K, Renault P, Sicheritz-Ponten T, de Vos WM, Zucker JD, Raes J, Hansen T, Meta HITC, Bork P, Wang J, Ehrlich SD, Pedersen O (2013) Richness of human gut microbiome correlates with metabolic markers. Nature 500(7464):541–546. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12506
Manichanh C, Rigottier-Gois L, Bonnaud E, Gloux K, Pelletier E, Frangeul L, Nalin R, Jarrin C, Chardon P, Marteau P, Roca J, Dore J (2006) Reduced diversity of faecal microbiota in Crohn’s disease revealed by a metagenomic approach. Gut 55(2):205–211. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2005.073817
Yang T, Santisteban MM, Rodriguez V, Li E, Ahmari N, Carvajal JM, Zadeh M, Gong M, Qi Y, Zubcevic J, Sahay B, Pepine CJ, Raizada MK, Mohamadzadeh M (2015) Gut dysbiosis is linked to hypertension. Hypertension 65(6):1331–1340. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.05315
Eckburg PB, Bik EM, Bernstein CN, Purdom E, Dethlefsen L, Sargent M, Gill SR, Nelson KE, Relman DA (2005) Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora. Science 308(5728):1635–1638. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1110591
Koliada A, Syzenko G, Moseiko V, Budovska L, Puchkov K, Perederiy V, Gavalko Y, Dorofeyev A, Romanenko M, Tkach S, Sineok L, Lushchak O, Vaiserman A (2017) Association between body mass index and Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio in an adult Ukrainian population. BMC Microbiol 17(1):120. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-017-1027-1
Schwiertz A, Taras D, Schafer K, Beijer S, Bos NA, Donus C, Hardt PD (2010) Microbiota and SCFA in lean and overweight healthy subjects. Obesity (Silver Spring) 18(1):190–195. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2009.167
Baxter NT, Zackular JP, Chen GY, Schloss PD (2014) Structure of the gut microbiome following colonization with human feces determines colonic tumor burden. Microbiome 2:20. https://doi.org/10.1186/2049-2618-2-20
Natividad JM, Pinto-Sanchez MI, Galipeau HJ, Jury J, Jordana M, Reinisch W, Collins SM, Bercik P, Surette MG, Allen-Vercoe E, Verdu EF (2015) ecobiotherapy rich in firmicutes decreases susceptibility to colitis in a humanized gnotobiotic mouse model. Inflamm Bowel Dis 21(8):1883–1893. https://doi.org/10.1097/MIB.0000000000000422
Cani PD, Amar J, Iglesias MA, Poggi M, Knauf C, Bastelica D, Neyrinck AM, Fava F, Tuohy KM, Chabo C, Waget A, Delmee E, Cousin B, Sulpice T, Chamontin B, Ferrieres J, Tanti JF, Gibson GR, Casteilla L, Delzenne NM, Alessi MC, Burcelin R (2007) Metabolic endotoxemia initiates obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 56(7):1761–1772. https://doi.org/10.2337/db06-1491
Fu X, Liu Z, Zhu C, Mou H, Kong Q (2019) Nondigestible carbohydrates, butyrate, and butyrate-producing bacteria. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 59(sup1):S130–S152. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2018.1542587
Tojo R, Suarez A, Clemente MG, de los Reyes-Gavilan CG, Margolles A, Gueimonde M, Ruas-Madiedo P (2014) Intestinal microbiota in health and disease: role of bifidobacteria in gut homeostasis. World J Gastroenterol 20(41):15163–15176. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i41.15163
Qin J, Li Y, Cai Z, Li S, Zhu J, Zhang F, Liang S, Zhang W, Guan Y, Shen D, Peng Y, Zhang D, Jie Z, Wu W, Qin Y, Xue W, Li J, Han L, Lu D, Wu P, Dai Y, Sun X, Li Z, Tang A, Zhong S, Li X, Chen W, Xu R, Wang M, Feng Q, Gong M, Yu J, Zhang Y, Zhang M, Hansen T, Sanchez G, Raes J, Falony G, Okuda S, Almeida M, LeChatelier E, Renault P, Pons N, Batto JM, Zhang Z, Chen H, Yang R, Zheng W, Li S, Yang H, Wang J, Ehrlich SD, Nielsen R, Pedersen O, Kristiansen K, Wang J (2012) A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 490(7418):55–60. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11450
Yang TW, Lee WH, Tu SJ, Huang WC, Chen HM, Sun TH, Tsai MC, Wang CC, Chen HY, Huang CC, Shiu BH, Yang TL, Huang HT, Chou YP, Chou CH, Huang YR, Sun YR, Liang C, Lin FM, Ho SY, Chen WL, Yang SF, Ueng KC, Huang HD, Huang CN, Jong YJ, Lin CC (2019) Enterotype-based analysis of gut microbiota along the conventional adenoma-carcinoma colorectal cancer pathway. Sci Rep 9(1):10923. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-45588-z
Rios-Covian D, Gueimonde M, Duncan SH, Flint HJ, de los Reyes-Gavilan CG (2015) Enhanced butyrate formation by cross-feeding between Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and Bifidobacterium adolescentis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fnv176
Wexler AG, Goodman AL (2017) An insider’s perspective: bacteroides as a window into the microbiome. Nat Microbiol 2:17026. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmicrobiol.2017.26
Gurung M, Li Z, You H, Rodrigues R, Jump DB, Morgun A, Shulzhenko N (2020) Role of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology. EBioMedicine 51:102590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.11.051
Lozupone CA, Stombaugh JI, Gordon JI, Jansson JK, Knight R (2012) Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota. Nature 489(7415):220–230. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11550
Frost F, Storck LJ, Kacprowski T, Gartner S, Ruhlemann M, Bang C, Franke A, Volker U, Aghdassi AA, Steveling A, Mayerle J, Weiss FU, Homuth G, Lerch MM (2019) A structured weight loss program increases gut microbiota phylogenetic diversity and reduces levels of Collinsella in obese type 2 diabetics: a pilot study. PLoS ONE 14(7):e0219489. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0219489
Rokkas T, Pistiolas D, Sechopoulos P, Margantinis G, Koukoulis G (2008) Risk of colorectal neoplasm in patients with acromegaly: a meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol 14(22):3484–3489. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.3484
Giustina A, Barkan A, Beckers A, Biermasz N, Biller BMK, Boguszewski C, Bolanowski M, Bonert V, Bronstein MD, Casanueva FF, Clemmons D, Colao A, Ferone D, Fleseriu M, Frara S, Gadelha MR, Ghigo E, Gurnell M, Heaney AP, Ho K, Ioachimescu A, Katznelson L, Kelestimur F, Kopchick J, Krsek M, Lamberts S, Losa M, Luger A, Maffei P, Marazuela M, Mazziotti G, Mercado M, Mortini P, Neggers S, Pereira AM, Petersenn S, Puig-Domingo M, Salvatori R, Shimon I, Strasburger C, Tsagarakis S, van der Lely AJ, Wass J, Zatelli MC, Melmed S (2020) A consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of acromegaly comorbidities: an update. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgz096
Murri M, Leiva I, Gomez-Zumaquero JM, Tinahones FJ, Cardona F, Soriguer F, Queipo-Ortuno MI (2013) Gut microbiota in children with type 1 diabetes differs from that in healthy children: a case–control study. BMC Med 11:46. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-11-46
de la Cuesta-Zuluaga J, Mueller NT, Corrales-Agudelo V, Velasquez-Mejia EP, Carmona JA, Abad JM, Escobar JS (2017) Metformin ıs associated with higher relative abundance of mucin-degrading Akkermansia muciniphila and several short-chain fatty acid-producing microbiota in the gut. Diabetes Care 40(1):54–62. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc16-1324
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor Dr. Kursad Unluhizarci for critical reading of the manuscript.
Funding
No funds, grants, or other support was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Zuleyha Karaca, Aysa Hacioglu, Aycan Gundogdu, Ufuk Nalbantoglu and Muhammed Emre Urhan. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Aysa Hacioglu and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Erciyes University School of Medicine (Approval Date: 24.07.2019, Approval Number: 2019/575).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hacioglu, A., Gundogdu, A., Nalbantoglu, U. et al. Gut microbiota in patients with newly diagnosed acromegaly: a pilot cross-sectional study. Pituitary 24, 600–610 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-021-01137-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-021-01137-4