Abstract
Background
IgG4-related hypophysitis is a rare clinical entity that forms part of an emerging group of multi-organ IgG4-related fibrosclerotic systemic diseases. The rare prevalence of the disease, presenting features that overlap with other sellar pathologies, and variable imaging features can make preoperative identification challenging.
Purpose and methods
We report three cases of isolated IgG4-related hypophysitis with atypical clinical and imaging features that mimicked those of pituitary apoplexy and other sellar lesions. Additionally, we review the literature of IgG4-related hypophysitis to provide context for individual patient data described herein.
Results
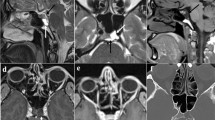
All patients presented with symptoms that mimicked those of pituitary apoplexy and visual disturbance, and MRI findings suggestive of pituitary macroadenoma, Rathke’s cleft cyst and craniopharyngioma. The clinical presentation warranted surgical decompression, resulting in rapid symptomatic improvement. Preoperative high-dose followed by postoperative low-dose glucocorticoid replacement therapy was administered in all cases. Histopathology showed dense infiltrate of IgG4 cells. Post-operative follow-up monitoring for 12–26 months revealed normal serum IgG4 levels with no other organ involvement, while endocrinological testing revealed persistent pituitary hormone deficiencies.
Conclusions
Our cases highlight the importance of considering IgG4-related hypophysitis in the differential diagnosis of solid and cystic sellar lesions presenting acutely with pituitary apoplexy symptoms. Existing diagnostic criteria may not be sufficiently precise to permit rapid and reliable identification, or avoidance of surgery in the acute setting. In contrast to other reports of the natural history of this condition, despite the severity of presenting features, the disease in our cases was pituitary-restricted with normal serum IgG4 levels.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buxton N, Robertson I (2001) Lymphocytic and granulocytic hypophysitis: a single centre experience. Br J Neurosurg 3(15):242–245 (discussion 245–246)
Caturegli P, Newschaffer C, Olivi A, Pomper MG, Burger PC, Rose NR (2005) Autoimmune hypophysitis. Endocr Rev 5(26):599–614
Shimatsu A, Oki Y, Fujisawa I, Sano T (2009) Pituitary and stalk lesions (infundibulo-hypophysitis) associated with immunoglobulin G4-related systemic disease: an emerging clinical entity. Endocr J 9(56):1033–1041
Sosa GA, Bell S, Christiansen SB, Pietrani M, Glerean M, Loto M et al (2014) Histologically confirmed isolated IgG4-related hypophysitis: two case reports in young women. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep 2014:140062
Tauziede-Espariat A, Polivka M, Bouazza S, Decq P, Robert G, Laloi-Michelin M et al (2015) The prevalence of IgG4-positive plasma cells in hypophysitis: a possible relationship to IgG4-related disease. Clin Neuropathol 4(34):181–192
Bando H, Iguchi G, Fukuoka H, Taniguchi M, Yamamoto M, Matsumoto R et al (2014) The prevalence of IgG4-related hypophysitis in 170 consecutive patients with hypopituitarism and/or central diabetes insipidus and review of the literature. Eur J Endocrinol 2(170):161–172
Imber BS, Lee HS, Kunwar S, Blevins LS, Aghi MK (2015) Hypophysitis: a single-center case series. Pituitary 5(18):630–641
Bernreuther C, Illies C, Flitsch J, Buchfelder M, Buslei R, Glatzel M et al (2017) IgG4-related hypophysitis is highly prevalent among cases of histologically confirmed hypophysitis. Brain Pathol 6(27):839–845
Wong S, Lam WY, Wong WK, Lee KC (2007) Hypophysitis presented as inflammatory pseudotumor in immunoglobulin G4-related systemic disease. Hum Pathol 11(38):1720–1723
Leporati P, Landek-Salgado MA, Lupi I, Chiovato L, Caturegli P (2011) IgG4-related hypophysitis: a new addition to the hypophysitis spectrum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 7(96):1971–1980
Caputo C, Bazargan A, McKelvie PA, Sutherland T, Su CS, Inder WJ (2014) Hypophysitis due to IgG4-related disease responding to treatment with azathioprine: an alternative to corticosteroid therapy. Pituitary 3(17):251–256
Decker L, Crawford AM, Lorenzo G, Stippler M, Konstantinov KN, SantaCruz K (2016) IgG4-related hypophysitis: case report and literature review. Cureus 12(8):e907
Hattori Y, Tahara S, Ishii Y, Kitamura T, Inomoto C, Osamura RY et al (2013) A case of IgG4-related hypophysitis without pituitary insufficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 5(98):1808–1811
Hsing MT, Hsu HT, Cheng CY, Chen CM (2013) IgG4-related hypophysitis presenting as a pituitary adenoma with systemic disease. Asian J Surg 2(36):93–97
Isaka Y, Yoshioka K, Nishio M, Yamagami K, Konishi Y, Inoue T et al (2008) A case of IgG4-related multifocal fibrosclerosis complicated by central diabetes insipidus. Endocr J 4(55):723–728
Kanoke A, Ogawa Y, Watanabe M, Kumabe T, Tominaga T (2013) Autoimmune hypophysitis presenting with intracranial multi-organ involvement: three case reports and review of the literature. BMC Res Notes 6:560
Patel SM, Szostek JH (2011) IgG4-related systemic disease in a Native American man. Intern Med 8(50):931–934
Tanabe T, Tsushima K, Yasuo M, Urushihata K, Hanaoka M, Koizumi T et al (2006) IgG4-associated multifocal systemic fibrosis complicating sclerosing sialadenitis, hypophysitis, and retroperitoneal fibrosis, but lacking pancreatic involvement. Intern Med 21(45):1243–1247
Tsuboi H, Inokuma S, Setoguchi K, Shuji S, Hagino N, Tanaka Y et al (2008) Inflammatory pseudotumors in multiple organs associated with elevated serum IgG4 level: recovery by only a small replacement dose of steroid. Intern Med 12(47):1139–1142
Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, Ohara M, Suzuki C, Naishiro Y, Yamamoto H et al (2006) A case of Mikulicz’s disease (IgG4-related plasmacytic disease) complicated by autoimmune hypophysitis. Scand J Rheumatol 5(35):410–411
Lee S, Choi JH, Kim CJ, Kim JH (2017) Clinical interrogation for unveiling an isolated hypophysitis mimicking pituitary adenoma. World Neurosurg 99:735–744
Shikuma J, Kan K, Ito R, Hara K, Sakai H, Miwa T et al (2017) Critical review of IgG4-related hypophysitis. Pituitary 2(20):282–291
Zen Y, Nakanuma Y (2011) Pathogenesis of IgG4-related disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol 1(23):114–118
Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, Kawano M, Yamamoto M, Saeki T et al (2012) A novel clinical entity, IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD): general concept and details. Mod Rheumatol 1(22):1–14
Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK, Yi EE, Sato Y, Yoshino T et al (2012) Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol 9(25):1181–1192
Stone JH, Khosroshahi A, Deshpande V, Chan JK, Heathcote JG, Aalberse R et al (2012) Recommendations for the nomenclature of IgG4-related disease and its individual organ system manifestations. Arthritis Rheum 10(64):3061–3067
Sah RP, Chari ST (2011) Serologic issues in IgG4-related systemic disease and autoimmune pancreatitis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 1(23):108–113
Koide H, Shiga A, Komai E, Yamato A, Fujimoto M, Tamura A et al (2017) Prednisolone-responsive postpartum IgG4-related hypophysitis. Intern Med. https://doi.org/10.2169/internalmedicine.8446-16
Takano K, Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, Himi T (2017) Recent advances in knowledge regarding the head and neck manifestations of IgG4-related disease. Auris Nasus Larynx 1(44):7–17
Anno T, Kawasaki F, Takai M, Shigemoto R, Kan Y, Kaneto H et al (2017) Clinical course of pituitary function and image in IgG4-related hypophysitis. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. https://doi.org/10.1530/EDM-16-0148
Harano Y, Honda K, Akiyama Y, Kotajima L, Arioka H (2015) A case of IgG4-related hypophysitis presented with hypopituitarism and diabetes insipidus. Clin Med Insights Case Rep 8:23–26
Hori M, Makita N, Andoh T, Takiyama H, Yajima Y, Sakatani T et al (2010) Long-term clinical course of IgG4-related systemic disease accompanied by hypophysitis. Endocr J 6(57):485–492
Chari ST (2007) Current concepts in the treatment of autoimmune pancreatitis. JOP 1(8):1–3
Kamisawa T, Shimosegawa T, Okazaki K, Nishino T, Watanabe H, Kanno A et al (2009) Standard steroid treatment for autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut 11(58):1504–1507
Gu WJ, Zhang Q, Zhu J, Li J, Wei SH, Mu YM (2017) Rituximab was used to treat recurrent IgG4-related hypophysitis with ophthalmopathy as the initial presentation: a case report and literature review. Medicine 24(96):e6934
Osawa S, Ogawa Y, Watanabe M, Tominaga T (2009) Hypophysitis presenting with atypical rapid deterioration: with special reference to immunoglobulin G4-related disease-case report. Neurol Med Chir 12(49):622–625
Khong P, Enno A, Darwish B (2014) Lymphoplasmacytic hypophysitis associated with immunoglobulin G4. J Clin Neurosci 2(21):342–344
Ebbo M, Grados A, Guedj E, Gobert D, Colavolpe C, Zaidan M et al (2014) Usefulness of 2-[18F]-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose-positron emission tomography/computed tomography for staging and evaluation of treatment response in IgG4-related disease: a retrospective multicenter study. Arthritis Care Res 1(66):86–96
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuen, K.C.J., Moloney, K.J., Mercado, J.U. et al. A case series of atypical features of patients with biopsy-proven isolated IgG4-related hypophysitis and normal serum IgG4 levels. Pituitary 21, 238–246 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-017-0852-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-017-0852-4