Abstract
Purpose
Transsphenoidal surgery is the treatment of choice for most pituitary adenomas (PA), except prolactinomas. Difficulties achieving radical resection with this method are encountered in patients with PAs invading the cavernous sinus (CS), due to the inability of the standard transsphenoidal approach to expose all tumors adequately. This study analyzed methods to resect PAs invading the CS and factors influencing the degree of tumor resection and occurrence of complications.
Methods
Outcomes were retrospectively analyzed in 52 patients with PA invading the CS who underwent surgery via the extended transsphenoidal approach utilizing multiple techniques, including microscopy, endoscopy, neuronavigation, and intraoperative Doppler ultrasonography.
Results
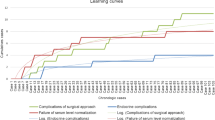
Gross-total resection (GTR) was achieved in 33 patients (63.5 %). GTR rate was significantly higher in patients with Knosp Grade 3 than Knosp Grade 4 (92.3 vs. 53.8 %) and in patients undergoing initial surgery than reoperation (77.1 vs. 35.3 %). One patient (2.9 %) undergoing initial surgery experienced transient cranial nerve palsy, without other postoperative complications. Postoperative complications were significantly higher after reoperation. Firm tumor consistency was significantly more frequent in patients undergoing reoperation than initial surgery (52.9 vs. 8.6 %).
Conclusion
Extended transsphenoidal surgery incorporating multiple complementary techniques was highly effective for PAs invading the CS. Postoperative complications rates were relatively low, especially for patients undergoing initial surgery and those with Knosp Grade 3 tumors. Total resection of PAs invading the CS remains challenging, especially in patients undergoing reoperation or having firm tumors.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jane JA Jr, Thapar K, Kaptain GJ, Maartens N, Laws ER Jr (2002) Pituitary surgery: transsphenoidal approach. Neurosurgery 51:435–442 (discussion 442-444)
Rhoton AL Jr (2003) Operative techniques and instrumentation for neurosurgery. Neurosurgery 53:907–934 (discussion 934)
Ciric I, Ragin A, Baumgartner C, Pierce D (1997) Complications of transsphenoidal surgery: results of a national survey, review of the literature, and personal experience. Neurosurgery 40:225–236 (discussion 236-237)
Couldwell WT (2004) Transsphenoidal and transcranial surgery for pituitary adenomas. J Neurooncol 69:237–256
Kurosaki M, Kambe A, Ishibashi M, Watanabe T, Horie Y (2014) A case report of sarcoma of the sella caused by postoperative radiotherapy for a prolactin-producing pituitary adenoma. Brain Tumor Pathol 31:187–191
Sheehan JP, Niranjan A, Sheehan JM, Jane JA Jr, Laws ER, Kondziolka D, Flickinger J, Landolt AM, Loeffler JS, Lunsford LD (2005) Stereotactic radiosurgery for pituitary adenomas: an intermediate review of its safety, efficacy, and role in the neurosurgical treatment armamentarium. J Neurosurg 102:678–691
Hayashi M, Chernov M, Tamura N, Nagai M, Yomo S, Ochiai T, Amano K, Izawa M, Hori T, Muragaki Y, Iseki H, Okada Y, Takakura K (2010) Gamma Knife robotic microradiosurgery of pituitary adenomas invading the cavernous sinus: treatment concept and results in 89 cases. J Neurooncol 98:185–194
Hakuba A, Tanaka K, Suzuki T, Nishimura S (1989) A combined orbitozygomatic infratemporal epidural and subdural approach for lesions involving the entire cavernous sinus. J Neurosurg 71:699–704
van Lindert EJ, Grotenhuis JA, Meijer E (1991) Results of follow-up after removal of non-functioning pituitary adenomas by transcranial surgery. Br J Neurosurg 5:129–133
Laws ER Jr, Onofrio BM, Pearson BW, McDonald TJ, Dirrenberger RA (1979) Successful management of bilateral carotid-cavernous fistulae with a trans-sphenoidal approach. Neurosurgery 4:162–167
Ceylan S, Koc K, Anik I (2010) Endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal approach for pituitary adenomas invading the cavernous sinus. J Neurosurg 112:99–107
Couldwell WT, Weiss MH, Rabb C, Liu JK, Apfelbaum RI, Fukushima T (2004) Variations on the standard transsphenoidal approach to the sellar region, with emphasis on the extended approaches and parasellar approaches: surgical experience in 105 cases. Neurosurgery 55:539–547 (discussion 547-550)
Fraioli B, Esposito V, Santoro A, Iannetti G, Giuffre R, Cantore G (1995) Transmaxillosphenoidal approach to tumors invading the medial compartment of the cavernous sinus. J Neurosurg 82:63–69
Frank G, Pasquini E (2006) Endoscopic endonasal cavernous sinus surgery, with special reference to pituitary adenomas. Front Horm Res 34:64–82
Hashimoto N, Kikuchi H (1990) Transsphenoidal approach to infrasellar tumors involving the cavernous sinus. J Neurosurg 73:513–517
Kitano M, Taneda M (2001) Extended transsphenoidal approach with submucosal posterior ethmoidectomy for parasellar tumors. J Neurosurg 94:999–1004
Kitano M, Taneda M, Shimono T, Nakao Y (2008) Extended transsphenoidal approach for surgical management of pituitary adenomas invading the cavernous sinus. J Neurosurg 108:26–36
Sabit I, Schaefer SD, Couldwell WT (2000) Extradural extranasal combined transmaxillary transsphenoidal approach to the cavernous sinus: a minimally invasive microsurgical model. Laryngoscope 110:286–291
Woodworth GF, Patel KS, Shin B, Burkhardt JK, Tsiouris AJ, McCoul ED, Anand VK, Schwartz TH (2014) Surgical outcomes using a medial-to-lateral endonasal endoscopic approach to pituitary adenomas invading the cavernous sinus. J Neurosurg 120:1086–1094
Zhao B, Wei YK, Li GL, Li YN, Yao Y, Kang J, Ma WB, Yang Y, Wang RZ (2010) Extended transsphenoidal approach for pituitary adenomas invading the anterior cranial base, cavernous sinus, and clivus: a single center experience with 126 consecutive cases. J Neurosurg 112:108–117
Li Y, Wang R, Li G (2009) Transsphenoidal approach to pituitary adenoma: surgical technique of the Peking Union Medical College Hospital. Chin Med J (Engl) 122:3086–3090
Knosp E, Steiner E, Kitz K, Matula C (1993) Pituitary adenomas with invasion of the cavernous sinus space: a magnetic resonance imaging classification compared with surgical findings. Neurosurgery 33:610–617 (discussion 617-618)
Kristof RA, Schramm J, Redel L, Neuloh G, Wichers M, Klingmüller D (2002) Endocrinological outcome following first time transsphenoidal surgery for GH-, ACTH-, and PRL-secreting pituitary adenomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 144:555–561
Kassam AB, Thomas A, Carrau RL, Snyderman CH, Vescan A, Prevedello D, Mintz A, Gardner P (2008) Endoscopic reconstruction of the cranial base using a pedicled nasoseptal flap. Neurosurgery 63:ONS44–ONS52 (discussion ONS52-53)
Dusick JR, Esposito F, Malkasian D, Kelly DF (2007) Avoidance of carotid artery injuries in transsphenoidal surgery with the Doppler probe and micro-hook blades. Neurosurgery 60:322–328 (discussion 328-329)
Gardner PA, Tormenti MJ, Pant H, Fernandez-Miranda JC, Snyderman CH, Horowitz MB (2013) Carotid artery injury during endoscopic endonasal skull base surgery: incidence and outcomes. Neurosurgery 73:ons261–ons269 (discussion ons269-270)
Berkmann S, Fandino J, Zosso S, Killer HE, Remonda L, Landolt H (2011) Intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging and early prognosis for vision after transsphenoidal surgery for sellar lesions. J Neurosurg 115:518–527
Nimsky C, von Keller B, Ganslandt O, Fahlbusch R (2006) Intraoperative high-field magnetic resonance imaging in transsphenoidal surgery of hormonally inactive pituitary macroadenomas. Neurosurgery 59:105–114 (discussion 105-114)
Schwartz TH, Stieg PE, Anand VK (2006) Endoscopic transsphenoidal pituitary surgery with intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging. Neurosurgery 58:ONS44–ONS51 (discussion ONS44-51)
Tabaee A, Anand VK, Fraser JF, Brown SM, Singh A, Schwartz TH (2009) Three-dimensional endoscopic pituitary surgery. Neurosurgery 64:288–293 (discussion 294-295)
Zhao Y, Yu S, Wang R, Zhao J (2006) Clinical application of a neuronavigation system in transsphenoidal surgery of pituitary macroadenoma. Neurosurg Rev 29:306–311 (discussion 311-312)
Jho HD, Carrau RL (1997) Endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal surgery: experience with 50 patients. J Neurosurg 87:44–51
Cappabianca P, Cavallo LM, de Divitiis O, Solari D, Esposito F, Colao A (2008) Endoscopic pituitary surgery. Pituitary 11:385–390
Jane JA Jr, Han J, Prevedello DM, Jagannathan J, Dumont AS, Laws ER Jr (2005) Perspectives on endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery. Neurosurg Focus 19:E2
Doglietto F, Lauretti L, Frank G, Pasquini E, Fernandez E, Tschabitscher M, Maira G (2009) Microscopic and endoscopic extracranial approaches to the cavernous sinus: anatomic study. Neurosurgery 64:413–421 (discussion 421-422)
Har-El G (2005) Endoscopic transnasal transsphenoidal pituitary surgery-comparison with the traditional sublabial transseptal approach. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 38:723–735
de Divitiis E (2006) Endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery: stone-in-the-pond effect. Neurosurgery 59:512–520 (discussion 512-520)
Locatelli D, Canevari FR, Acchiardi I, Castelnuovo P (2010) The endoscopic diving technique in pituitary and cranial base surgery: technical note. Neurosurgery 66:E400–E401 (discussion E401)
Ammirati M, Wei L, Ciric I (2013) Short term outcome of endoscopic versus microscopic pituitary adenoma surgery: a systemic review and meta-analysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 84:843–849
Dallapiazza RF, Grober Y, Starke RM, Laws ER Jr, Jane JA Jr (2015) Long-term results of endonasal endoscopic transsphenoidal resection of nonfunctioning pituitary macroadenomas. Neurosurgery 76:42–53
Catapano D, Sloffer CA, Frank G, Pasquini E, D’Angelo VA, Lanzino G (2006) Comparison between the microscope and endoscope in the direct endonasal extended transsphenoidal approach: anatomical study. J Neurosurg 104:419–425
Al-Mefty O, Pravdenkova S, Gragnaniello C (2010) A technical note on endonasal combined microscopic endoscopic with free head navigation technique of removal of pituitary adenomas. Neurosurg Rev 33:243–248 (discussion 248-249)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by The Capital Medical Development Research Foundation of China (Grant No. 2011-4001-06) and the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2014BAI04B03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We do not have a financial relationship with the organizations that sponsored the research. None of the authors has any potential financial conflicts of interests in relation to this article.
Additional information
Xinjie Bao and Kan Deng have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, X., Deng, K., Liu, X. et al. Extended transsphenoidal approach for pituitary adenomas invading the cavernous sinus using multiple complementary techniques. Pituitary 19, 1–10 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-015-0675-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-015-0675-0