Abstract
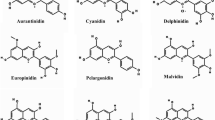
Flavonoids are major constituents of flower colour. Plants accumulate specific flavonoids and thus every species often exhibits a limited flower colour range. Three cytochromes P450 play critical roles in the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway. Flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase (F3′H, CYP75B) and flavonoid 3′,5′-hydroxylase (F3′5′H, CYP75A) catalyze the hydroxylation of the B-ring of flavonoids and are necessary to biosynthesize cyanidin-(red to magenta) and delphinidin-(violet to blue) based anthocyanins, respectively. Pelargonidin-based anthocyanins (orange to red) are synthesized in their absence. Some species such as roses, carnations and chrysanthemums do not have violet/blue flower colour due to deficiency of F3′5′H. Successful expression of heterologous F3′5′H genes in roses and carnations results in delphinidin production, causing a novel blue/violet flower colour. Down-regulation of F3′H and F3′5′H genes has yielded orange petunia and pink torenia colour that accumulate pelargonidin-based anthocyanins. Flavone synthase II (CYP93B) catalyzes the synthesis of flavones that contribute to the bluing of flower colour, and modulation of FNSII gene expression in petunia and tobacco changes their flower colour. Extensive engineering of the anthocyanin pathway is therefore now possible, and can be expected to enhance the range of flower colours.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DFR:
-
dihydroflavonol 4-reductase
- DHK:
-
dihydrokaempferol
- DHQ:
-
dihydroquercetin
- DHM:
-
dihydromyricetin
- F3H:
-
flavanone 3-hydroxylase
- F3′H:
-
flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase
- F3′5′H:
-
flavonoid 3′,5′-hydroxylase
- FLS:
-
flavonol synthase
- FNS:
-
flavone synthase
References
Akashi T, Fukuchi-Mizutani M, Aoki T, Ueyama Y, Yonekura-Sakakibara K, Tanaka Y, Kusumi T, Ayabe S (1999) Molecular cloning and biochemical characterization of a novel cytochrome P450, flavone synthase II, that catalyzes direct conversion of flavanones to flavones. Plant Cell Physiol 40:1182–1187
Ayabe S, Akashi T (2006) Cytochrome P450s in flavonoid metabolism. Phytochem Rev DOI 10.1007/s11101-006-9007-3 (this issue)
Brugliera F, Barri-rewell G, Holton TA, Mason GM (1999) Isolation and characterization of a flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase cDNA clone corresponding to the Ht1 locus of Petunia hybrida. Plant J 19:441–451
Brugliera F, Tanaka Y, Mason J (2004) Flavonoid 3′,5′-hydroxylase gene sequences and uses therefor. Patent publication number WO 2004/020637
de Vetten N, ter Horst J, van Schaik HP, de Boer A, Mol J, Koes R (1999) A cytochrome b5 is required for full activity of flavonoid 3′,5′-hydroxylase, a cytochrome P450 involved in the formation of blue flower colors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:778–783
Forkmann G, Heller W (1999) Biosynthesis of flavonoids. In: Sankawa U (ed) Polyketides and other secondary metabolites including fatty acid and their derivatives, vol 1. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 713–748
Fukui Y, Tanaka Y, Kusumi T, Iwashita T, Nomoto K (2003) A rationale for the shift in colour towards blue in transgenic carnation flowers expressing the flavonoid 3′,5′-hydroxylase gene. Phytochem 63:15–23
Halbwirth H, Forkmann G, Stich K (2004) The A-ring specific hydroxylation of flavonols in position 6 in Tagetes sp. is catalyzed by a cytochrome P450 dependent monooxygenase. Plant Sci 167:129–135
Harborne JB, Williams CA (2000) Advances in flavonoid research since 1992. Phytochem 55:481–504
Holton TA, Tanaka Y (1994) Blue roses – a pigment of our imagination? Trends Biotechnol 12:40–43
Holton TA (1996) Transgenic plants exhibiting altered flower color & methods for producing same. Patent publication number PCT/AU96/00296
Holton TA, Brugliera F, Lester DR, Tanaka Y, Hyland CD, Menting JGT, Lu C-Y, Farcy E, Stevenson TW, Cornish EC (1993) Cloning and expression of cytochrome P450 genes controlling flower colour. Nature 366:276–279
Latunde-Dada AO, Cabbello-Hurtado F, Czittrich N, Didierjean L, Schopfer C, Hertkorn N, Werk-Reichhart D, Ebel J (2001) Flavonoid 6-hydroxylase from soybean (Glycine max L.), a novel plant P-450 monooxygenase. J Biol Chem 276:1688–1695
Martens S, Forkmann G (1999) Cloning and expression of flavone synthase II from Gerbera hybrida. Plant J 20:611–618
Martens S, Mithofer A (2005) Flavones and flavone synthases. Phytochem 66:2399–2407
Mori S, Kobayashi H, Hoshi Y, Kondo M, Nakano M (2004) Heterologous expression of the flavonoid 3′,5′-hydroxylase gene of Vinca major alters flower color in transgenic Petunia hybrida. Plant Cell Rep 22:415–421
Nakamura N, Fukuchi-Mizutani M, Suzuki K, Miyazaki K, Tanaka Y (2006) RNAi suppression of the anthocyanidin synthase gene in Torenia hybrida yields white flowers with higher frequency and better stability than antisense and sense suppression. Plant Biotechnol 23:13–18
Nakatsuka T, Nishihara M, Mishiba K, Yamamura S (2006) Heterologous expression of two gentian cytochrome P450 genes can modulate the intensity of flower pigmentation in transgenic tobacco plants. Mol Breeding 17:91–99
Okinaka Y, Shimada Y, Nakano-Shimada R, Ohbayashi M, Kiyokawa S, Kikuchi Y (2003) Selective accumulation of delphinidin derivatives in tobacco using a putative flavonoid 3′,5′-hydroxylase cDNA from Campanula medium. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 67:161–165
Shimada Y, Nakano-Shimada R, Ohbayashi M, Okinaka Y, Kiyokawa S, Kikuchi Y (1999) Expression of chimeric P450 genes encoding flavonoid-3′,5′-hydroxylase in transgenic tobacco and petunia plants. FEBS Lett 461:241–245
Shimada Y, Ohbayashi M, Nakano-Shimada R, Okinaka Y, Kiyokawa S, Kikuchi Y (2001) Genetic engineering of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway with flavonoid 3′,5′-hydroxylase: specific switching of the pathway in petunia. Plant Cell Rep 20:456–462
Suzuki K, Zue H, Tanaka Y, Fukui Y, Fukuchi-Mizutani M, Murakami Y, Katsumoto Y, Tsuda S, Kusumi T (2000) Flower color modifications of Torenia hybrida by cosuppression of anthocyanin biosynthesis genes. Mol Breeding 6:239–246
Tanaka Y, Brugliera F (2006) Flower colour. In: Ainsworth C (ed) Flowering and its manipulation. Blackwell, London, pp 201–239
Tanaka Y, Katsumoto Y, Brugliera F, John M (2005a) Genetic engineering in floriculture. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 80:1–24
Tanaka Y, Fukui Y, Togami J, Mizutani M, Katsumoto Y (2005b) Process for producing rose with modified color, Patent publication number WO 2005/017147
Togami J, Tamura M, Ishiguro K, Hirose C, Okuhara H, Ueyama Y, Nakamura N, Yonekura-Sakakibara K, Fukuchi-Mizutani M, Suzuki K, Fukui Y, Kusumi T, Tanaka Y (2006) Molecular characterization of the flavonoid biosynthesis of Verbena hybrida and functional analysis of verbena and Clitoria ternatea F3′5′H genes in transgenic verbena. Plant Biotechnol 23:5–11
Tsuda S, Fukui Y, Nakamra N, Katsumoto Y, Yonekura-Sakakibara K, Fukuchi-Mizutani M, Ohira K, Ueyama Y, Ohkawa H, Holton TA, Kusumi T, Tanaka Y (2004) Flower color modification of Petunia hybrida commercial varieties by metabolic engineering. Plant Biotechnol 21:377–386
Ueyama Y, Katsumoto K, Fukui Y, Fukuchi-Mizutani M, Ohkawa H, Kusumi T, Iwashita T, Tanaka Y (2006) Molecular characterization of the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway and flower colour modification of Nierembergia sp. Plant Biotechnol 23:19–24
Ueyama Y, Suzuki K, Fukuchi-Mizutani M, Fukui Y, Miyazaki K, Ohkawara H, Kusumi T, Tanaka Y (2002) Molecular and biochemical characterization of torenia flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase and flavone synthase II and modification of flower color by modulating the expression of these genes. Plant Sci 163:253–263
Acknowledgements
The author is grateful for the collaboration received from Suntory Ltd. (Japan) and Florigene Ltd. (Australia) and for research grants provided by Bio-oriented Technology Research Advancement Institute (Japan). Dr Chandler (Florigene Ltd.) and Dr Yamamura (Iwate Biotechnology Research Center) are acknowledged for improving the manuscript, especially the rose section, and providing a preprint, respectively. Due to space constraints, only a limited number of publications have been cited.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, Y. Flower colour and cytochromes P450. Phytochem Rev 5, 283–291 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-006-9003-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-006-9003-7