Abstract
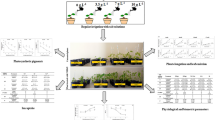
This study aimed to determine the effects of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria Bacillus subtilis JS on the growth and physiological changes of Populus euramericana and Populus deltoides × P. nigra. Poplar seedlings were treated with B. subtilis JS and their growth was monitored for up to 120 d. Three different types of treatments [control, B1 (B. subtilis:double-distilled water, 1:100, v/v), and B2 (1:50)] were established. B. subtilis JS enhanced seedling height by 62% and total biomass by 37% after 120 d. Physiologically, the photosynthetic rate increased by 54%, and the total chlorophyll (Chl) content, foliage nitrogen and phosphate content were significantly higher after treatment with B2 than that of the control. These results suggest that the total Chl content is directly related to not only the photosynthetic capacity of the foliage but also to the nitrogen content, indicating that the strain JS may promote the growth of poplar.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- B1:
-
Bacillus subtilis JS inoculation with double-distilled water (dilution rate of 1 in 100)
- B2:
-
Bacillus subtilis JS inoculation with double-distilled water (dilution rate of 1 in 50)
- CarT:
-
total carotenoid
- ChlT:
-
total chlorophyll
- CFUs:
-
colonyforming units
- DDW:
-
double-distilled water
- E :
-
transpiration rate
- gs:
-
stomatal conductance
- NLeaf :
-
total nitrogen content of leaf
- PGPR:
-
plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria
- PLeaf :
-
phosphate content of leaf
- P N :
-
net photosynthetic rate
- RGR:
-
relative growth rate
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- SRCs:
-
short rotation coppice cultures
- TF:
-
triphenyl formazan
- TTC:
-
triphenyltetrazolium chloride
- WUE:
-
water-use efficiency
References
Adams M.A., Turnbull T.L., Sprent J.I. et al.: Legumes are different: Leaf nitrogen, photosynthesis, and water use efficiency.–P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 113: 4098–4103, 2016.
Arkhipova T.N., Veselov S.U., Melentiev A.I. et al.: Ability of bacterium Bacillus subtilis to produce cytokinins and to influence the growth and endogenous hormone content of lettuce plants.–Plant Soil 272: 201–209, 2005.
Arnon D.I.: Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris.–Plant Physiol. 24: 1, 1949.
Asaka O., Shoda M.: Biocontrol of Rhizoctonia solani dampingoff of tomato with Bacillus subtilis RB14.–Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62: 4081–4085, 1996.
Aslantas R., Ramazan Ç., Fikrettin S.: Effect of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on young apple tree growth and fruit yield under orchard conditions.–Sci. Hortic.-Amsterdam 111: 371–377, 2007.
Badizi B.M., Zarandi M.M.: Some physiological and growth parameters of Pistachio vera L. under coinoculation with endomycorrhizae and Bacillus subtilis in response to salinity.–Bull. Environ. Pharmacol. Life Sci. 1: 70–77, 2016.
Bandopadhyay S.: Effects of dual inoculation of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on different non-leguminous plants under pot condition.–Indian J. Microbiol. Res. 2: 20–26, 2015.
Bianco R.L., Policarpo M., Scariano L.: Effects of rootstock vigour and in-row spacing on stem and root growth, conformation and dry-matter distribution of young apple trees.–J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 78: 828–836, 2003.
Biswas J.C., Ladha J.K., Dazzo F.B.: Rhizobia inoculation improves nutrient uptake and growth of lowland rice.–Soil Sci. Soc. Am J. 64: 1644–1650, 2000.
Bremner J.M.: Nitrogen-total.–In: Sparks D.L. Page A.L., Helmke P.A., et al. (ed.): Methods of Soil Analysis, part 3. Chemical methods. Pp. 1085–1122. SSSA, ASA, Madison 1996.
Cernusak L.A., Aranda J., Marshall J.D. et al.: Large variation in whole-plant water use efficiency among tropical tree species.–New Phytol. 173: 294–305, 2006.
Ciompi S., Gentili E., Guidi L. et al.: The effect of nitrogen deficiency on leaf gas exchange and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters.–Plant Sci. 118: 177–184, 1996.
Coleman M.D., Dickson R.E., Isebrands J.G.: Growth and physiology of aspen supplied with different fertilizer addition rates.–Physiol. Plantarum 103: 513–526, 1998.
Cooke J.E., Martin T.A., Davis J.M.: Short-term physiological and developmental responses to nitrogen availability in hybrid poplar.–New. Phytol. 167: 41–52, 2005.
Cui X., Dong Y., Gi P. et al.: Relationship between root vigour, photosynthesis and biomass in soybean cultivars during 87 years of genetic improvement in the northern China.–Photosynthetica 54: 81–86, 2016.
Dickmann D.I., Nguyen P.V., Pregitzer K.S.: Effects of irrigation and coppicing on above-ground growth, physiology and fine root-dynamics of two field-grown hybrid poplar clones.–Forest Ecol. Manag. 80: 163–174, 1996.
Earl A.M., Losick R., Kolter R.: Ecology and genomics of Bacillus subtilis.–Trends Microbiol. 16: 269–275, 2008.
Emmert E.A.B., Handelsman J.: Biocontrol of plant disease: A Gram-positive perspective.–FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 171: 1–9, 1999.
Esitken A., Karlidag H., Ercisli S. et al.: Effects of foliar application of Bacillus subtilis OSU-142 on the yield, growth and control of shot-hole disease (Coryneum blight) of Apricot.–Gartenbauwissenschaft 67: 139–142, 2002.
Gordon J.C., Promnitz L.C.: Photosynthetic and enzymatic criteria for the early selection of fast-growing Populus clones.–In: Cannell M.G.R, Last F.T. (ed.): Tree Physiology and Yield Improvement-Carbon Fixation Efficiency. Pp. 79–97. New York Academic Press, New York 1976.
Han H.S., Lee K.D.: Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria effect on antioxidant status, photosynthesis, mineral uptake and growth of lettuce under soil salinity.–Res. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 1: 210–215, 2005.
Han M.H.: [Effect of Bacillus subtilis JS on the Growth Promotion and the Tolerance Induction to a Biotic Stress in Plants.]–Dissertation, University of Seoul, Seoul 2014. [In Korean]
Han Q.Q., Lü X.P., Bai J.P. et al.: Beneficial soil bacterium Bacillus subtilis (GB03) augments salt tolerance of white clover.–Front. Plant Sci. 5: 1–8, 2014.
Hanson W.C.: The photometric determination of phosphorus in fertilizers using the phosphovanadomolybdate complex.–J. Sci. Food Agric. 1: 172–173, 1950.
Heidari M., Mousavinik S.M., Golpayegani A.: Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) effect on physiological parameters and mineral uptake in basil (Ociumum basilicm L.) under water stress.–ARPN J. Agr. Biol. Sci. 6: 6–11, 2011.
Hartmann A., Schmid M., van Tuinen D. et al.: Plant-driven selection of microbes.–Plant Soil 321: 235–257, 2009.
Hernandez V., López A., Hellín P. et al.: Functional quality of lettuce treated with growth promoting bacteria and different nitrogen doses.–Int. Con. Agr. Eng. 542: 1, 2014.
Hirata H.: [Plant Nutritional Experimental Method.] Pp. 52–55. Hakuyusha, Tokyo 1990. [In Japanese]
Ibrahim L., Proe M.F., Cameron A.D.: Main effects of nitrogen supply and drought stress upon whole-plant carbon allocation in poplar.–Can. J. Forest Res. 27: 1413–1419, 1997.
Jang H.S.: [Effect of Bacillus subtilis JS on the Salt and Drought Stress of Ricinus communis L.]–Dissertation. Dongguk University, Dongguk 2015. [In Korean]
Joslin J.D., Henderson G.S.: The determination of percentages of living tissue in woody fine root samples using triphenyltetrazolium chloride.–Forest Sci. 30: 965–970, 1984.
Karami Chame S., Khalil-Tahmasbi B., ShahMahmoodi P. et al.: Effects of salinity stress, salicylic acid and Pseudomonas on the physiological characteristics and yield of seed beans (Phaseolus vulgaris).–Sci. Agri. 14: 234–238, 2016.
Khan Z.U., McNeil D.L., Samad A.: Root pruning reduces the vegetative and reproductive growth of apple trees growing under an ultra high density planting system.–Sci. Hortic.-Amsterdam 77: 165–176, 1998.
Kim H.C., Yeo J.K., Koo Y.B. et al.: [Growth and biomass production of fast growing tree species treated with slurry composting and biofiltration liquid fertilizer.]–Korean J. Soil Sci. Fert. 44: 206–214, 2011. [In Korean]
Kim J.S., Lee J., Lee C.H. et al.: Activation of pathogenesisrelated genes by the rhizobacterium, Bacillus sp. JS, which induces systemic resistance in tobacco plants.–Plant Pathol. J. 31: 195–201, 2015a.
Kim J.S., Lee J., Seo S.G. et al.: Gene expression profile affected by volatiles of new plant growth promoting rhizobacteria, Bacillus subtilis strain JS, in tobacco.–Genes Genom. 37: 387–397, 2015b.
Kloepper J.W., Ryu C.M., Zhang S.: Induced systemic resistance and promotion of plant growth by Bacillus spp.–Phytopathology 94: 1259–1266, 2004.
Kochot C.K., Golabale S.B., Purohit, A.: A Textbook of Pharmacognosy. Pp. 17–18. Nirali Prakashan, Pune 1998.
Ku S.B., Edwards G.E., Tanner C.B.: Effects of light, carbon dioxide, and temperature on photosynthesis, oxygen inhibition of photosynthesis, and transpiration in Solanum tuberosum.–Plant Physiol. 59: 868–872, 1977.
Kunst F., Ogasawara N., Moszer I. et al.: The complete genome sequence of the Gram-positive bacterium Bacillus subtilis.–Nature 390: 249–256, 1997.
Lassheikki M., Puttonen P., Räsänen P.K.: Planting performance potential of Pinus sylvestris seedlings as evaluated by root growth capacity and triphenyl tetrazolium chloride reduction method.–Scand. J. Forest Res. 6: 91–104, 1991.
Lee Y.S., Park D.J., Kim J.H. et al.: [Growth promotion of lettuce by biofertilizer, BIOACTIVE, prepared from Bacillus subtilis HR-1019 and N-acetyl-thioproline.]–J. Life Sci. 23: 79–83, 2013. [In Korean]
Lefebvre S., Lawson T., Zakhleniuk O.V. et al.: Increased sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase activity in transgenic tobacco plants stimulates photosynthesis and growth from an early stage in development.–Plant Physiol. 138: 451–460, 2005.
Leister D.: Genomics-based dissection of the cross-talk of chloroplasts with the nucleus and mitochondria in Arabidopsis.–Gene 354: 110–116, 2005.
Lenin G., Jayanthi M.: Efficiency of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on enhancement of growth, yield and nutrient content of Catharanthus roseus.–Int. J. Res. Pure. Appl. Microbiol. 2: 37–42, 2012.
Li Y., Xu S., Gao J. et al.: Bacillus subtilis-regulation of stomatal movement and instantaneous water use efficiency in Vicia faba.–Plant Growth Regul. 78: 43–55, 2016.
Lima J.D., Mosquim P.R., Da Matta F.M.: Leaf gas exchange and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters in Phaseolus vulgaris as affected by nitrogen and phosphorus deficiency.–Photosynthetica 37: 113–121, 1999.
Lindström A., Nyström C.: Seasonal variation in root hardiness in container grown Scots pine, Norway spruce, and Lodgepole pine seedlings.–Can. J. Forest Res. 17: 787–793, 1987.
Lucy M., Reed E., Glick B.R.: Application of free living plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria.–Antonie van Leeuw. 86: 1–25, 2004.
Makkonen K., Helmisaari H.S.: Seasonal and yearly variations of fine-root biomass and necromass in a Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) stand.–Forest Ecol. Manage. 102: 283–290, 1998.
Mathivanan S., Chidambaram A.A., Robert, G.A. et al.: Impact of PGPR inoculation on photosynthetic pigment and protein contents in Arachis hypogaea L.–J. Sci. Agr. 1: 29–36, 2017.
Misson L., Gershenson A., Tang J.W. et al.: Influences of canopy photosynthesis and summer rain pulses on root dynamics and soil respiration in a young ponderosa pine forest.–Tree Physiol. 26: 833–844, 2006.
Miyagawa Y., Tamoi M., Shigeoka S.: Over expression of a cyanobacterial fructose-1,6-/sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase in tobacco enhances photosynthesis and growth.–Nat. Biotechnol. 19: 965–969, 2001.
Mohamed H.I., Gomaa E.Z.: Effect of plant growth promoting Bacillus subtilis and Psedomonas fluorescens on growth and pigment composition of radish plants (Raphanus sativus) under NaCl stress.–Photosynthetica 50: 263–272, 2012.
Netto A.T., Campostrini E., de Oliveira J.G. et al..: Photosynthetic pigments, nitrogen, chlorophyll a fluorescence and SPAD-502 readings in coffee leaves.–Sci. Hortic.-Amsterdam 104: 199–209, 2005.
Ni B.R., Pallardy S.G.: Response of gas exchange to water stress in seedlings of woody angiosperms.–Tree Physiol. 8: 1–9, 1991.
Park P.S., Kim K.Y., Jang W.S. et al.: [Comparison of seedling survival rate and growth among 8 different tree species in Seosan reclamation area.]–J. Korean For. Soc. 98: 496–503, 2009. [In Korean]
Pichersky E., Hoffman N.E., Malik V.S. et al.: The tomato Cab-4 and Can-5 genes encode a second type of CAB polypeptides localized in photosystem II.–Plant Mol. Biol. 9: 109–120, 1987.
Poorter H., Remkes C.: Leaf area ratio and net assimilation rate of 24 wild species differing in relative growth rate.–Oecologia 83: 553–559, 1990.
Richter A.K.: Fine Root Growth and Vitality of European Beech in Acid Forest Soils with a Low Base Saturation.–Dissertation, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Zurich 2007.
Ryu C.M., Farag M.A., Hu C.H. et al.: Bacterial volatiles promote growth in Arabidopsis.–P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100: 4927–4932, 2003.
Salisbury F.B., Ross C.W.: Plant Physiology. Pp. 329–407. Wadsworth, Belmont 1992.
Seo Y.K.: [The Effect of Bacillus subtilis JS (PGPR) on the Growth of Several Indoor Plants Foliar Application.]–Dissertation, University of Seoul, Seoul 2015. [In Korean]
Shin H.N., Kim H.C., Kang K.S. et al.: [Differences in biomass production by rotation interval and planting density in Short-Rotation Forestry.]–P. Annu. Meet. Korean For. Soc. 2012: 43–45, 2012. [In Korean]
Singh N., Pandey P., Dubey R.C. et al.: Biological control of root rot fungus Macrophomina phaseolina and growth enhancement of Pinus roxburghii (Sarg.) by rhizosphere competent Bacillus subtilis BN1.–World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 24: 1669–1679, 2008.
Song J.Y., Kim H.A., Kim J.S. et al.: Genome sequence of the plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium Bacillus sp. Strain JS.–J. Bacteriol. 194: 3760–3761, 2012.
Sturite I., Henriksen T.M., Breland T.A.: Distinguishing between metabolically active and inactive roots by combined staining with 2,3, 5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride and image colour analysis.–Plant Soil 271: 75–82, 2005.
Tolentino Jr E.L., Lee D.K., Woo S.Y. et al.: Photosynthesis, transpiration and water use efficiency of six (6) indigenous tree seedlings for two (2) years in a nursery in the Philippines.–Forest Sci. Technol. 2: 18–26, 2006.
Utkhede R.S., Smith E.M.: Promotion of apple tree growth and fruit production by the EBW-4 strain of Bacillus subtilis in apple replant disease soil.–Can. J. Microbiol. 38: 1270–1273, 1992.
Vafadar F., Amooaghaie R., Otroshy M.: Effects of plantgrowth-promoting rhizobacteria and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on plant growth, stevioside, NPK, and chlorophyll content of Stevia rebaudiana.–J. Plant Interact. 9: 128–136, 2014.
Vessey J.K.: Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria as biofertilizers.–Plant Soil 255: 571–586, 2003.
Weih M., Roennberg-Wästljung A: Shoot biomass growth is related to the vertical leaf nitrogen gradient in Salix canopies.–Tree Physiol. 27: 1551–1559, 2007.
Wilson K.B., Baldocchi D.D., Hanson P.J.: Spatial and seasonal variability of photosynthetic parameters and their relationship to leaf nitrogen in a deciduous forest.–Tree Physiol. 20: 565–578, 2000.
Wright J.P., Jones C.G.: The concept of organisms as ecosystem engineers ten years on: Progress, limitations, and challenges.–BioScience 56: 203–209, 2006.
Xie X., Zhang H., Paré P.: Sustained growth promotion in Arabidopsis with long-term exposure to the beneficial soil bacterium Bacillus subtilis (GB03).–Plant Signal Bahav. 4: 948–953, 2009.
Xu L.K., Hsiao T.C.: Predicted versus measured photosynthetic water-use efficiency of crop stands under dynamically changing field environments.–J. Exp. Bot. 55: 2395–2411, 2004.
Yadav R.L., Dwivedi B.S., Prasad K. et al.: Yield trends and changes in soil organic-C and available NPK in a long-term rice-wheat system under integrated use of manure and fertilizers.–Field Crops Res. 68: 219–246, 2000.
Yeo J.K., Park J.H., Koo Y.B. et al.: [Effects of NaCl concentration on the growth of native willow species collected in a coastal reclaimed land.]–Korean J. Soil Sci. Fert. 43: 124–131, 2010. [In Korean]
Yoshida O.K.: Analytical method of root activity.–J. Japan Soc. Soil Sci. Fert. 37: 63–68, 1966.
Zhang H., Kim M.S., Krishnamachari V. et al.: Rhizobacterial volatile emissions regulate auxin homeostasis and cell expansion in Arabidopsis.–Planta 226: 839–851, 2007.
Zou C., Li Z., Yu D.: Bacillus megaterium strain XTBG34 promotes plant growth by producing 2-pentylfuran.–J. Microbiol. 48: 460–466, 2010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Acknowledgements: This work was carried out with the support of the Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science & Technology Development (Project No. PJ01168801) Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, J.H., Kim, S.H., Khaine, I. et al. Physiological changes and growth promotion induced in poplar seedlings by the plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria Bacillus subtilis JS. Photosynthetica 56, 1188–1203 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-018-0801-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-018-0801-0